Abstract
Two proteins (21 and 48 kilodaltons) purified from endospore-spherule culture filtrates of Coccidioides immitis are identified as precipitin and complement-fixing antigens, respectively. To allow specific structural comparison to antigens identified by other investigators and as a first step to eventual serodiagnostic antigen production by recombinant DNA technology, amino-terminal amino acid sequences were determined for these antigens.
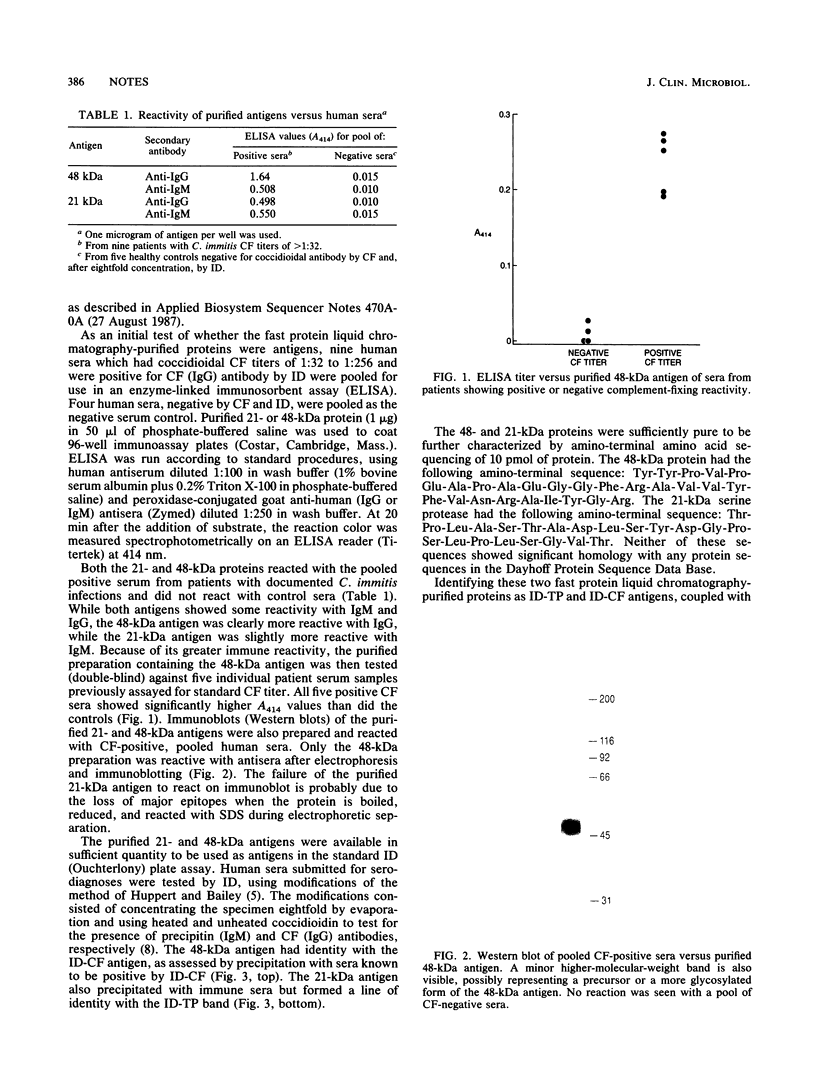
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apodaca G., McKerrow J. H. Purification and characterization of a 27,000-Mr extracellular proteinase from Trichophyton rubrum. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3072–3080. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3072-3080.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. L., Osir E. O., Dugger K. O., Galgiani J. N., Law J. H. Humoral antibody responses to specific antigens of Coccidioides immitis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):265–272. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Britt L. A. Isolation of a coccidioidin component that reacts with immunoglobulin M precipitin antibody. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):449–453. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.449-453.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Britt L. A., Michael R. A. Isolation of Coccidioides immitis F antigen by immunoaffinity chromatography with monospecific antiserum. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):227–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.227-232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE H. B., COBB J. M., SMITH C. E. Immunity to coccidioi-domycosis induced in mice by purified spherule, arthrospore, and mycelial vaccines. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Apr;22:436–449. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1960.tb00711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick S., Pappagianis D., McKerrow J. H. Proteinase production by the parasitic cycle of the pathogenic fungus Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2807–2815. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2807-2815.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Cole G. T. Isolation and characterization of an extracellular proteinase of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1970–1978. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1970-1978.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer B. L., Pappagianis D. Comparison of immunoblot analyses of spherule-endospore-phase extracellular protein and mycelial-phase antigen of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):64–70. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.64-70.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]