Abstract
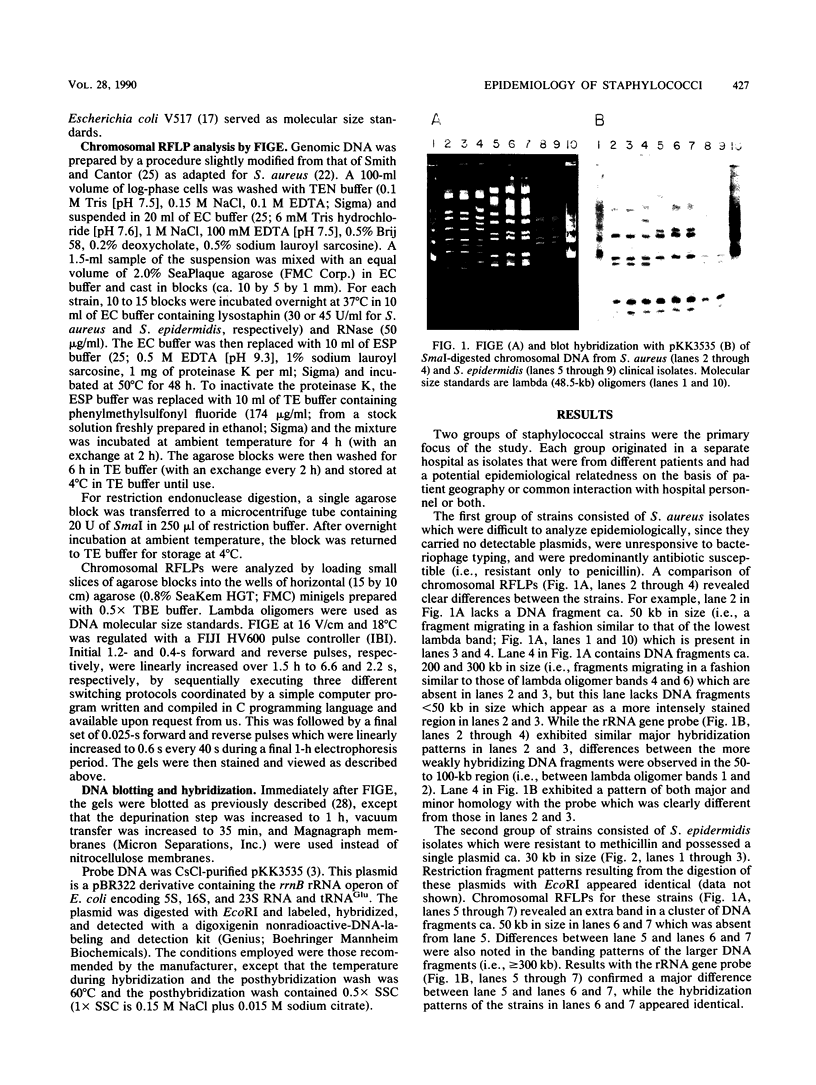
A rapid field inversion gel electrophoresis (FIGE) protocol was combined with an rRNA gene probe in the analysis of staphylococci that were difficult to study epidemiologically by conventional means. The following groups of clinical isolates were examined: (i) predominantly antibiotic-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus strains containing no detectable plasmids and unresponsive to bacteriophage typing and (ii) methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strains carrying a single plasmid ca. 30 kilobases in size. The results indicated that strain interrelationships could be established on the basis of SmaI-generated chromosomal restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) analyzed by FIGE. RFLP analysis of strains known to be unrelated established the importance of minor differences in DNA banding patterns as indicators of strain dissimilarities. Hybridization studies with an rRNA gene probe confirmed this conclusion. These results suggest that FIGE analysis of chromosomal RFLPs (especially in combination with molecular probes) is an important addition to the armamentarium of molecular epidemiology.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L., Johnston J. L. Self-transmissible plasmids in staphylococci that encode resistance to aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):70–77. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Ullrich A., Raker M. A., Gray A., Dull T. J., Gutell R. R., Noller H. F. Construction and fine mapping of recombinant plasmids containing the rrnB ribosomal RNA operon of E. coli. Plasmid. 1981 Jul;6(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Buyser M. L., Morvan A., Grimont F., el Solh N. Characterization of Staphylococcus species by ribosomal RNA gene restriction patterns. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Apr;135(4):989–999. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-4-989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J. B., Chikashige Y., Smith C. L., Niwa O., Yanagida M., Cantor C. R. Construction of a Not I restriction map of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2801–2818. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes B. A., Schaberg D. R. Transfer of resistance plasmids from Staphylococcus epidermidis to Staphylococcus aureus: evidence for conjugative exchange of resistance. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):627–634. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.627-634.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frutos R., Pages M., Bellis M., Roizes G., Bergoin M. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis determination of the genome size of obligate intracellular bacteria belonging to the genera Chlamydia, Rickettsiella, and Porochlamydia. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4511–4513. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4511-4513.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston M. A., Duff P. S., Naidoo J., Ellis K., Roberts J. I., Richardson J. F., Marples R. R., Cooke E. M. Evaluation of electrophoretic methods for typing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(3):189–197. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-3-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goering R. V., Ruff E. A. Comparative analysis of conjugative plasmids mediating gentamicin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Sep;24(3):450–452. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.3.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grothues D., Koopmann U., von der Hardt H., Tümmler B. Genome fingerprinting of Pseudomonas aeruginosa indicates colonization of cystic fibrosis siblings with closely related strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):1973–1977. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.1973-1977.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartstein A. I., Morthland V. H., Eng S., Archer G. L., Schoenknecht F. D., Rashad A. L. Restriction enzyme analysis of plasmid DNA and bacteriophage typing of paired Staphylococcus aureus blood culture isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1874–1879. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1874-1879.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Jones R., Patel Y., Nelson M. Restriction endonucleases for pulsed field mapping of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5985–6005. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvey M., Arbuthnott J. P., Coleman D. C. Molecular typing of methicillin and gentamicin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Dublin. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;5(6):719–725. doi: 10.1007/BF02013312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel A. H., Foster T. J., Pattee P. A. Physical and genetic mapping of the protein A gene in the chromosome of Staphylococcus aureus 8325-4. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jul;135(7):1799–1807. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-7-1799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud F., Freney J., Etienne J., Bes M., Brun Y., Barsotti O., Andre S., Fleurette J. Restriction endonuclease analysis of Staphylococcus epidermidis DNA may be a useful epidemiological marker. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1729–1734. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1729-1734.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Saffran W., Welsh J., Haas R., Goldenberg M., Cantor C. R. New techniques for purifying large DNAs and studying their properties and packaging. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):189–195. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Purification, specific fragmentation, and separation of large DNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:449–467. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Econome J. G., Schutt A., Klco S., Cantor C. R. A physical map of the Escherichia coli K12 genome. Science. 1987 Jun 12;236(4807):1448–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.3296194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele P. E., Carle G. F., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Electrophoretic analysis of Histoplasma capsulatum chromosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):983–987. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber D. A., Goering R. V. Tn4201, a beta-lactamase transposon in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1164–1169. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]