Abstract
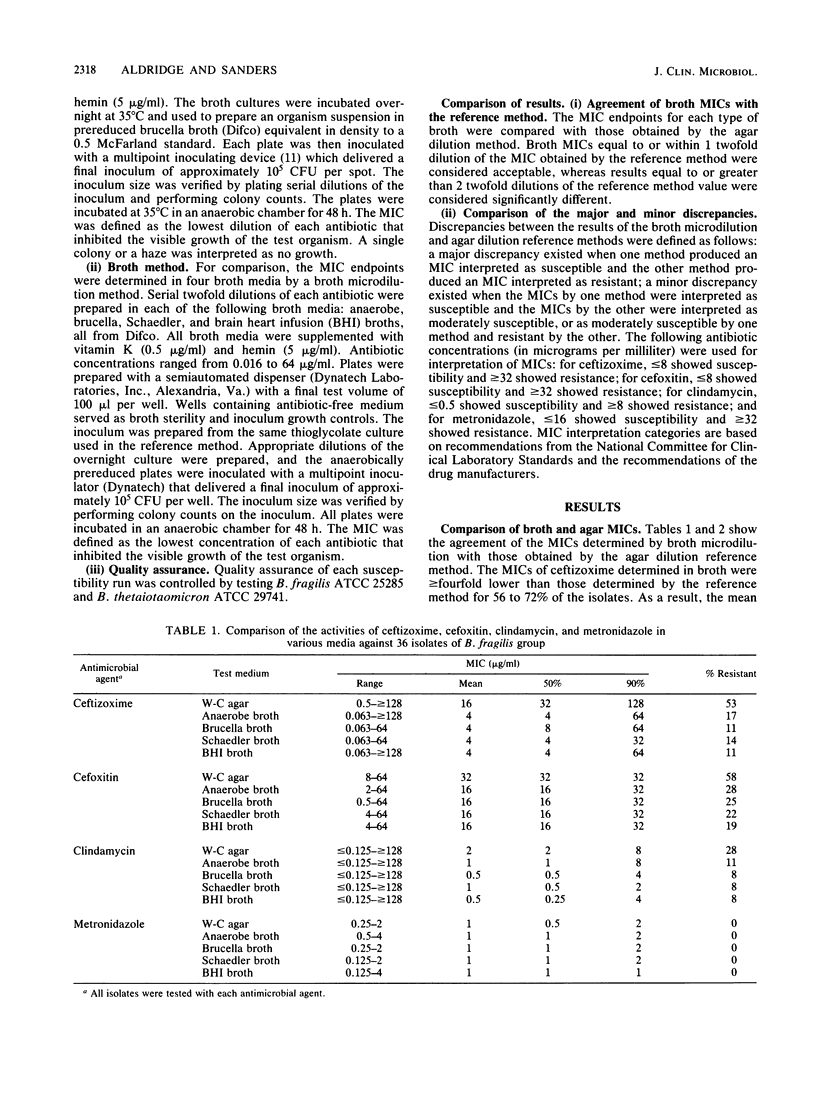
The susceptibilities of 36 isolates of the Bacteroides fragilis group to ceftizoxime, cefoxitin, clindamycin, and metronidazole were determined by using the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards agar dilution reference method and a broth microdilution method using anaerobe, brucella, Schaedler, and brain heart infusion broths. MICs that were greater than or equal to fourfold higher or lower than those of the reference method were considered significant. Major and minor discrepancies in susceptibility interpretation (SI) were also noted. Ceftizoxime showed the greatest number of variations and SI discrepancies. In 72% of the cases, MICs in broth were greater than or equal to fourfold lower than those obtained by the reference method, resulting in 33% of the major and 22% of the minor discrepancies in SI. A total of 53% of the isolates were resistant to ceftizoxime by the reference method, but only 11 to 17% were resistant in the various broths. Significant variations in MICs of cefoxitin occurred in 19 to 22% of the isolates; 17 to 19% of the isolates showed major discrepancies and 31 to 58% showed minor discrepancies in SI. A total of 58% of the isolates were resistant to cefoxitin by the reference method, but only 19 to 28% were resistant in the various broths. Significant variations with clindamycin in broths ranged from 32 to 53% and resulted in 3 to 8% of the isolates showing major discrepancies and 33 to 44% showing minor discrepancies in SI. Metronidazole yielded significant variations in MICs in 6 to 28% of the isolates, but no major or minor SI discrepancies were noted. This study indicates that significant differences in susceptibility results, which appear to be method related, can result when isolates of the B. fragilis group are tested. Therefore, studies correlating in vitro results, determined by various methods, to clinical outcome are essential.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron E. J., Bruckner D. A. Comparison of susceptibilities of anaerobic bacteria determined by agar dilution and by a microbroth method. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;6 (Suppl 1):S249–S253. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_1.s249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Barry A. L., Cotton J. L., Sutter V. L., Swenson J. M. Collaborative evaluation of the micro-media systems anaerobe susceptibility panel: comparisons with reference methods and test reproducibility. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):245–249. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.245-249.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J. E., Murray P. R., Sonnenwirth A. C., Joyce J. L. Comparison of anaerobic susceptibility results obtained by different methods. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):351–355. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Barry A. L., Wilkins T. D., Zabransky R. J. Collaborative evaluation of a proposed reference dilution method of susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):495–502. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Cuchural G. J., Jr, Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L., Aldridge K., Cleary T., Finegold S. M., Hill G., Iannini P., O'Keefe J. P. Nationwide study of the susceptibility of the Bacteroides fragilis group in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):675–677. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


