Abstract
The genetics underlying the autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) is complex and remains poorly understood. Previous work has demonstrated an important role for structural variation in a subset of cases, but has lacked the resolution necessary to move beyond detection of large regions of potential interest to identification of individual genes. To pinpoint genes likely to contribute to ASD etiology, we performed high density genotyping in 912 multiplex families from the Autism Genetics Resource Exchange (AGRE) collection and contrasted results to those obtained for 1,488 healthy controls. Through prioritization of exonic deletions (eDels), exonic duplications (eDups), and whole gene duplication events (gDups), we identified more than 150 loci harboring rare variants in multiple unrelated probands, but no controls. Importantly, 27 of these were confirmed on examination of an independent replication cohort comprised of 859 cases and an additional 1,051 controls. Rare variants at known loci, including exonic deletions at NRXN1 and whole gene duplications encompassing UBE3A and several other genes in the 15q11–q13 region, were observed in the course of these analyses. Strong support was likewise observed for previously unreported genes such as BZRAP1, an adaptor molecule known to regulate synaptic transmission, with eDels or eDups observed in twelve unrelated cases but no controls (p = 2.3×10−5). Less is known about MDGA2, likewise observed to be case-specific (p = 1.3×10−4). But, it is notable that the encoded protein shows an unexpectedly high similarity to Contactin 4 (BLAST E-value = 3×10−39), which has also been linked to disease. That hundreds of distinct rare variants were each seen only once further highlights complexity in the ASDs and points to the continued need for larger cohorts.
Author Summary
Autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) are common neurodevelopmental syndromes with a strong genetic component. ASDs are characterized by disturbances in social behavior, impaired verbal and nonverbal communication, as well as repetitive behaviors and/or a restricted range of interests. To identify genes likely to contribute to ASD etiology, we performed high density genotyping in 912 multiplex families from the Autism Genetics Resource Exchange (AGRE) collection and contrasted results to those obtained for 1,488 healthy controls. To enrich for variants most likely to interfere with gene function, we restricted our analyses to deletions and gains encompassing exons. Of the many genomic regions highlighted, 27 were seen to harbor rare variants in cases and not controls, both in the first phase of our analysis, and also in an independent replication cohort comprised of 859 cases and 1,051 controls. More work in a larger number of individuals will be required to determine which of the rare alleles highlighted here are indeed related to the ASDs and how they act to shape risk.
Introduction
The Autism spectrum disorders (ASDs, MIM: 209850) are a heterogeneous group of childhood diseases characterized by abnormalities in social behavior and communication, as well as patterns of restricted and repetitive behaviors [1]. Twin studies have demonstrated much higher concordance rates of ASD in monozygotic twins (92%) than dizygotic twins (10%) [2],[3], indicating a strong genetic basis for autism susceptibility. Although previous work has implicated numerous genomic regions of interest [4]–[8], the identification of specific genetic variants that contribute to ASD risk remains challenging.
Substantial progress towards the identification of genetic risk variants has come from recent characterization of structural variation (i.e., copy number variation or CNV). For example, an initial report involving patients with syndromic autism characterized genomic variation using array comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) and identified large de novo CNVs in 28% of cases [9]. Similarly, subsequent work demonstrated that the frequency of de novo CNVs is higher in cases versus controls [7],[8]. CNV analyses have proven useful in the identification of regions that are potentially disease-related [8], [10]–[13] and have begun to be employed to advance the candidacy of individual genes, including NRXN1, CNTNAP2, and NHE9 [6], [14]–[16]. Recent work characterizing structural variation in cases and ethnically matched controls associating ubiquitin-pathway genes with autism with replicating this finding in the AGRE dataset is likewise notable [17], although family data was not reported here. Using the AGRE dataset as a discovery cohort, along with family information available for AGRE samples, we describe distinct and complementary analyses, prioritizing exonic events over CNVs in introns and intergenic intervals, which provide important new insights into the genetic architecture of the ASDs.
Towards the identification of additional genes and regions that may modulate disease risk, we have assembled a resource characterizing genome-wide structural variation from over nine hundred multiplex ASD families. Presented below are results from analyses contrasting events observed in cases and healthy ethnically matched controls, focusing on three classes of genic events: exonic deletions (eDels), exonic duplications (eDups), and whole gene duplication (gDups). Recovery of known ASD loci – together with the identification of novel regions harboring variants in multiple cases but no controls – supports the utility of this dataset. Consistent with enormous inter-individual variation, we further document a large number of events observed in only individual cases (Table S4). Importantly, all of these data have been made available to the scientific community pre-publication (www.agre.org), greatly enhancing the utility of existing publicly accessible biomaterials and phenotype data. These data further highlight the extent of structural variation in both human and the ASDs and offer an important resource for hypothesis-generation and interrogation of individual loci.
Results/Discussion
To characterize structural variation in ASD multiplex families and unrelated controls, we typed individuals at 561,466 SNP markers using Illumina HumanHap550 version 3 arrays. After excluding samples that failed to meet QC thresholds (see Table S1), we obtained array data on 3832 individuals from 912 multiplex families enrolled in the Autism Genetic Resource Exchange (AGRE) [18], 1070 disease-free children from the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP), and 418 neurologically normal adults and seniors from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) control collection [19]. Using the PennCNV software [20], we detected CNVs with a mean size of 59.9 Kb and mean frequency of 24.3 events per individual (see Table S2). Sensitivity compares favorably with previous BAC array-based [9],[21] and SNP-based methods [8], in which mean resolution was observed to be in the range of Mbs and hundreds of Kbs, respectively.
As a first step towards validation of genotyping accuracy we examined the inheritance of CNVs in the AGRE cohort. Consistent with high quality, 96.2% of CNV calls made in children were also detected in a parent. To explore the issue of genotyping accuracy further, we generated CNV calls for an independently generated data set in which an overlapping set of 2,518 AGRE samples were genotyped using the Affymetrix 5.0 platform [11]. For CNVs (>500 kb) in known ASD regions (e.g. 15q11–13, 16p11.2, and 22q11.21; Table 1) [8],[11],[21],[22], we observed 100% correspondence between the two platforms for individuals genotyped on both platforms. For further confirmation of CNV calls, we compared de novo variants identified here to those highlighted in previous analyses of AGRE families. We identified all five de novo CNVs reported by Sebat et al [7], three of the five de novo CNVs reported by Szatmari et al [6], one de novo CNV within A2BP1 reported by Martin et al [23], and all five 16p11.2 de novo deletions reported by Weiss et al [11] and Kumar et al [10]. Of the two of thirteen de novo CNVs reported by Szatmari et al not detected as de novo in our study, one was very small (2 SNPs, 180 bp on 8p23.2), and the second clearly appears to be inherited (469 SNPs, 1.4 Mb on 17p12). Thus, our data are concordant with several other studies, and provide a more comprehensive picture of de novo CNVs in multiplex autism families. To further evaluate the quality of these data on another independent platform, we used Taqman to determine relative copy number at 12 previously unreported de novo CNVs identified in AGRE probands, confirming 11/12 loci (Figure 1 and Table S3). Together these results suggest that the CNVs calls we report are consistent and reliable.
Table 1. CNVs (>500 kb) on 16p11, 15q11–13, and 22q11 are present in a subset of AGRE families.
| Region | #SNP | Length (bp) | Type | AGRE ID | Scored status | Inheritance status | Shared by affected sibling? | Previous reports |
| 15q11–13 | 1246 | 5,902,313 | dup | AU010601 | parent | [22] | ||
| 15q11–13 | 1246 | 5,902,313 | dup | AU010604 | Autism | Inherited | No | [22] |
| 15q11–13 | 1246 | 5,902,313 | dup | AU1331202 | parent | |||
| 15q11–13 | 1246 | 5,902,313 | dup | AU1331302 | Autism | inherited | Yes | |
| 15q11–13 | 1246 | 5,902,313 | dup | AU1331303 | Autism | inherited | Yes | |
| 15q11–13 | 1130 | 5,008,629 | dup | AU006501 | parent | |||
| 15q11–13 | 1130 | 5,008,629 | dup | AU006503 | Spectrum | inherited | Yes | AGRE cytogenetic annotation |
| 15q11–13 | 1130 | 5,008,629 | dup | AU006504 | Autism | inherited | Yes | AGRE cytogenetic annotation, [21] |
| 15q11–13 | 1130 | 5,008,629 | dup | AU1135202 | Autism | de novo | NA | |
| 15q11–13 | 1127 | 4,993,869 | dup | AU023303 | Spectrum | NA | Yes | [22] |
| 15q11–13 | 1127 | 4,993,869 | dup | AU023304 | Autism | NA | Yes | [21],[22] |
| 15q11–13 | 1127 | 4,993,869 | dup | AU1607307 | Autism | de novo | No | |
| 15q11–13 | 569 | 3,540,078 | del | AU1024202 | parent | |||
| 15q11–13 | 569 | 3,540,078 | del | AU1024301 | Autism | inherited | NA | |
| 15q11–13 | 437 | 1,347,744 | dup | AU038504 | Autism | de novo | No | [22] |
| 15q11–13 | 287 | 1,578,642 | dup | AU1208301 | Autism | de novo | No | |
| 15q11–13 | 273 | 1,517,841 | dup | AU1875202 | parent | |||
| 15q11–13 | 98 | 572,462 | dup | AU052003 | Autism | NA | Yes | [21] |
| 15q11–13 | 98 | 572,462 | dup | AU052004 | Autism | NA | Yes | |
| 16p11.2 | 47 | 530,466 | del | AU0154302 | Autism | de novo | Yes | [10],[11] |
| 16p11.2 | 47 | 530,466 | del | AU0154303 | Autism | de novo | Yes | [10],[11],[21] |
| 16p11.2 | 47 | 530,466 | del | AU029803 | Autism | de novo | No | [10],[11],[21] |
| 16p11.2 | 47 | 530,466 | del | AU041905 | Autism | de novo | No | [10],[11], |
| 16p11.2 | 47 | 530,466 | del | AU0938301 | Autism | de novo | No | [10],[11],[21] |
| 16p11.2 | 47 | 530,466 | dup | AU002901 | parent | [11] | ||
| 16p11.2 | 47 | 530,466 | dup | AU002903 | Autism | inherited | Yes | [11] |
| 16p11.2 | 47 | 530,466 | dup | AU002904 | None | inherited | [11] | |
| 16p11.2 | 47 | 530,466 | dup | AU002905 | Autism | inherited | Yes | [10],[11] |
| 22q11.21 | 512 | 2,534,567 | dup | AU001802 | parent | [22] | ||
| 22q11.21 | 512 | 2,534,567 | dup | AU001804 | Autism | inherited | No | [21],[22] |
| 22q11.21 | 512 | 2,534,567 | dup | AU004903 | Autism | de novo | No | [21], |
| 22q11.21 | 335 | 1,429,207 | dup | AU0991301 | Autism | NA | No | |
| 22q11.21 | 177 | 728,859 | dup | AU1334201 | parent | |||
| 22q11.21 | 177 | 728,859 | dup | AU1334302 | Spectrum | inherited | No | |
| 22q11.21 | 149 | 601,423 | del | AU1555302 | Autism | NA | NA |
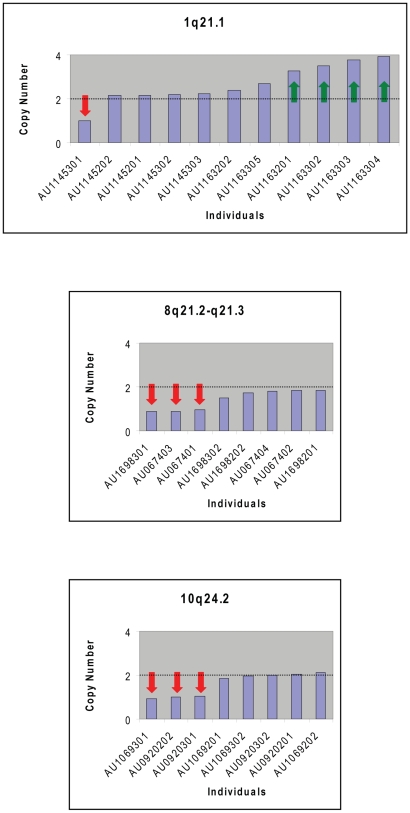
Figure 1. TaqMan experiments validate large de novo CNV calls.
To validate results using an independent method we designed TaqMan assays to evaluate gene dosage. Results from representative experiments highlight results at loci at 1q21, 8q21, and 10q24. AGRE individual harboring deletions (red arrows) or gains (green arrows) are indicated.
We therefore undertook additional analyses to identify specific loci in which structural variants were enriched in cases versus controls. Because the majority of such variants were intronic or intergenic, we sought to prioritize CNVs most likely to interfere with the molecular function of specific genes. We first filtered CNV calls to include only exonic deletions (eDels) observed to overlap with a RefSeq gene. Overall, such eDels were observed at similar frequencies in AGRE cases, 1st degree relatives of AGRE cases, and unrelated controls (CHOP and NINDS cohorts), with an average of ∼2 such variants per person (Table S2). To identify events related to the ASDs we then looked for genes harboring eDels in at least one case but no unrelated controls. Among the 284 genes that met this criteria (Table S4) we observed several known ASD or mental retardation genes including: ASPM [24], DPP10 [8], CNTNAP2 [25],[26], PCDH9 [16], and NRXN1 [6].
To enrich for genes most likely to contribute to ASD risk, we used family-based calling to evaluate which of these genes carried eDels in three or more cases from at least two unrelated families (Table S5). This stringent filtering resulted in 72 genes at 55 loci, including NRXN1. This is notable, given that eleven distinct disease-linked NRXN1 variants have been identified [6],[8],[15],[27],[28]. Neurexin family members are known to interact functionally with ASD-related neuroligins [29]–[32], and likewise play an important role in synaptic specification and specialization [33],[34]. eDels in more recently identified candidates, including DPP10 and PCDH9, were likewise retained. Similarly, recovery of RNF133 and RNF148 within intron 2 of CADPS2 [7],[35] highlights additional complexity at this locus. Although CNV breakpoints cannot be mapped precisely using SNP data alone, it is possible to determine overlap with protein coding exons and use these data to predict impact on gene function. Consistent with perturbation of function, distinct alleles at the loci highlighted here are predicted to eliminate or truncated the corresponding protein products (Figure 2).
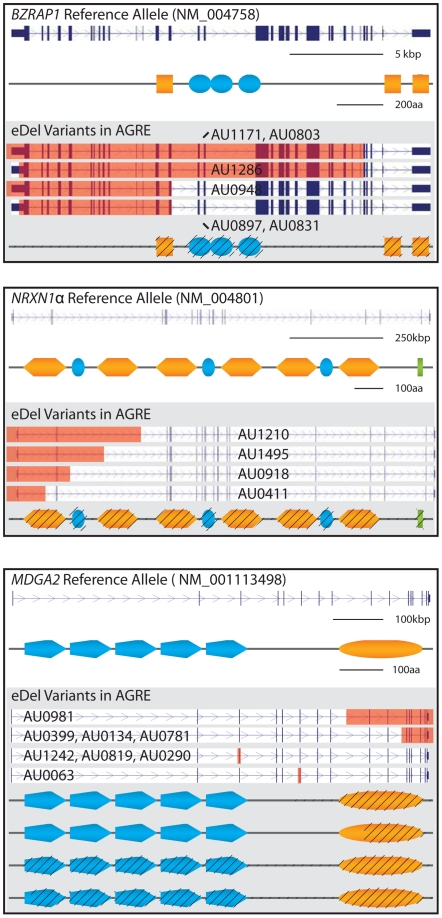
Figure 2. Rare exonic deletions (eDels) in NRXN1 and novel candidate genes alter predicted protein structures.
For each of BZRAP1 (a) NRXN1 (b) and MDGA2 (c) reference loci and encoded proteins (top) are contrasted against mutant loci and corresponding proteins (bottom; grey shading). Unique genomic deletions and corresponding protein truncations are highlighted in red and with black hatching, respectively. Schematized protein domains genes are as follows: BZRAP1—Src homology-3 (orange square), Fibronectin, type III (blue oval); NRXN1—Laminin G (orange hexagon), EGF-like (blue oval), 4.1 binding motif (green rectangle); MDGA2—IG-like domains (blue pentagon), MAM aka Meprin/A5-protein/PTPmu (blue oval).
Importantly, CNVs at a majority of these eDel loci show unique breakpoints in different families and/or result in the loss of distinct exons, demonstrating that they are independent. Moreover, because it is well established that CNVs at a subset of loci show identical breakpoints in unrelated individuals [10], this result is likely to underestimate the extent to which variants described here arose independently. Results from multi-dimensional scaling are likewise consistent with the interpretation that variants we highlight arose independently (Figure S1).
Given the large number of variants identified, it was critically important to confirm in an independent case-control analysis, how many of these eDels were truly overrepresented in cases, as opposed to being potentially attributable to Type I error. To address this concern, we sought to determine eDel frequency in these same genes in a replication dataset comprising 859 independently ascertained ASD cases and 1051 unrelated control subjects from the Autism Case Control cohort (ACC, see Description in Methods). One third of the loci identified in the discovery phase were observed in one or more ACC controls (18/55; 32.7%), suggesting that while rare, eDels at these loci are not limited to ASD cases and family members. In contrast, and providing evidence for formal replication, 14 separate loci encompassing 22 genes were observed to carry eDels in both AGRE and ACC cases, but none of 2539 controls (Table S2).
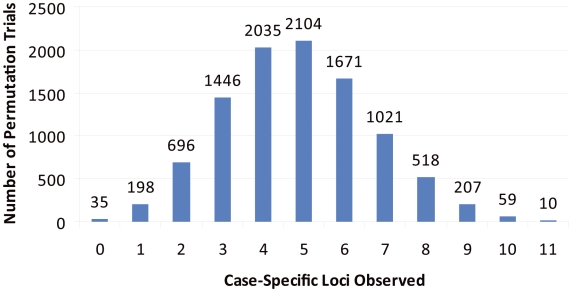
Our replication data lend strong support to the involvement of specific loci in the ASDs (Table 2). However, to ensure that these results were not observed by chance alone, we performed 10,000 permutation trials on data from the replication cohort by permuting case/control status across individuals. In each permuted dataset, we maintained the same numbers of cases and controls as in the original data, and calculated the number of genes harboring CNVs exclusively in cases. None of the 10,000 permutation trials gave results comparable to experimental observations for replicated case-specific loci (n = 14; p<0.0001; Figure 3). In contrast, findings comparable to those for non-replicated loci (highlighted as case-specific in the discovery phase but subsequently seen in replication controls) were seen in controls in 246/10,000 trials (n = 18; p = 0.02; Figure S2). Although additional experimental work in independent cohorts will be required to determine if variation in any of the genes highlighted here do in fact impact ASD risk, no more than 5 replicated loci would be predicted to be observed by chance alone.
Table 2. A subset of eDel loci were observed to harbor rare variants in both discovery and replication cohorts, but none of 2539 controls. eDel: exonic deletion; ACRD: autism chromosome rearrangement database (http://projects.tcag.ca/autism/).
| Gene | LocusA | Unrelated Discovery Cases (n = 912) | UnrelatedDiscovery Controls (n = 1488) | Unaffected Carrier FractionB | Unrelated Replication cases (n = 859) | Unrelated Replication controls (n = 1051) | ACRD? | Combined P-value (Fisher Exact) |
| - CA6 | 1p36 | 3 | 0 | 0.50 | 1 | 0 | No | 0.028 |
| - OR1C1 | 1q44 | 3 | 0 | 0.40 | 1 | 0 | No | 0.028 |
| - NRXN1 | 2p16 | 5 | 0 | 0.46 | 4 | 0 | Yes | 3.3×10−4 |
| - GALNT13 | 2q23.3 | 4 | 0 | 0.54 | 1 | 0 | Yes | 0.012 |
| - SUCLG2 | 3p14 | 2 | 0 | 0.25 | 1 | 0 | Yes | 0.069 |
| - KIAA1586 | 6p12 | 3 | 0 | 0.36 | 2 | 0 | No | 0.012 |
| - RNF133 | 7q31.3 | 3 | 0 | 0.60 | 1 | 0 | Yes | 0.028 |
| - RNF148 | ||||||||
| - SSSCA1 | 11q13 | 3 | 0 | 0.43 | 1 | 0 | No | 0.028 |
| - FAM89B | ||||||||
| - UNC93B1 | 11q13 | 3 | 0 | 0.25 | 1 | 0 | No | 0.028 |
| - MDGA2 | 14q21.3 | 8 | 0 | 0.56 | 2 | 0 | No | 1.4×10−4 |
| - LOC650137 C | 15q11.2 | 26 | 0 | 0.64 | 2 | 0 | Yes | 1.3×10−11 |
| - OR4M2 | ||||||||
| - OR4N4 | ||||||||
| - FLYWCH1 D | 16p13 | 3 | 0 | 0.40 | 3 | 0 | No | 4.8×10−3 |
| - KREMEN2 | ||||||||
| - PAQR4 | ||||||||
| - PKMYT1 | ||||||||
| - BZRAP1 E | 17q22 | 6 | 0 | 0.50 | 2 | 0 | No | 8.0×10−4 |
| - C19orf19 F | 19p13 | 3 | 0 | 0.40 | 8 | 0 | No | 5.5×10−5 |
| - MADCAM1 |
Predicted event sizes in bps for unrelated AGRE* and ACC# cases are as follows: CA6 - 2317*, 12464*, 19146*, 19145#; OR1C1 - 44644*, 577691*, 1464677*, 44643#; NRXN1 - 19979*, 152437*, 241327*, 373015*, 439406*, 134010#, 161199#, 256373#, 533842#; GALNT13 - 14126*, 46413*, 113282*, 24100#; SUCLG2 - 2192*, 1389749*, 1389748#; KIAA1586 - 36354*, 36902*,157321*, 36901#, 67160#; RNF133/RNF148 - 33473*, 37226*, 1515817*, 43966#; SSSCA1/FAM89B – 21993*, 21993*, 21993*, 123569#; UNC93B1 - 11410*, 19223*, 84727*, 159861#; MDGA2 – 19651*, 23292*, 57714*, 58528*, 122985*, 131623*, 150178*, 226468*, 194601#, 288518#; LOC650137/OR4M2/OR4N4 – 591007* in 26 families, 24941# and 926360#; FLYWCH1/KREMEN2/PAQR4/PKMYT1 - 40468*, 81127*, 88373*, 82786#, 82786#, 124947#; BZRAP1 – 10102*, 10102*, 16897*, 18532*, 22806*, 34235*, 29600#, 28360#; C19orf19 / MADCAM1 - 100187*, 171989*, 187147*, 98264#, 103788#, 277715#, 280201#, 292525#, 294446#, 344224#, 384324#.
For eDels at a given locus, the ratio of unaffected carriers (siblings or parents) to total number of carriers (cases and family members).
The significant difference in CNV frequency between AGRE and ACC cases (p = 2.6×10−6), along with multiple instances of similar variation in the DGV (see Tables S4 and Table S5), suggests that additional factors – including some potentially unrelated to diagnosis – may be relevant here. Sparse SNP coverage along with regional complexity (large segmental duplications) is also likely to increase false positive and false negatives at this locus. Replication data (and corresponding p Value) is for OR4N4, as only one eDel at either LOC650137 or OR4M2 was observed amongst ACC cases.
A comparable number of eDels were observed at multiple neighboring genes; carrier fraction corresponds to FLYWCH1, the lowest observed at this locus.
Joint consideration of eDels (n = 8) and eDups (n = 4) at BZRAP1 further improves statistical support for this locus (p = 2.3×10−5).
Note extreme telomeric position of this locus which may undermine/interfere with reliable calling of structural variants. CNV counts and carrier fraction corresponds to MADCAM1; fewer variants were observed at C19orf19 amongst ACC cases and carrier fraction was higher than that for MADCAM1.
Figure 3. Observed replication unlikely to be attributable to chance alone.
We performed 10,000 phenotype permutation trials on replication data and determined for each the number of loci harboring CNVs in cases but not controls. Thus, within each trial, the number of loci absent from controls in the replication cohort was determined. None of the permutation trials generated as many case-specific loci as observed in our actual dataset (n = 14; p<0.0001).
Despite the challenges associated with obtaining statistical support for individually rare events [7],[36] we next sought to assign P values for replicated eDel loci. We were able to obtain support for each of the following loci: BZRAP1 at 17q22 (p = 8.0×10−4), NRXN1 at 2p16.3 (p = 3.3×10−4), MDGA2 at 14q21.3 (p = 1.3×10−4), MADCAM1 at 19q13 (p = 5.5×10−5), and a three gene locus at 15q11 (p = 1.3×10−11). CNV calls at each of 15q11 and 19p13 are highly-error prone, suggesting that results here be interpreted with caution (see footnotes C and F in Table 2). Recovery of NRXN1, however, provides confidence for involvement of additional loci that were likewise replicated. Benzodiazapine receptor (peripheral) associated protein 1 (BZRAP1, alternatively referred to as RIMBP1), is an adaptor molecule thought to regulate synaptic transmission by linking vesicular release machinery to voltage gated Ca2+ channels [37]. Identification of this synaptic component here, in a hypothesis-free manner, is particularly satisfying and also provides additional support for synaptic dysfunction in the ASDs [29],[38]. Less is known about MDGA2 [39], although comparison of the predicted protein to all others within GenBank by BLASTP indicated an unexpectedly high similarity to Contactin 4 (24% identity over more than 500 amino acids; Expect = 3×10−39). Given previous reports of hemizygous loss of CNTN4 in individuals with mental retardation [40] and autism [17],[41]. similarity between MDGA2 and CNTN4, surpassed only by resemblance to MDGA1, is notable. Likewise intriguing in light of the suggestion that common variation in cell adhesion molecules may contribute to autism risk [42] is the structural likeness of MDGA2 to members of this family of molecules.
Although some published analyses emphasize the greater contribution of gene deletion events in autism pathogenesis [7], there are also clear examples of duplications that strongly modulate ASD risk [43],[44]. We therefore conducted a parallel analysis of duplications, distinguishing between events involving entire genes (gDups) which might increase dosage and those restricted to internal exons (eDups) which could give rise to a frameshift or map to a chromosomal region distinct from the reference gene. For gDups, we identified 449 genes that were duplicated in at least one AGRE case but no CHOP/NINDS controls (Table S4). Of those, 200 genes at an estimated 63 loci, including genes at 15q11.2 [43], met the more stringent criteria of being present in three or more cases from at least two independent families (Table S5). Of these, 11.5% (23/200) were also seen in ACC controls, whereas 24.5% (49/200) were case-specific in the replication cohort. Strong statistical support was obtained for established loci (e.g. p = 9.3×10−6 for UBE3A and other genes in the PWS/AS region at 15q11–q13), and nominal evidence was observed for the following novel loci: CD8A at 2p11.2 (p = 0.069), LOC285498 at 4p16.3 (p = 0.028), and CARD9/LOC728489 at 9q34.3 (p = 0.005).
For eDups, we reasoned that duplication of one or more internal exons could serve to disrupt the corresponding open reading frame and be predicted to impair gene function as a result. Despite the caveat that observed copy number gains need not map to the wild-type locus, known ASD genes including TSC2 [45] and RAI1 [44],[46] within the Potocki-Lupski Syndrome critical interval were amongst the 159 loci observed in at least one AGRE case, but no CHOP/NINDS controls (Table S4). Such events were also seen in one family at the NLGN1 locus, which is of interest given previous support for NLGN3 and NLGN4 [29]. Filtering of these results, using the more stringent criteria employed above in consideration of eDels, limited this set of events to 76 loci observed in at least three cases from two separate families (Table S5). Interestingly, BZRAP1, reported above to harbor eDels at significantly higher frequencies in AGRE and ACC cases versus controls (p = 8.0×10−4), was amongst these, with eDups observed here in four unrelated AGRE cases (screening p = 0.021). Eight other genes, including the voltage gated potassium channel subunit KCNAB2 (p = 4.7×10−3) remained absent from ACC controls and were also replicated in the independent case cohort. Although eDups at BZRAP1 were not detected in ACC cases, eDels at this locus were replicated, underscoring the importance of variation here. When considering eDels and eDups at the BZRAP1 locus together, the likelihood of such an observation occurring by chance alone is small (p = 2.3×10−5).
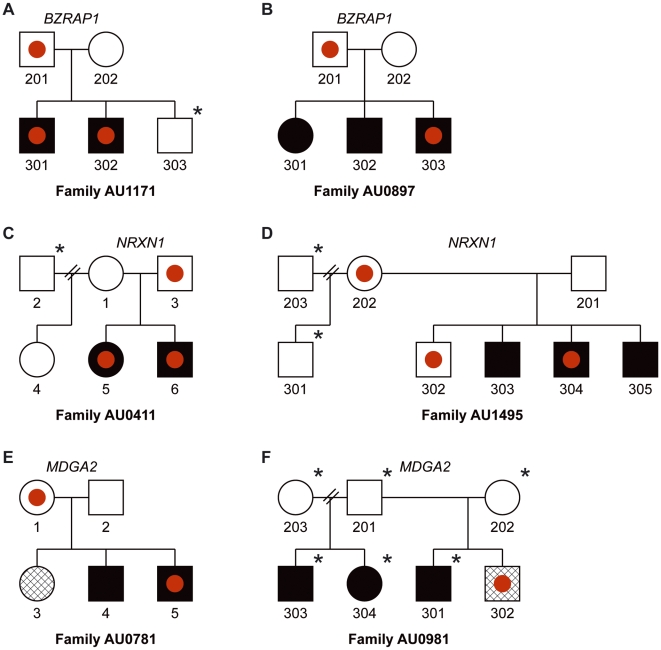
Although none of the variants we highlight were observed in any of 2539 unrelated controls, key events, including eDels at NRXN1, BZRAP1, and MDGA2 were observed in both cases and non-autistic family members (Figure 4). This is in keeping with previous work which suggests that haploinsufficiency at NRXN1 may contribute to the ASDs [15], but is insufficient to cause disease. Such data are also consistent with the well established finding of the “broader autism phenotype”, such as subclinical language and social impairment in first degree relatives of cases with an ASD, which supports a multi-locus model [47],[48]. We were also surprised to see that key variants at these loci appear to be transmitted to only a subset of affected individuals in some families (Figure 4). These observations parallel findings at other major effect loci including 16p11.2 [11] and DISC1 [49],[50] and are consistent with a model in which multiple variants, common and rare, act in concert to shape clinical presentation [51]–[53]. Results are also consistent with the idea that true risk loci are likely to show incomplete penetrance and imperfect segregation with disease [13], a reality that will complicate gene finding efforts. Related to this is that substantial effort will be required to determine whether rare alleles of moderate effect act independently on distinct aspects of disease (endophenotype model) or together to undermine key processes in brain development (threshold model). How distinct alleles may interact to shape presentation is yet another question that will require larger cohorts along with multigenerational families to resolve [54].
Figure 4. Exonic deletions, although enriched in cases versus controls, show imperfect segregation with disease in multiplex families.
Pedigrees for representative AGRE families harboring exonic deletions in BZRAP1 (A,B), kb), NRXN1 (C,D), and MDGA2 (E,F) are illustrated. Red filled circles correspond to exonic deletions. Black stars (upper right) highlight individuals for which CNV calls were not obtained (not genotyped or failing to meet criteria for quality control).
By limiting CNV calls to include only exonic deletions (eDels) and duplications (eDups and gDups), we have attempted to enrich for variants most likely to impact gene function and in doing so improve the signal to noise ratio similar to work in other complex diseases [55]. At the same time, like other gene-based strategies, we preserve our ability to consider eDels involving the same transcriptional unit as separate but equivalent. Given that such events appear rare, this is an important consideration.
Pathway analysis by DAVID [56] found support for overrepresentation of cell adhesion molecules amongst recurrent eDel genes (uncorrected p = 0.002; CDH17, PCDH9, LAMA2, MADCAM1, NRXN1, POSTN, SPON2) , although it should be noted that this analysis does not adjust for gene size and may favor larger genes. Nevertheless, aside from SPON2 no eDels in these genes were observed in any of the controls interrogated. In contrast, no evidence for such overrepresentation was observed for genes in the ubiquitin degradation pathway and neither term was highlighted as overrepresented amongst eDups or gDups. Given that this study focused only on events encompassing RefSeq exons, differences from Glessner and colleagues [17] are to be expected.
Despite the large cohorts interrogated at each phase of our investigations, only a minority of loci (established or novel) were replicated between AGRE and ACC cases. For example, variants at each of the following previously reported loci were observed multiple times in AGRE cases but not once amongst ACC probands: PCDH10 and DPP10 (eDels), RAI and TSC2 (eDups), and DIDO1 (gDups). This suggests that even with current numbers, the present experiments are underpowered to obtain replication for a subset of recurrent variants. Because events seen only in single cases collectively account for a substantial fraction of observed variation even larger cohorts still will be required for a thorough understanding of the genetic basis of complex disorders like the ASDs.
In summary, we have performed a high resolution genome-wide analysis to characterize the genomic landscape of copy number variation in ASDs. Through comparison of structural variation in 1,771 ASD cases and 2,539 controls and prioritization of events encompassing exons we identified more than 150 loci harboring rare variants in multiple probands but no control individuals. For each class of structural variant interrogated, the recovery of known loci serves to validate the methods employed and results obtained. Greatest confidence should be placed in loci harboring variants in multiple unrelated cases but no controls and also recovered in both screening and replication cohorts. Amongst novel genes, best support was obtained for BZRAP1 and MDGA2, intriguing candidate genes for which additional study is warranted.
Methods
Sample ascertainment
For initial screening we assembled three sample collections: 1) 943 ASD families (4,444 unique subjects) from the Autism Genetic Resource Exchange (AGRE) collection; 2) 1,070 de-identified and unrelated children of European ancestry from the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP), with no evidence of neurological disorders; 3) 542 unrelated neurologically normal adults and seniors of European ancestry from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) control collection. The AGRE families include 917 multiplex families, 24 simplex families and 2 families without an ASD diagnosis. For all analyses, AGRE cases annotated with “Autism” (n = 1,463), “Broad Spectrum” (n = 149) or “Not Quite Autism” (n = 71) were treated equally and as affected. Samples from AGRE and NINDS were genotyped using DNA extracted from Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines, while the CHOP controls were genotyped using DNA extracted from whole blood. All AGRE and control samples included in these analyses were genotyped on the Illumina HumanHap550 version 3 arrays, and 281 samples genotyped on version 1 arrays were excluded from the present analysis. Since the NINDS controls were genotyped at a different location and time, they were used to assess the frequency of specific CNVs in an independent cohort and to address concerns of cell line artifacts. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. All subjects provided written informed consent for the collection of samples and subsequent analysis.
The Autism Case-Control (ACC) cohort included 859 cases from multiple sites within the United States, all of whom were of European ancestry affected with ASD. Of those, 703 were male and 156 were female; 828 met diagnostic criteria for autism, and 31 met criteria for other ASDs. Subjects ranged from 2–21 years of age when the Autism Diagnostic Interview (ADI) was given. Of the case subjects, 54% were from simplex families with the balance coming from multiplex families. The control group used for replication included 1051 children of self-reported Caucasian ancestry who had no history of ASDs. These controls were recruited by CHOP nursing and medical assistant staff under the direction of CHOP clinicians within the CHOP Health Care Network, including four primary care clinics and several group practices and outpatient practices that included well child visits.
Detection and annotation of copy number variation
For each data set, we applied identical and stringent quality control criteria to remove samples with low signal quality. CNV calls were generated using PennCNV [20], an algorithm which employs multiple sources of information, including total signal intensity, allelic intensity ratios, SNP allele frequencies, distance between neighboring SNPs, and family information to generate calls. We excluded samples meeting any of the following criteria: a) standard deviation for autosomal log R ratio values (LRR_SD) higher than 0.28, b) median B Allele Frequency (BAF_median) higher than 0.55 or lower than 0.45, c) fraction of markers with BAF values between 0.2 and 0.25 or 0.75 and 0.8 (BAF_drift) exceeded 0.002. We also excluded from our analysis CNVs within IGLC1 (22q11.22), IGHG1 (14q32.33) and IGKC (2p11.2), and the T cell receptor constant chain locus (14q11.2), as well as CNVs in chromosomes showing evidence of heterosomic aberrations (chromosome rearrangements in sub-populations of cells) in BeadStudio.
CNV calls were mapped onto genes by identifying overlap with RefSeq exons, the coordinates of which we obtained from the UCSC table browser. Deletion events overlapping with exons retrieved in this way were listed as eDels. eDups were defined as gains overlapping one or more coding exons and seen to be internal to the beginning and end of the corresponding transcript. Gains observed to encompass all exons for a given gene were annotated as gDups. P values for relative CNV burden in cases and controls were calculated at each locus by Fisher's exact test. P values presented in Table S2, S4, S5 have not been subjected to correction for multiple testing. To compare our CNV calls with other publications that have used AGRE families [10],[11],[21],[22], we examined published calls on the same individuals with the same AGRE identifiers. The CNV calls were retrieved from the Supplementary Materials of each corresponding publication.
Quantitative PCR for CNV validation
TaqMan primer/probe sets were designed to query random CNVs using FileBuilder 3.0 on the repeat-masked human genome (NCBI_36; March 2006 release; http://genome.ucsc.edu/). For each assay, 10 ng of genomic DNA was assayed in quadruplicate in 10-µL reactions containing 1× final concentration TaqMan Universal Master Mix (ABI part number 4304437), and 200 nM of each primer and probe. Cycling was performed under default conditions in 384-well optical PCR plates on an ABI 7900 machine. Copy number was defined as 2−ΔΔCT, where ΔC T is the difference in threshold cycles for the sample in question normalized against an endogenous reference (RNAseP) and expressed relative to the average values obtained by three arbitrary control DNAs. A list of TaqMan probes against the 12 CNVs tested is included in Table S3.
Supporting Information
Multi-dimensional scaling plot of AGRE affected subjects, with red cross highlighting subjects carrying the eDels. Subjects of European ancestry are clustered toward the right side of the triangle.
(0.11 MB DOC)
We performed 10,000 phenotype permutation trials on replication data and determined for each the number of loci harboring CNVs exclusively in controls. During each trial a new set of control-specific loci was identified and the number of these absent from cases determined. We observed results comparable to those obtained experimentally (n = 18) in 246 of 10,000 trials (p = 0.02).
(0.03 MB DOC)
Description of AGRE sample used in the analysis.
(0.03 MB DOC)
Summary of CNVs in AGRE cases, first-degree relatives, and unrelated controls.
(0.04 MB DOC)
TaqMan primers and probes used in CNV validation.
(0.04 MB DOC)
Exonic del/dups (Singletons and recurrent).
(0.14 MB XLS)
Exonic del/dups (Recurrent in unrelated families).
(0.45 MB XLS)
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the resources provided by the Autism Genetic Resource Exchange (AGRE) Consortium and the participating AGRE families. We also gratefully thank the children and their families who donated blood samples to CHOP for research purposes. We also acknowledge the technical staff at the Center for Applied Genomics for producing the genotypes used for analyses and members of the Bucan lab for performing additional resequencing experiments and validation experiments.
The AGRE Consortium
Dan Geschwind, M.D., Ph.D., UCLA, Los Angeles, CA; Maja Bucan, Ph.D., University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA; W.Ted Brown, M.D., Ph.D., F.A.C.M.G., N.Y.S. Institute for Basic Research in Developmental Disabilities, Staten Island, NY; Rita M. Cantor, Ph.D., UCLA School of Medicine, Los Angeles, CA; John N. Constantino, M.D., Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO; T.Conrad Gilliam, Ph.D., University of Chicago, Chicago, IL; Martha Herbert, M.D., Ph.D., Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; Clara Lajonchere, Ph.D, Autism Speaks, Los Angeles, CA; David H. Ledbetter, Ph.D., Emory University, Atlanta, GA; Christa Lese-Martin, Ph.D., Emory University, Atlanta, GA; Janet Miller, J.D., Ph.D., Autism Speaks, Los Angeles, CA; Stanley F. Nelson, M.D., UCLA School of Medicine, Los Angeles, CA; Gerard D. Schellenberg, Ph.D., University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA; Carol A. Samango-Sprouse, Ed.D., George Washington University, Washington, D.C.; Sarah Spence, M.D., Ph.D., UCLA, Los Angeles, CA; Matthew State, M.D., Ph.D., Yale University, New Haven, CT; Rudolph E. Tanzi, Ph.D., Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA.
Footnotes
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
The Autism Genetic Resource Exchange is a program of Autism Speaks and is supported, in part, by grant 1U24MH081810 from the National Institute of Mental Health to Clara M. Lajonchere (PI). This work is supported by a seed grant from Penn/CHOP Center for Autism Research, by NIH grant R01MH604687, and a NARSAD Distinguished Investigator Award (MB); by Pennsylvania Commonwealth HRFF and P20-GM69012 (JK); by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services (1 Z01 AG000949-02 to AS); by a fellowship from the Tourette Syndrome Association (BSA); by an Autism Center of Excellence Award (P50HD055784-01 to MS, DHG, co-PI); by an Autism Center of Excellence Genetics Network grant (MH081754 to DHG); by a Research Award from the Margaret Q. Landenberger Foundation (HH); by a Research Development Award from the Cotswold Foundation (HH and SFAG); and by UL1-RR024134-03 (HH). The genotyping and other aspects of the study were funded by an Institutional Development Award to the Center for Applied Genomics (HH) from the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Abrahams BS, Geschwind DH. Advances in autism genetics: on the threshold of a new neurobiology. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:341–355. doi: 10.1038/nrg2346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bailey A, Le Couteur A, Gottesman I, Bolton P, Simonoff E, et al. Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: evidence from a British twin study. Psychol Med. 1995;25:63–77. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700028099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Steffenburg S, Gillberg C, Hellgren L, Andersson L, Gillberg IC, et al. A twin study of autism in Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1989;30:405–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1989.tb00254.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cantor RM, Kono N, Duvall JA, Alvarez-Retuerto A, Stone JL, et al. Replication of autism linkage: fine-mapping peak at 17q21. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;76:1050–1056. doi: 10.1086/430278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vorstman JA, Staal WG, van Daalen E, van Engeland H, Hochstenbach PF, et al. Identification of novel autism candidate regions through analysis of reported cytogenetic abnormalities associated with autism. Mol Psychiatry. 2006;11:18–28. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Szatmari P, Paterson AD, Zwaigenbaum L, Roberts W, Brian J, et al. Mapping autism risk loci using genetic linkage and chromosomal rearrangements. Nat Genet. 2007;39:319–328. doi: 10.1038/ng1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sebat J, Lakshmi B, Malhotra D, Troge J, Lese-Martin C, et al. Strong association of de novo copy number mutations with autism. Science. 2007;316:445–449. doi: 10.1126/science.1138659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Marshall CR, Noor A, Vincent JB, Lionel AC, Feuk L, et al. Structural variation of chromosomes in autism spectrum disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;82:477–488. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.12.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jacquemont ML, Sanlaville D, Redon R, Raoul O, Cormier-Daire V, et al. Array-based comparative genomic hybridisation identifies high frequency of cryptic chromosomal rearrangements in patients with syndromic autism spectrum disorders. J Med Genet. 2006;43:843–849. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2006.043166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kumar RA, Karamohamed S, Sudi J, Conrad DF, Brune C, et al. Recurrent 16p11.2 microdeletions in autism. Hum Mol Genet. 2007 doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Weiss LA, Shen Y, Korn JM, Arking DE, Miller DT, et al. Association between Microdeletion and Microduplication at 16p11.2 and Autism. N Engl J Med. 2008 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa075974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sharp AJ, Mefford HC, Li K, Baker C, Skinner C, et al. A recurrent 15q13.3 microdeletion syndrome associated with mental retardation and seizures. Nat Genet. 2008;40:322–328. doi: 10.1038/ng.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mefford HC, Sharp AJ, Baker C, Itsara A, Jiang Z, et al. Recurrent rearrangements of chromosome 1q21.1 and variable pediatric phenotypes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1685–1699. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0805384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Alarcon M, Abrahams BS, Stone JL, Duvall JA, Perederiy JV, et al. Linkage, Association, and Gene-Expression Analyses Identify CNTNAP2 as an Autism-Susceptibility Gene. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;82:150–159. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.09.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kim HG, Kishikawa S, Higgins AW, Seong IS, Donovan DJ, et al. Disruption of neurexin 1 associated with autism spectrum disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;82:199–207. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.09.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Morrow EM, Yoo SY, Flavell SW, Kim TK, Lin Y, et al. Identifying autism loci and genes by tracing recent shared ancestry. Science. 2008;321:218–223. doi: 10.1126/science.1157657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Glessner JT, Wang K, Cai G, Korvatska O, Kim CE, et al. Autism genome-wide copy number variation reveals ubiquitin and neuronal genes. Nature. 2009 doi: 10.1038/nature07953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Geschwind DH, Sowinski J, Lord C, Iversen P, Shestack J, et al. The autism genetic resource exchange: a resource for the study of autism and related neuropsychiatric conditions. Am J Hum Genet. 2001;69:463–466. doi: 10.1086/321292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nalls MA, Simon-Sanchez J, Gibbs JR, Paisan-Ruiz C, Bras JT, et al. Measures of autozygosity in decline: globalization, urbanization, and its implications for medical genetics. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000415. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000415. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang K, Li M, Hadley D, Liu R, Glessner J, et al. PennCNV: an integrated hidden Markov model designed for high-resolution copy number variation detection in whole-genome SNP genotyping data. Genome Res. 2007;17:1665–1674. doi: 10.1101/gr.6861907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Christian SL, Brune CW, Sudi J, Kumar RA, Liu S, et al. Novel submicroscopic chromosomal abnormalities detected in autism spectrum disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;63:1111–1117. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.01.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cai G, Edelmann L, Goldsmith JE, Cohen N, Nakamine A, et al. Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification for genetic screening in autism spectrum disorders: Efficient identification of known microduplications and identification of a novel microduplication in ASMT. BMC Med Genomics. 2008;1:50. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-1-50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Martin CL, Duvall JA, Ilkin Y, Simon JS, Arreaza MG, et al. Cytogenetic and molecular characterization of A2BP1/FOX1 as a candidate gene for autism. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2007;144:869–876. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bond J, Roberts E, Mochida GH, Hampshire DJ, Scott S, et al. ASPM is a major determinant of cerebral cortical size. Nat Genet. 2002;32:316–320. doi: 10.1038/ng995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bakkaloglu B, O'Roak BJ, Louvi A, Gupta AR, Abelson JF, et al. Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis and Resequencing of Contactin Associated Protein-Like 2 in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;82:165–173. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.09.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Strauss KA, Puffenberger EG, Huentelman MJ, Gottlieb S, Dobrin SE, et al. Recessive symptomatic focal epilepsy and mutant contactin-associated protein-like 2. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1370–1377. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Feng J, Schroer R, Yan J, Song W, Yang C, et al. High frequency of neurexin 1beta signal peptide structural variants in patients with autism. Neurosci Lett. 2006;409:10–13. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yan J, Noltner K, Feng J, Li W, Schroer R, et al. Neurexin 1alpha structural variants associated with autism. Neurosci Lett. 2008;438:368–370. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.04.074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jamain S, Quach H, Betancur C, Rastam M, Colineaux C, et al. Mutations of the X-linked genes encoding neuroligins NLGN3 and NLGN4 are associated with autism. Nat Genet. 2003;34:27–29. doi: 10.1038/ng1136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Comoletti D, De Jaco A, Jennings LL, Flynn RE, Gaietta G, et al. The Arg451Cys-neuroligin-3 mutation associated with autism reveals a defect in protein processing. J Neurosci. 2004;24:4889–4893. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0468-04.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Laumonnier F, Bonnet-Brilhault F, Gomot M, Blanc R, David A, et al. X-linked mental retardation and autism are associated with a mutation in the NLGN4 gene, a member of the neuroligin family. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;74:552–557. doi: 10.1086/382137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yan J, Oliveira G, Coutinho A, Yang C, Feng J, et al. Analysis of the neuroligin 3 and 4 genes in autism and other neuropsychiatric patients. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10:329–332. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Scheiffele P, Fan J, Choih J, Fetter R, Serafini T. Neuroligin expressed in nonneuronal cells triggers presynaptic development in contacting axons. Cell. 2000;101:657–669. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80877-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Graf ER, Zhang X, Jin SX, Linhoff MW, Craig AM. Neurexins induce differentiation of GABA and glutamate postsynaptic specializations via neuroligins. Cell. 2004;119:1013–1026. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sadakata T, Washida M, Iwayama Y, Shoji S, Sato Y, et al. Autistic-like phenotypes in Cadps2-knockout mice and aberrant CADPS2 splicing in autistic patients. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:931–943. doi: 10.1172/JCI29031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Walsh T, McClellan JM, McCarthy SE, Addington AM, Pierce SB, et al. Rare structural variants disrupt multiple genes in neurodevelopmental pathways in schizophrenia. Science. 2008;320:539–543. doi: 10.1126/science.1155174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wang Y, Sugita S, Sudhof TC. The RIM/NIM family of neuronal C2 domain proteins. Interactions with Rab3 and a new class of Src homology 3 domain proteins. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:20033–20044. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M909008199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zoghbi HY. Postnatal neurodevelopmental disorders: meeting at the synapse? Science. 2003;302:826–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1089071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Litwack ED, Babey R, Buser R, Gesemann M, O'Leary DD. Identification and characterization of two novel brain-derived immunoglobulin superfamily members with a unique structural organization. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2004;25:263–274. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2003.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fernandez T, Morgan T, Davis N, Klin A, Morris A, et al. Disruption of contactin 4 (CNTN4) results in developmental delay and other features of 3p deletion syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;74:1286–1293. doi: 10.1086/421474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Roohi J, Montagna C, Tegay DH, Palmer LE, DeVincent C, et al. Disruption of contactin 4 in three subjects with autism spectrum disorder. J Med Genet. 2009;46:176–182. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2008.057505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wang K, Zhang H, Ma D, Bucan M, Glessner JT, et al. Common genetic variants on 5p14.1 associate with autism spectrum disorders. Nature. 2009 doi: 10.1038/nature07999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cook EH, Jr, Lindgren V, Leventhal BL, Courchesne R, Lincoln A, et al. Autism or atypical autism in maternally but not paternally derived proximal 15q duplication. Am J Hum Genet. 1997;60:928–934. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Potocki L, Bi W, Treadwell-Deering D, Carvalho CM, Eifert A, et al. Characterization of Potocki-Lupski syndrome (dup(17)(p11.2p11.2)) and delineation of a dosage-sensitive critical interval that can convey an autism phenotype. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;80:633–649. doi: 10.1086/512864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Identification and characterization of the tuberous sclerosis gene on chromosome 16. Cell. 1993;75:1305–1315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90618-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Slager RE, Newton TL, Vlangos CN, Finucane B, Elsea SH. Mutations in RAI1 associated with Smith-Magenis syndrome. Nat Genet. 2003;33:466–468. doi: 10.1038/ng1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bolton P, Macdonald H, Pickles A, Rios P, Goode S, et al. A case-control family history study of autism. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1994;35:877–900. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1994.tb02300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bishop DV, Maybery M, Maley A, Wong D, Hill W, et al. Using self-report to identify the broad phenotype in parents of children with autistic spectrum disorders: a study using the Autism-Spectrum Quotient. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2004;45:1431–1436. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2004.00849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Millar JK, Wilson-Annan JC, Anderson S, Christie S, Taylor MS, et al. Disruption of two novel genes by a translocation co-segregating with schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:1415–1423. doi: 10.1093/hmg/9.9.1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sachs NA, Sawa A, Holmes SE, Ross CA, DeLisi LE, et al. A frameshift mutation in Disrupted in Schizophrenia 1 in an American family with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10:758–764. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Risch N, Spiker D, Lotspeich L, Nouri N, Hinds D, et al. A genomic screen of autism: evidence for a multilocus etiology. Am J Hum Genet. 1999;65:493–507. doi: 10.1086/302497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Rzhetsky A, Wajngurt D, Park N, Zheng T. Probing genetic overlap among complex human phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:11694–11699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704820104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bodmer W, Bonilla C. Common and rare variants in multifactorial susceptibility to common diseases. Nat Genet. 2008;40:695–701. doi: 10.1038/ng.f.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Yang S, Wang K, Gregory B, Berrettini W, Wang LS, et al. Genomic landscape of a three-generation pedigree segregating affective disorder. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e4474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004474. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ji W, Foo JN, O'Roak BJ, Zhao H, Larson MG, et al. Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation. Nat Genet. 2008;40:592–599. doi: 10.1038/ng.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Dennis G, Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang J, Gao W, et al. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 2003;4:P3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Multi-dimensional scaling plot of AGRE affected subjects, with red cross highlighting subjects carrying the eDels. Subjects of European ancestry are clustered toward the right side of the triangle.
(0.11 MB DOC)
We performed 10,000 phenotype permutation trials on replication data and determined for each the number of loci harboring CNVs exclusively in controls. During each trial a new set of control-specific loci was identified and the number of these absent from cases determined. We observed results comparable to those obtained experimentally (n = 18) in 246 of 10,000 trials (p = 0.02).
(0.03 MB DOC)
Description of AGRE sample used in the analysis.
(0.03 MB DOC)
Summary of CNVs in AGRE cases, first-degree relatives, and unrelated controls.
(0.04 MB DOC)
TaqMan primers and probes used in CNV validation.
(0.04 MB DOC)
Exonic del/dups (Singletons and recurrent).
(0.14 MB XLS)
Exonic del/dups (Recurrent in unrelated families).
(0.45 MB XLS)