Abstract
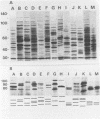
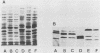
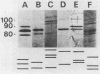
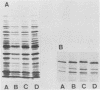
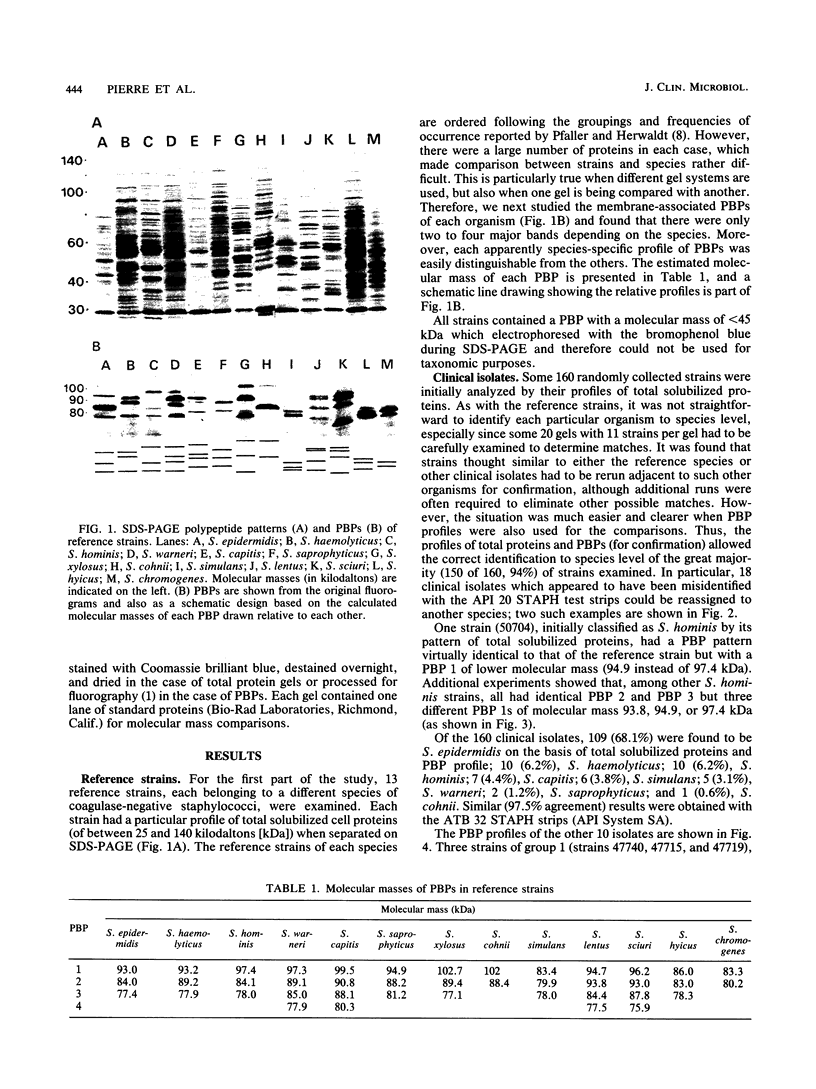
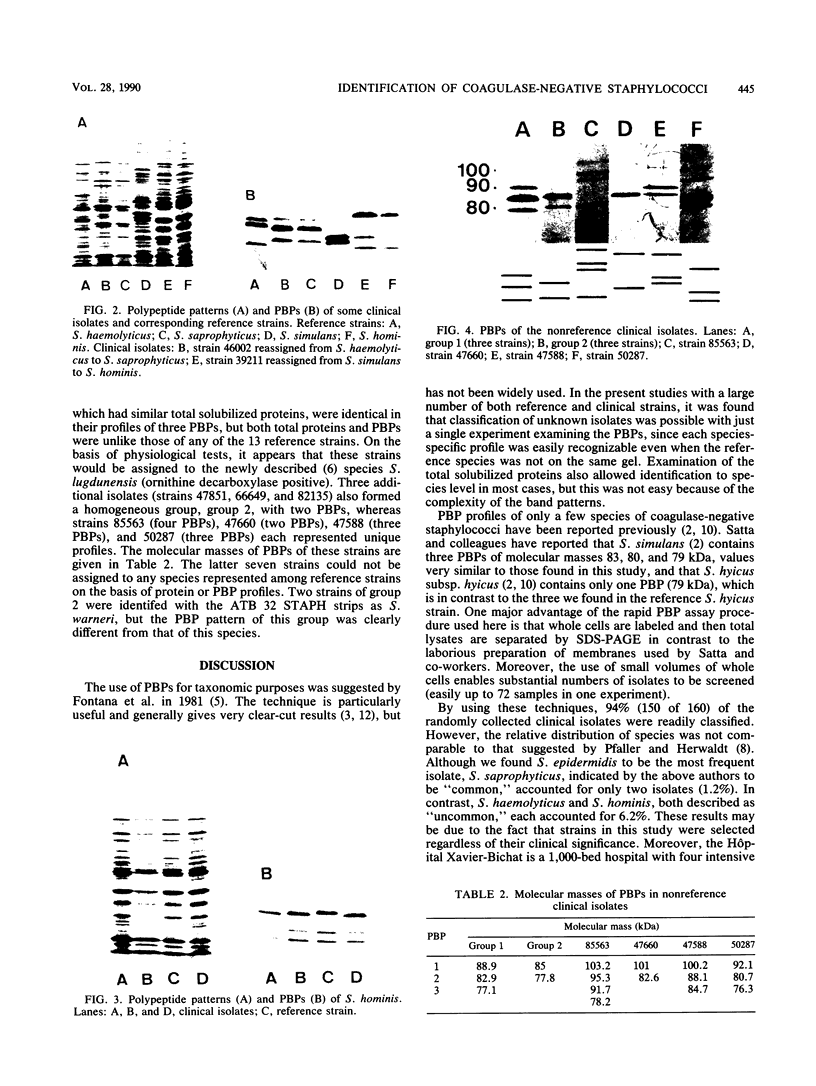
Analyses of total solubilized proteins and penicillin-binding proteins by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis were demonstrated to be accurate methods for the identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci. However, penicillin-binding protein profiles were found to be much clearer for the identification of these organisms to species level than was examination of the total solubilized proteins. By using the former technique, 13 reference strains were found to have species-specific penicillin-binding protein profiles, and 150 of 160 randomly collected clinical isolates were identified as belonging to eight of these species. A group of three clinical strains probably represents the recently described species Staphylococcus lugdunensis; the other seven clinical isolates belonging to five species remained unclassified.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canepari P., Varaldo P. E., Fontana R., Satta G. Different staphylococcal species contain various numbers of penicillin-binding proteins ranging from four (Staphylococcus aureus) to only one (Staphylococcus hyicus). J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):796–798. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.796-798.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. D., Facklam R. R., Farrow J. A., Williamson R. Enterococcus raffinosus sp. nov., Enterococcus solitarius sp. nov. and Enterococcus pseudoavium sp. nov. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Feb;57(3):283–288. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90315-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk D., Guering S. J. Differentiation of Staphylococcus and Micrococcus spp. with the Taxo A bacitracin disk. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):719–721. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.719-721.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi J. T. Coagulase-negative staphylococci and the epidemiological typing of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Jun;49(2):126–139. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.2.126-139.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Herwaldt L. A. Laboratory, clinical, and epidemiological aspects of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jul;1(3):281–299. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson-Carter F. M., Pennington T. H. Characterisation of methicillin-resistant isolates of Staphylococcus aureus by analysis of whole-cell and exported proteins. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jan;28(1):25–32. doi: 10.1099/00222615-28-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varaldo P. E., Hájek V., Canepari P., Satta G. Additional differentiating characters of the two subspecies of Staphylococcus hyicus. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2231–2235. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Gutmann L., Horaud T., Delbos F., Acar J. F. Use of penicillin-binding proteins for the identification of enterococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jul;132(7):1929–1937. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-7-1929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]