Abstract
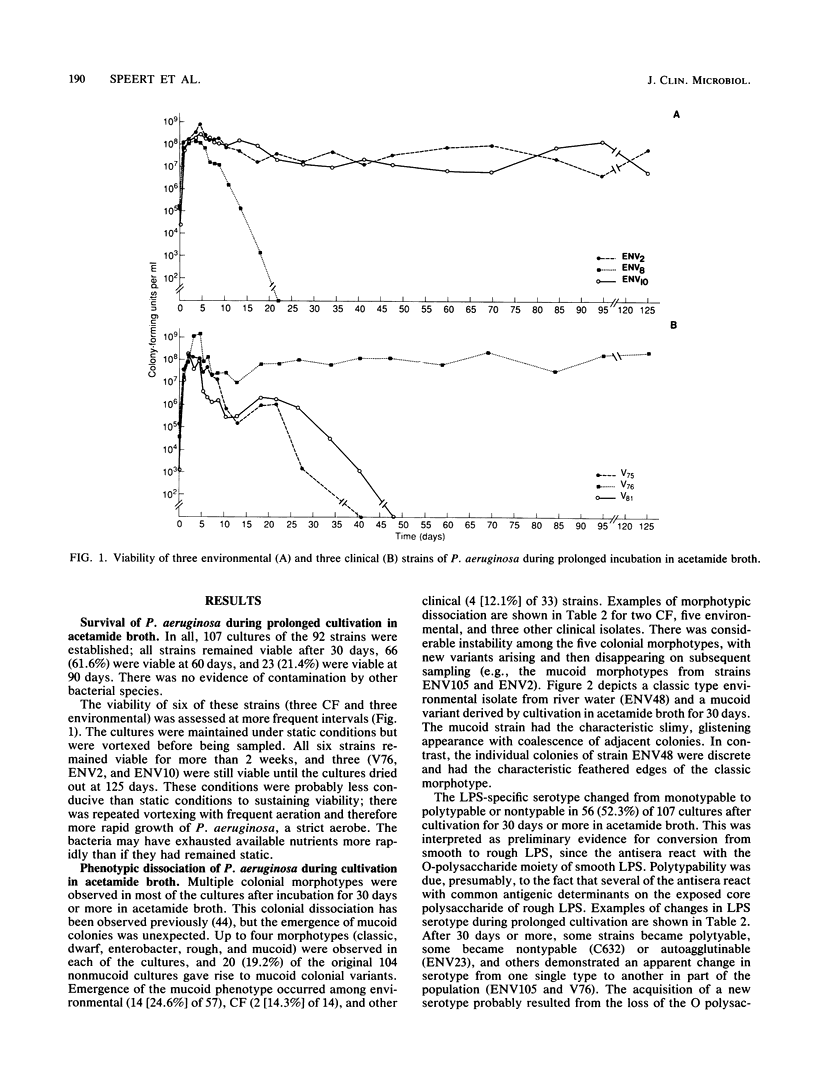
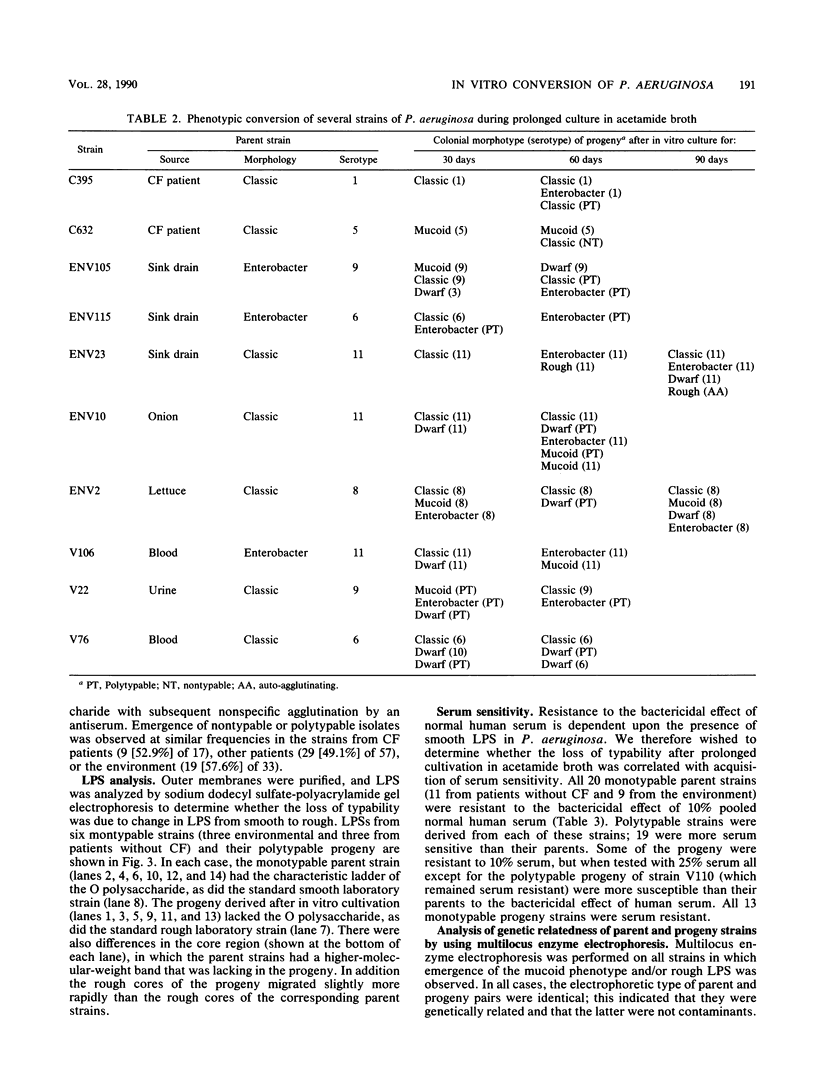
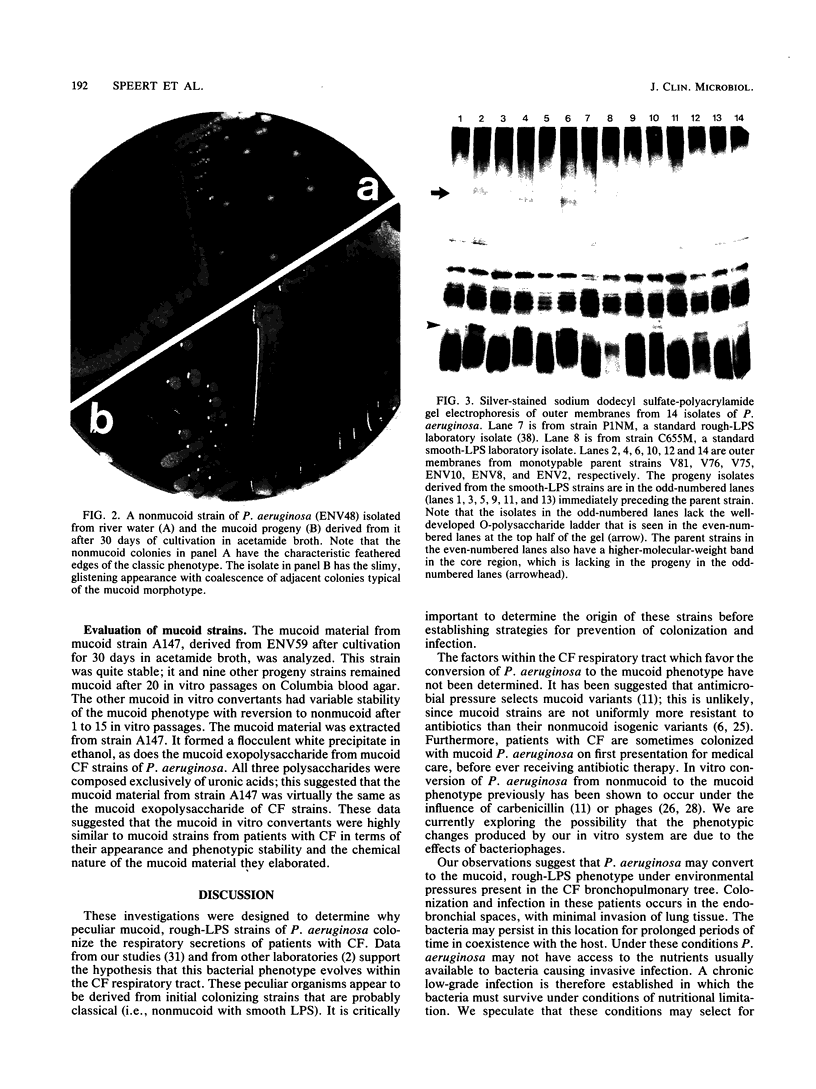
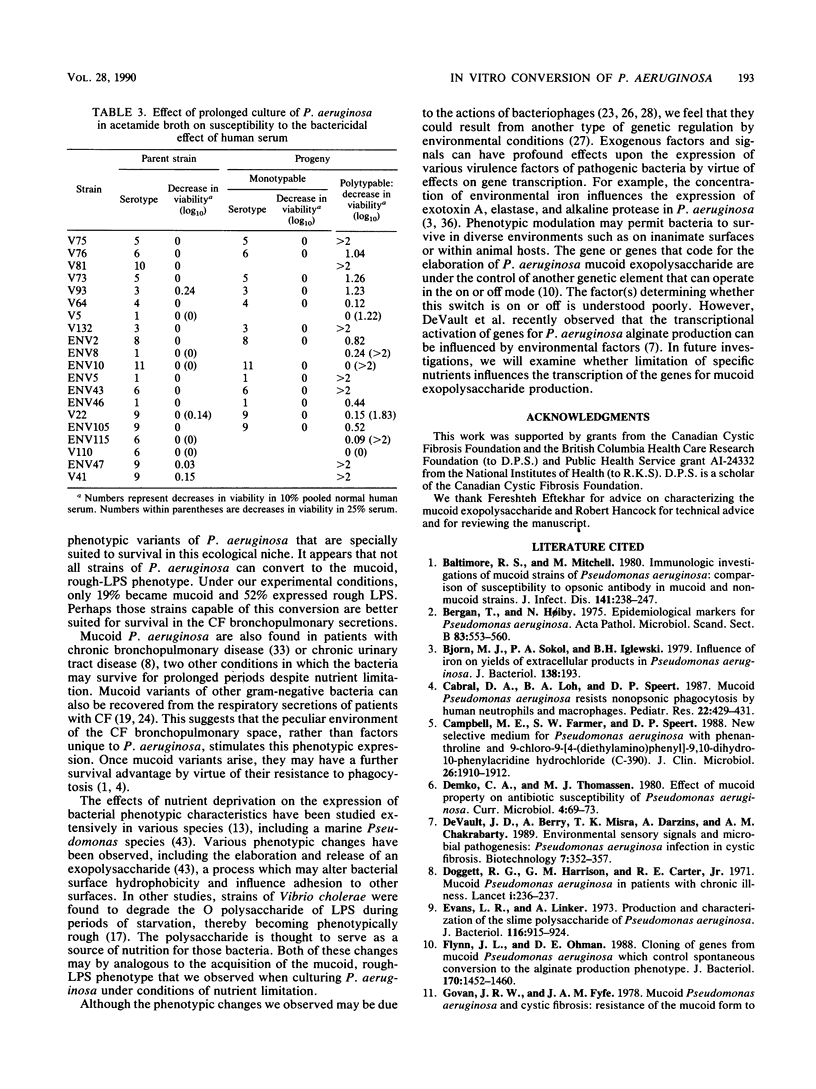
Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis patients are unusual; they are often susceptible to the bactericidal effect of human serum, have a rough lipopolysaccharide, and produce an exopolysaccharide that is responsible for the characteristic mucoid phenotype. In contrast, strains from the environment and from patients with other diseases usually have smooth lipopolysaccharide, do not produce very much mucoid exopolysaccharide, and are phenotypically nonmucoid. The predominance of mucoid strains of P. aeruginosa in infections of patients with cystic fibrosis has not been explained. In the lower airways, where P. aeruginosa persists in cystic fibrosis, nutrients for bacterial growth may be limited. We investigated whether growth of P. aeruginosa under conditions of suboptimal nutrition causes conversion to the characteristic cystic fibrosis phenotype. Ninety-two strains of P. aeruginosa were maintained for up to 90 days in a minimal medium with acetamide as the sole carbon source. In 56 (52%) of 107 cultures, isolates with rough lipopolysaccharide emerged, and in 20 (19%) of 104 nonmucoid cultures, mucoid isolates were recovered. Strains with rough lipopolysaccharide also were sensitive to the bactericidal effect of normal human serum. Under conditions of suboptimal nutrition in vitro, isolates of P. aeruginosa emerged that produced rough lipopolysaccharide and were mucoid, typical of many isolates from cystic fibrosis patients. This peculiar phenotype may arise as a consequence of nutritional limitation within the cystic fibrosis respiratory tract rather than from features unique to these strains of bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore R. S., Mitchell M. Immunologic investigations of mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of susceptibility to opsonic antibody in mucoid and nonmucoid strains. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):238–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergan T., Hoiby N. Epidemiological markers for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 6. Relationship between concomitant non-mucoid and mucoid strains from the respiratory tract in cystic fibrosis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1975 Dec;83(6):553–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorn M. J., Sokol P. A., Iglewski B. H. Influence of iron on yields of extracellular products in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):193–200. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.193-200.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral D. A., Loh B. A., Speert D. P. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa resists nonopsonic phagocytosis by human neutrophils and macrophages. Pediatr Res. 1987 Oct;22(4):429–431. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198710000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Farmer S. W., Speert D. P. New selective medium for Pseudomonas aeruginosa with phenanthroline and 9-chloro-9-[4-(diethylamino)phenyl]-9,10-dihydro-10- phenylacridine hydrochloride (C-390). J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1910–1912. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1910-1912.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett R. G., Harrison G. M., Carter R. E. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with chronic illnesses. Lancet. 1971 Jan 30;1(7692):236–237. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90973-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. R., Linker A. Production and characterization of the slime polysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):915–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.915-924.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn J. L., Ohman D. E. Cloning of genes from mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa which control spontaneous conversion to the alginate production phenotype. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1452–1460. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1452-1460.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mutharia L. M., Chan L., Darveau R. P., Speert D. P., Pier G. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis: a class of serum-sensitive, nontypable strains deficient in lipopolysaccharide O side chains. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.170-177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder W., Dijkhuizen L. Physiological responses to nutrient limitation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:1–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holby N., Olling S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Bactericidal effect of serum from normal individuals and patients with cystic fibrosis on P. aeruginosa strains from patients with cystic fibrosis or other diseases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Apr;85(2):107–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood M. A., Guckert J. B., White D. C., Deck F. Effect of nutrient deprivation on lipid, carbohydrate, DNA, RNA, and protein levels in Vibrio cholerae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):788–793. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.788-793.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Rosendal K. Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in patients treated at a cystic fibrosis centre. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Jun;88(3):125–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly N. M., Falkiner F. R., Keane C. T. Acetamide broth for isolation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):159–159. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.159-.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly N. M., Falkiner F. R., Keane C. T., Fitzgerald M. X., Tempany E. Mucoid gram-negative bacilli in cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1983 Mar 26;1(8326 Pt 1):705–705. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91992-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson C. A., Jeanes A. A new modification of the carbazole analysis: application to heteropolysaccharides. Anal Biochem. 1968 Sep;24(3):470–481. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama H., Ishimoto M., Jono A., Okuda U. [Isolation and serotyping distribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from river water]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1974 Oct;49(10):385–393. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.48.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M. H., Weinstein R. A., Nathan C., Selander R. K., Ochman H., Kabins S. A. Association of infection caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa serotype O11 with intravenous abuse of pentazocine mixed with tripelennamine. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):758–762. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.758-762.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Changes in somatic antigens of Pseudomonas aeruginosa induced by bacteriophages. J Infect Dis. 1969 Mar;119(3):237–246. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.3.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macone A. B., Pier G. B., Pennington J. E., Matthews W. J., Jr, Goldmann D. A. Mucoid Escherichia coli in cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 11;304(24):1445–1449. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106113042401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S. M., Macrina F. L., Phibbs P. V., Jr Antimicrobial susceptibility of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their spontaneously occurring non-mucoid derivatives. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Mar;6(2):251–260. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. R. Mucoid variation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa induced by the action of phage. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):111–118. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Mekalanos J. J., Falkow S. Coordinate regulation and sensory transduction in the control of bacterial virulence. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):916–922. doi: 10.1126/science.2537530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Rubero V. J. Mucoid conversion by phages of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):717–719. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.717-719.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel L. H., Ahl L. A., Fisher M. W. Sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to normal serum and to polymyxin. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):453–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.453-457.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. S., Koch C., Høiby N., Rosendal K. An epidemic spread of multiresistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a cystic fibrosis centre. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17(4):505–516. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.4.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Desjardins D., Aguilar T., Barnard M., Speert D. P. Polysaccharide surface antigens expressed by nonmucoid isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):189–196. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.189-196.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt T. L., MacDougall J., Penketh A. R., Cooke E. M. Polyagglutinating and non-typable strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Mar;21(2):179–186. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera M., Nicotra M. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid strain. Its significance in adult chest diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;126(5):833–836. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.5.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller N. L., Hatch R. A. The serum sensitivity, colonial morphology, serogroup specificity, and outer membrane protein of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from several clinical sites. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;1(2):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(83)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol P. A., Cox C. D., Iglewski B. H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants altered in their sensitivity to the effect of iron on toxin A or elastase yields. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):783–787. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.783-787.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speert D. P., Campbell M. E. Hospital epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Hosp Infect. 1987 Jan;9(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(87)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speert D. P., Eftekhar F., Puterman M. L. Nonopsonic phagocytosis of strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1006–1011. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1006-1011.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speert D. P., Lawton D., Damm S. Communicability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a cystic fibrosis summer camp. J Pediatr. 1982 Aug;101(2):227–228. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80127-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Doershuk C. F., Root J. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates: comparisons of isolates from campers and from sibling pairs with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1985 Jan-Feb;1(1):40–45. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950010110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A. Serum bactericidal effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):512–518. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.512-518.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAHBA A. H., DARRELL J. H. THE IDENTIFICATION OF ATYPICAL STRAINS OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Mar;38:329–342. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrangstadh M., Conway P. L., Kjelleberg S. The production and release of an extracellular polysaccharide during starvation of a marine Pseudomonas sp. and the effect thereof on adhesion. Arch Microbiol. 1986 Aug;145(3):220–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00443649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Schmidt P. J. Dissociation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1003–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1003-1010.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimakoff J., Høiby N., Rosendal K., Guilbert J. P. Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and the role of contamination of the environment in a cystic fibrosis clinic. J Hosp Infect. 1983 Mar;4(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(83)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]