Abstract
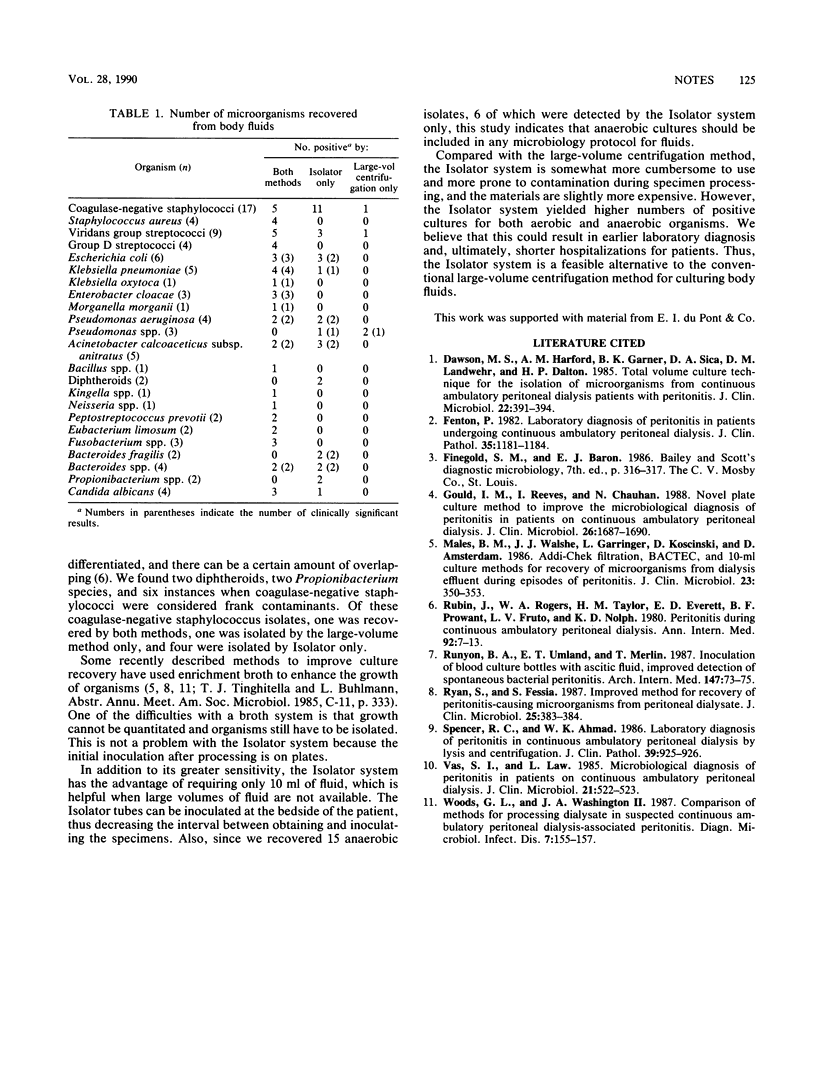
The Isolator system was compared with the large-volume centrifugation method for processing and recovering organisms from body fluids other than blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and urine. A total of 155 body fluid samples were processed for the recovery of clinically significant organisms. Of the 55 positive cultures, Isolator detected 94% and the large-volume centrifugation method detected 64%. The time necessary to indicate positivity was not significantly different in the two methods; however, in five cases, the Isolator system yielded clinically significant organisms 24 h sooner than the conventional method. The Isolator system was found to be a more sensitive alternative than the conventional large-volume centrifugation method.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dawson M. S., Harford A. M., Garner B. K., Sica D. A., Landwehr D. M., Dalton H. P. Total volume culture technique for the isolation of microorganisms from continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients with peritonitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):391–394. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.391-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton P. Laboratory diagnosis of peritonitis in patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Nov;35(11):1181–1184. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.11.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould I. M., Reeves I., Chauhan N. Novel plate culture method to improve the microbiological diagnosis of peritonitis in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1687–1690. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1687-1690.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Males B. M., Walshe J. J., Garringer L., Koscinski D., Amsterdam D. Addi-Chek filtration, BACTEC, and 10-ml culture methods for recovery of microorganisms from dialysis effluent during episodes of peritonitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):350–353. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.350-353.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J., Rogers W. A., Taylor H. M., Everett E. D., Prowant B. F., Fruto L. V., Nolph K. D. Peritonitis during continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jan;92(1):7–13. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-1-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runyon B. A., Umland E. T., Merlin T. Inoculation of blood culture bottles with ascitic fluid. Improved detection of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Jan;147(1):73–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan S., Fessia S. Improved method for recovery of peritonitis-causing microorganisms from peritoneal dialysate. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):383–384. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.383-384.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R. C., Ahmad W. K. Laboratory diagnosis of peritonitis in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis by lysis and centrifugation. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Aug;39(8):925–926. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.8.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vas S. I., Law L. Microbiological diagnosis of peritonitis in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):522–523. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.522-523.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods G. L., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of methods for processing dialysate in suspected continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;7(2):155–157. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


