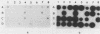Abstract
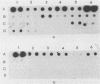
Enteroviruses were specifically detected in crude clinical specimens or in cell cultures in which the viruses were amplified by dot hybridization by using poliovirus type 1-derived, subgenomic radiolabeled cRNA probes (riboprobes). The sensitivity of this test varied from 2.5 to 33%, when clinical specimens without cell culture were examined, and was about 85% in cell culture lysates. The specificity of the test was 90 to 100%. The riboprobe corresponding to the 5'-noncoding sequence specifically detected the majority of enteroviruses (56 of 57 tested); the riboprobe derived from the VPI capsid region hybridized with the three poliovirus serotypes and with some coxsackieviruses type A and with echovirus type 7. Echovirus 22 did not hybridize with any riboprobe. In stool specimens, nasal aspirates, and cerebrospinal fluids from patients with meningitis, only one type of virus was identified in different clinical samples from the same patient by the seroneutralization test. Hybridization allowed the detection of enteroviral RNAs easily in stool specimens and nasal aspirates but with a low efficiency in cerebrospinal fluids without amplification of the viruses in cell cultures.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cova L., Kopecka H., Aymard M., Girard M. Use of cRNA probes for the detection of enteroviruses by molecular hybridization. J Med Virol. 1988 Jan;24(1):11–18. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890240103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyypiä T., Stålhandske P., Vainionpä R., Pettersson U. Detection of enteroviruses by spot hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):436–438. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.436-438.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X., Estes M. K., Metcalf T. G. Detection of hepatitis A virus by hybridization with single-stranded RNA probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2487–2495. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2487-2495.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecka H., Prévot J., Girard M., Fuchs F., Aymard M. Intérêt des sondes ARNc (ribosondes) synthétisés in vitro dans la détection des entérovirus par hybridation moléculaire. Ann Inst Pasteur Virol. 1988 Apr-Jun;139(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2617(88)80019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M., Imai M., Bellamy A. R., Ikegami N., Furuichi Y., Summers D., Nuss D. L., Deibel R. Diagnosis of rotavirus infection with cloned cDNA copies of viral genome segments. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):509–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.509-512.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotbart H. A., Abzug M. J., Levin M. J. Development and application of RNA probes for the study of picornaviruses. Mol Cell Probes. 1988 Mar;2(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(88)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotbart H. A., Levin M. J., Villarreal L. P., Tracy S. M., Semler B. L., Wimmer E. Factors affecting the detection of enteroviruses in cerebrospinal fluid with coxsackievirus B3 and poliovirus 1 cDNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):220–224. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.220-224.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotbart H. A., Levin M. J., Villarreal L. P. Use of subgenomic poliovirus DNA hybridization probes to detect the major subgroups of enteroviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1105–1108. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1105-1108.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålhandske P., Hyypiä T., Allard A., Halonen P., Pettersson U. Detection of adenoviruses in stool specimens by nucleic acid spot hybridization. J Med Virol. 1985 Jul;16(3):213–218. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiff H. E., Seidlin M., Krause P., Rooney J., Brandt C., Rodriguez W., Yolken R., Straus S. E. Detection of enteric adenoviruses by dot-blot hybridization using a molecularly cloned viral DNA probe. J Med Virol. 1985 Jun;16(2):107–118. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]