Abstract
Two hundred and fifty clinical fecal specimens collected over a 7-month period were analyzed for the presence of salmonellae by a rapid DNA hybridization procedure. Hybridizations were performed by using a novel specimen processing protocol called wicking and a previously unreported 1,600-base-pair probe cloned from Salmonella enteritidis DNA. The probe was shown to be reactive with all 70 Salmonella serotypes tested and not reactive with 101 stock strains of other enteric bacteria. Southern analysis of 30 Salmonella isolates representing 22 serotypes suggested that the probe sequence was highly conserved, appearing as a 1,600-base-pair band in a BglII digest of isolate DNA in 29 of 30 isolates and as a 2,300-base-pair fragment in 1 of the isolates. The probe correctly identified all salmonellae (nine isolates) among 47 H2S-producing colonies tested from among 250 clinical specimens cultured on xylose-lysine-desoxycholate medium. Salmonellae grown on xylose-lysine-desoxycholate medium gave consistently higher hybridization values than did those grown on either MacConkey or Hektoen enteric agar. In addition, of eight gram-negative broth enrichments in which salmonellae were identified by conventional means, seven were probe positive. The use of this nucleic acid probe and hybridization technique provides a simple and rapid identification of Salmonella species.
Full text
PDF

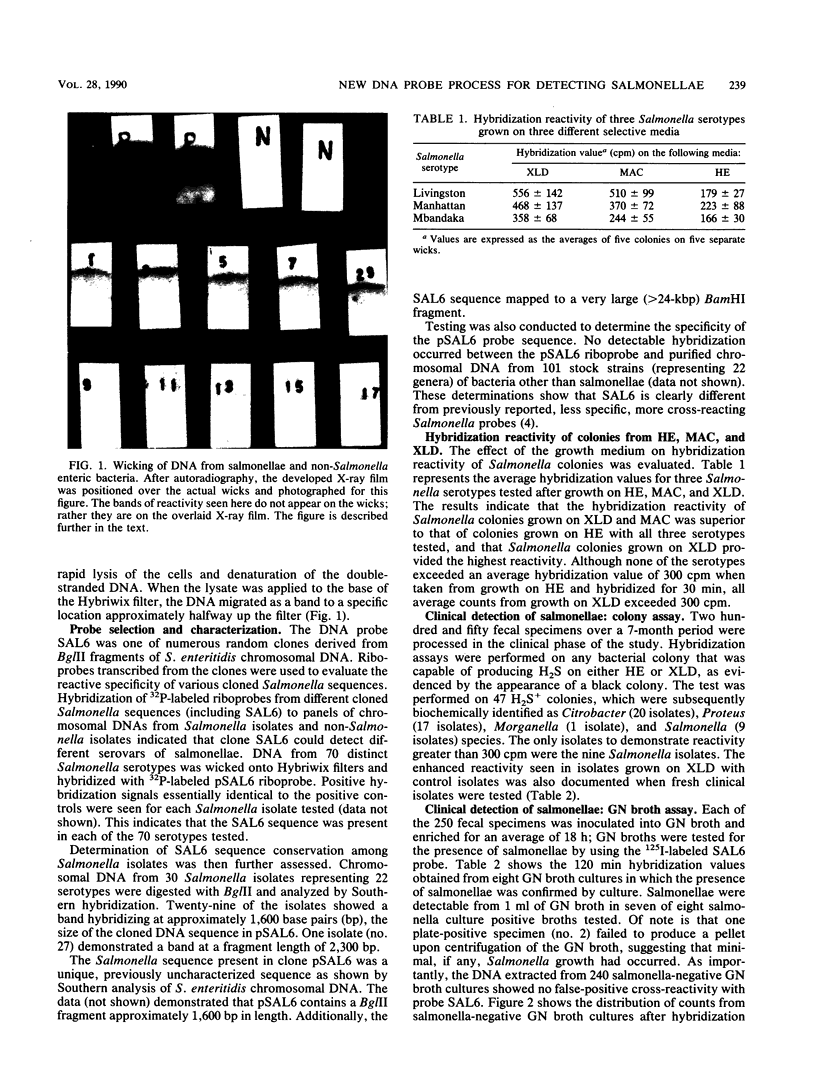
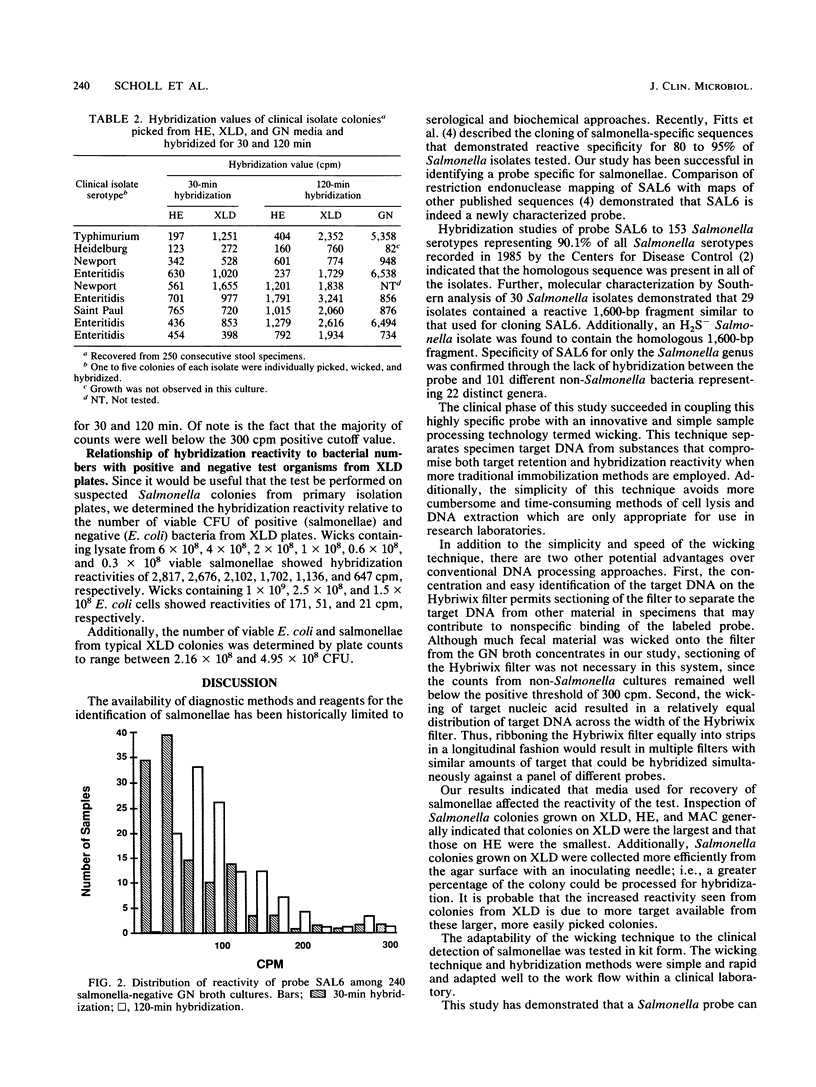

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commerford S. L. Iodination of nucleic acids in vitro. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):1993–2000. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitts R., Diamond M., Hamilton C., Neri M. DNA-DNA hybridization assay for detection of Salmonella spp. in foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1146-1151.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. C., Appelbaum P. C., Kellogg J. A. Evaluation of a two-hour method for screening pathogens from stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):285–287. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.285-287.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzler J., Nachamkin I. Evaluation of a latex agglutination test for the detection of Salmonella and Shigella spp. by using broth enrichment. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2501–2504. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2501-2504.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swierkosz E. M., Scholl D. R., Brown J. L., Jollick J. D., Gleaves C. A. Improved DNA hybridization method for detection of acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1465–1469. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]