Abstract
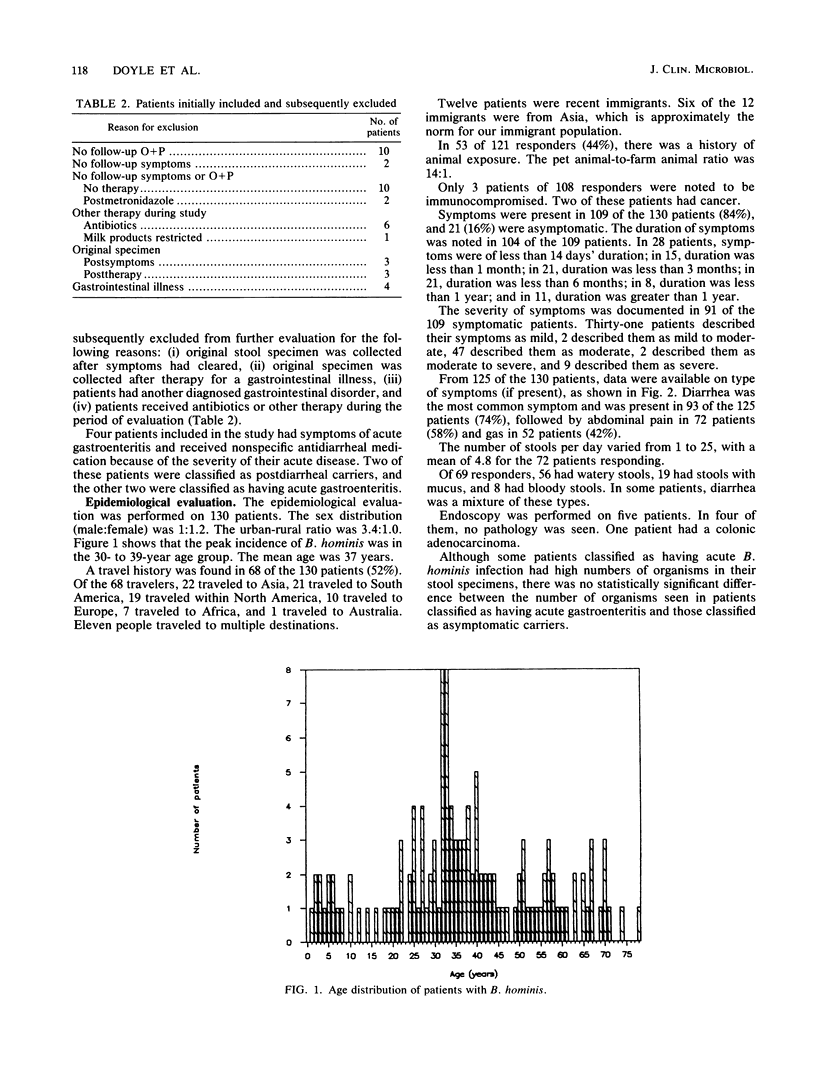
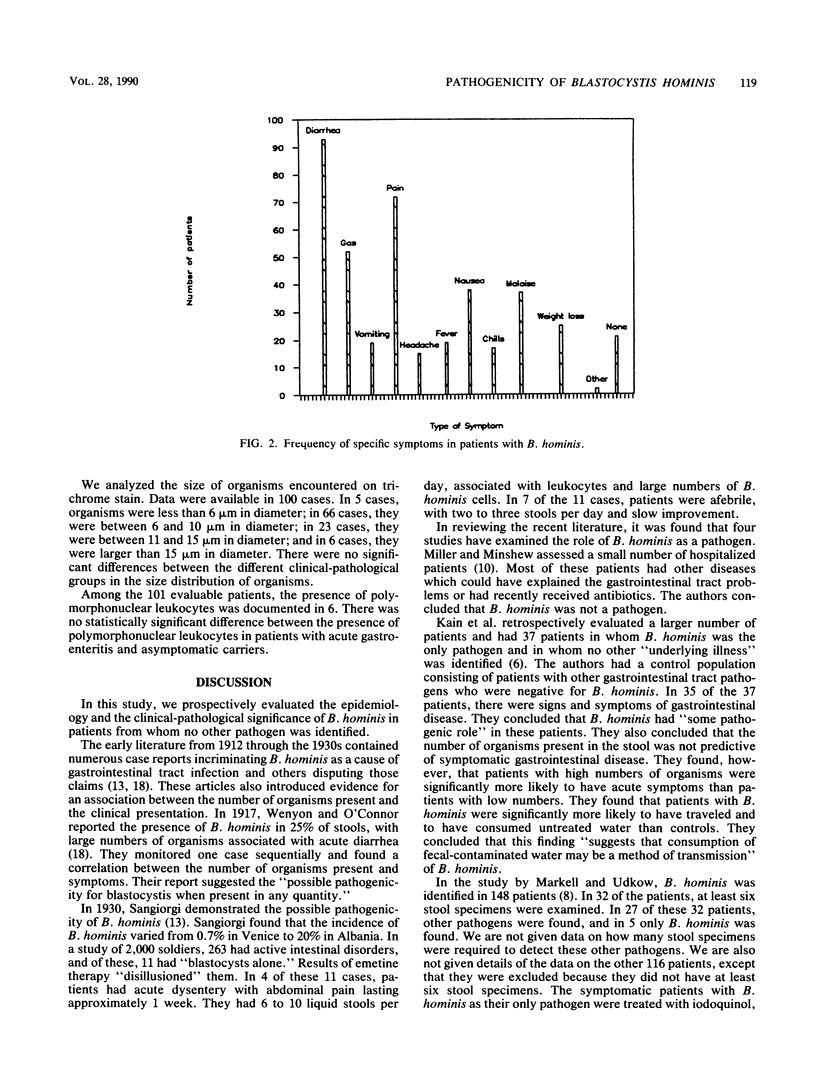
A prospective study was performed on a large outpatient population to evaluate the epidemiology and pathogenicity of Blastocystis hominis. Patients with stool specimens positive for B. hominis and negative for other bacterial and parasitic pathogens were sent a questionnaire and were requested to submit a follow-up specimen for ova-and-parasite examination. B. hominis was identified in 530 of 16,545 specimens (3.2%). There was a spectrum of clinical-pathological presentations in the 143 patients evaluated. An asymptomatic carrier state was seen in 19 patients. Fifteen patients had an illness consistent with acute self-limited B. hominis gastroenteritis, and 21 patients had chronic gastroenteritis associated with B. hominis. In the epidemiological evaluation of 130 patients, the most common symptoms were watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and gas. We did not find a statistically significant association between the number of organisms present and the disease state. In summary, our results are consistent with a role for B. hominis in acute and chronic gastroenteritis; however, further detailed studies are necessary to determine whether that role is one of association or causation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Diaczok B. J., Rival J. Diarrhea due to Blastocystis hominis: an old organism revisited. South Med J. 1987 Jul;80(7):931–932. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198707000-00034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher P. G., Venglarcik J. S., 3rd Blastocystis hominis enteritis. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1985 Sep-Oct;4(5):556–557. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198509000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guirges S. Y., Al-Waili N. S. Blastocystis hominis: evidence for human pathogenicity and effectiveness of metronidazole therapy. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1987 Apr;14(4):333–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1987.tb00979.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kain K. C., Noble M. A., Freeman H. J., Barteluk R. L. Epidemiology and clinical features associated with Blastocystis hominis infection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 Dec;8(4):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBar W. D., Larsen E. C., Patel K. Afebrile diarrhea and Blastocystis hominis. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Aug;103(2):306–306. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-2-306_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markell E. K., Udkow M. P. Blastocystis hominis: pathogen or fellow traveler? Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Sep;35(5):1023–1026. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMyne P. M., Penner J. L., Mathias R. G., Black W. A., Hennessy J. N. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from sporadic cases and outbreaks in British Columbia. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):281–285. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.281-285.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Minshew B. H. Blastocystis hominis: an organism in search of a disease. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):930–938. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.5.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. P., Zierdt C. H. Blastocystis hominis: pathogenic potential in human patients and in gnotobiotes. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Jun;39(3):358–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo A. R., Stone S. L., Taplin M. E., Snapper H. J., Doern G. V. Presumptive evidence for Blastocystis hominis as a cause of colitis. Arch Intern Med. 1988 May;148(5):1064–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter M. T., Sheps S. B. Diagnostic testing revisited: pathways through uncertainty. Can Med Assoc J. 1985 Apr 1;132(7):755–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan D. J., Raucher B. G., McKitrick J. C. Association of Blastocystis hominis with signs and symptoms of human disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):548–550. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.548-550.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Houston R., Shlim D. R., Bhaibulaya M., Ungar B. L., Echeverria P. Etiology of diarrhea among travelers and foreign residents in Nepal. JAMA. 1988 Sep 2;260(9):1245–1248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannatta J. B., Adamson D., Mullican K. Blastocystis hominis infection presenting as recurrent diarrhea. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Apr;102(4):495–496. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-4-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Rude W. S., Bull B. S. Protozoan characteristics of Blastocystis hominis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1967 Nov;48(5):495–501. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/48.5.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Tan H. Endosymbiosis in Blastocystis hominis. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Jun;39(3):422–430. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


