Abstract
Eastern equine encephalitis (EEE) virus was isolated from the cerebrospinal fluid of a 6-year-old male who had clinically diagnosed aseptic meningitis and subsequently died. Several standard serologic tests that use polyclonal antibody and indirect immunofluorescence and hemagglutination inhibition tests that use monoclonal antibody provided evidence that the isolate was an antigenic subtype of prototype North American EEE virus. We believe that this is the first evidence of an antigenic subtype of EEE virus.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandt W. E., Buescher E. L., Hetrick F. M. Production and characterization of arbovirus antibody in mouse ascitic fluid. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967 May;16(3):339–347. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1967.16.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
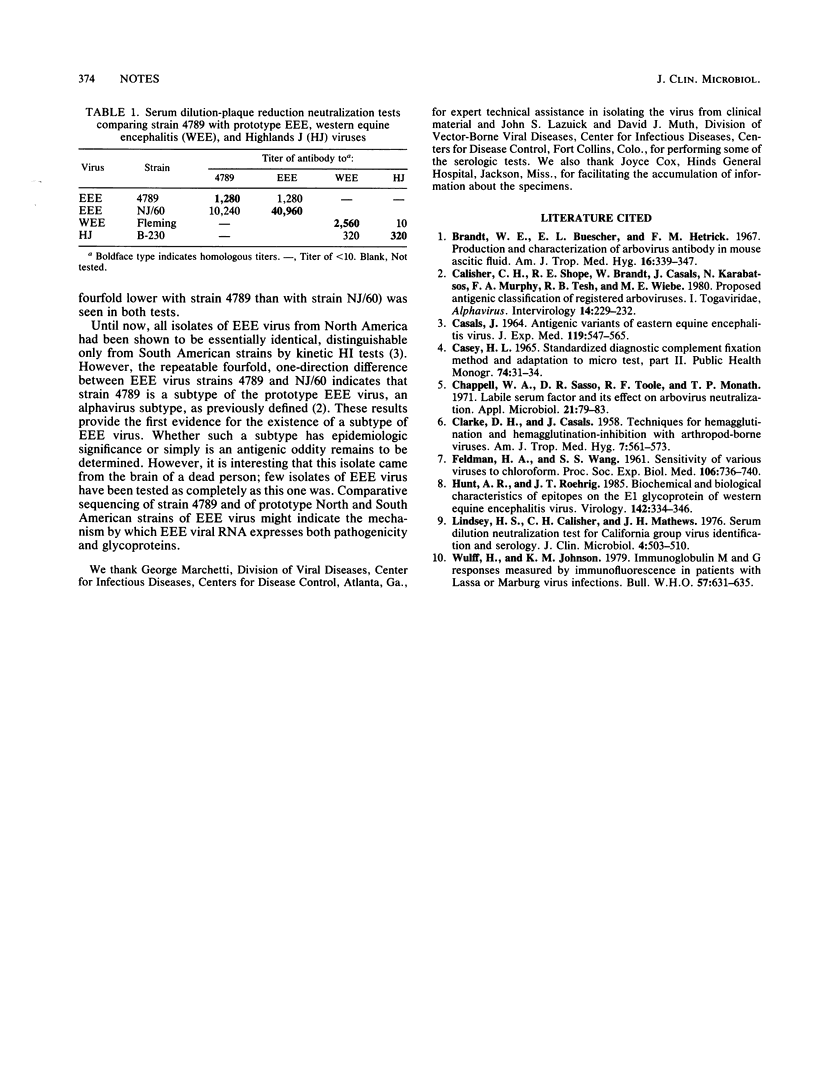
- CASALS J. ANTIGENIC VARIANTS OF EASTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS. J Exp Med. 1964 Apr 1;119:547–565. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASEY H. L. STANDARDIZED DIAGNOSTIC COMPLEMENT FIXATION METHOD AND ADAPTATION TO MICRO TEST. I. LABORATORY BRANCH COMPLEMENT FIXATION METHOD BY LABORATORY BRANCH TASK FORCE. II. ADAPTATION OF LBCF METHOD TO MICRO TECHNIQUE. Public Health Monogr. 1965;74:1–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calisher C. H., Shope R. E., Brandt W., Casals J., Karabatsos N., Murphy F. A., Tesh R. B., Wiebe M. E. Proposed antigenic classification of registered arboviruses I. Togaviridae, Alphavirus. Intervirology. 1980;14(5-6):229–232. doi: 10.1159/000149190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappell W. A., Sasso D. R., Toole R. F., Monath T. P. Labile serum factor and its effect on arbovirus neutralization. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jan;21(1):79–83. doi: 10.1128/am.21.1.79-83.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDMAN H. A., WANG S. S. Sensitivity of various viruses to chloroform. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Apr;106:736–738. doi: 10.3181/00379727-106-26459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt A. R., Roehrig J. T. Biochemical and biological characteristics of epitopes on the E1 glycoprotein of western equine encephalitis virus. Virology. 1985 Apr 30;142(2):334–346. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90342-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey H. S., Calisher C. H., Mathews J. H. Serum dilution neutralization test for California group virus identification and serology. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Dec;4(6):503–510. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.6.503-510.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulff H., Johnson K. M. Immunoglobulin M and G responses measured by immunofluorescence in patients with Lassa or Marburg virus infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57(4):631–635. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


