Abstract
Nineteen Mycobacterium paratuberculosis strains, including strains of bovine, caprine, ovine, cervid, subhuman primate, and human origins, were compared with organisms of the M. avium complex by restriction fragment length polymorphism with a 5S rRNA gene probe as the reference DNA. Mycobacterial DNA was extracted, digested with several restriction enzymes, subjected to electrophoresis and Southern blotting, and then hybridized with a 5S rRNA gene probe from Escherichia coli. Hybridizing bands were visualized by autoradiography, and the sizes of the resulting rRNA fragments in kilobases were determined. Base substitutions were calculated on the basis of the number of shared fragments between species and strains. It was determined that M. paratuberculosis and the M. avium complex possess a single copy of the rRNA genes within their genomes and that the M. avium complex and M. paratuberculosis are a group of closely related organisms, likely with a common ancestral link. In proximity to the 5S rRNA gene exists a region or regions which display polymorphisms that are capable of species and subspecies differentiation. M. paratuberculosis strains isolated from humans, subhuman primates, and animals were found to be genetically identical to each other. M. paratuberculosis strains lacked the genetic heterogeneity (restriction fragment length polymorphisms) characteristic of most species, suggesting that this organism has unidirectional genetic selection. It is therefore assumed to be biologically isolated, occupying a unique and specific biological niche. This homogeneity was present in all strains, including those of animal and primate (subhuman and human) origin and strains isolated from different parts of the world.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J., Rothman E. D. Estimation of phylogenetic relationships from DNA restriction patterns and selection of endonuclease cleavage sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3560–3564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brega A., Gardella R., Semino O., Morpurgo G., Astaldi Ricotti G. B., Wallace D. C., Santachiara Benerecetti A. S. Genetic studies on the Tharu population of Nepal: restriction endonuclease polymorphisms of mitochondrial DNA. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;39(4):502–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J. Biochemical characteristics of various strains of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;47(7):1442–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J. Crohn's disease and the mycobacterioses: a review and comparison of two disease entities. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):90–117. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J. Characterization of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis of bovine, caprine, and ovine origin by gas-liquid chromatographic analysis of fatty acids in whole-cell extracts. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Sep;46(9):1980–1989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S. Ruminant paratuberculosis (Johne's disease): the current status and future prospects. Cornell Vet. 1984 Jul;74(3):218–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., van Kruiningen H. J. The prevalence of paratuberculosis in culled New England cattle. Cornell Vet. 1986 Jan;76(1):91–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake T. A., Hindler J. A., Berlin O. G., Bruckner D. A. Rapid identification of Mycobacterium avium complex in culture using DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1442–1445. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1442-1445.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh O., Hayashi J. I., Yonekawa H., Tagashira Y. An improved method for estimating sequence divergence between related DNAs from changes in restriction endonuclease cleavage sites. J Mol Evol. 1979 Dec;14(4):301–310. doi: 10.1007/BF01732497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES D. E. A press for disrupting bacteria and other micro-organisms. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Apr;32(2):97–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl D. L., Dykhuizen D. E. The population genetics of Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:31–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehn T. E., Edwards F. F. Rapid identification using a specific DNA probe of Mycobacterium avium complex from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1551–1552. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1551-1552.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebke H., Hatfull G. The sequence of the distal end of the E. coli ribosomal RNA rrnE operon indicates conserved features are shared by rrn operons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5515–5525. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
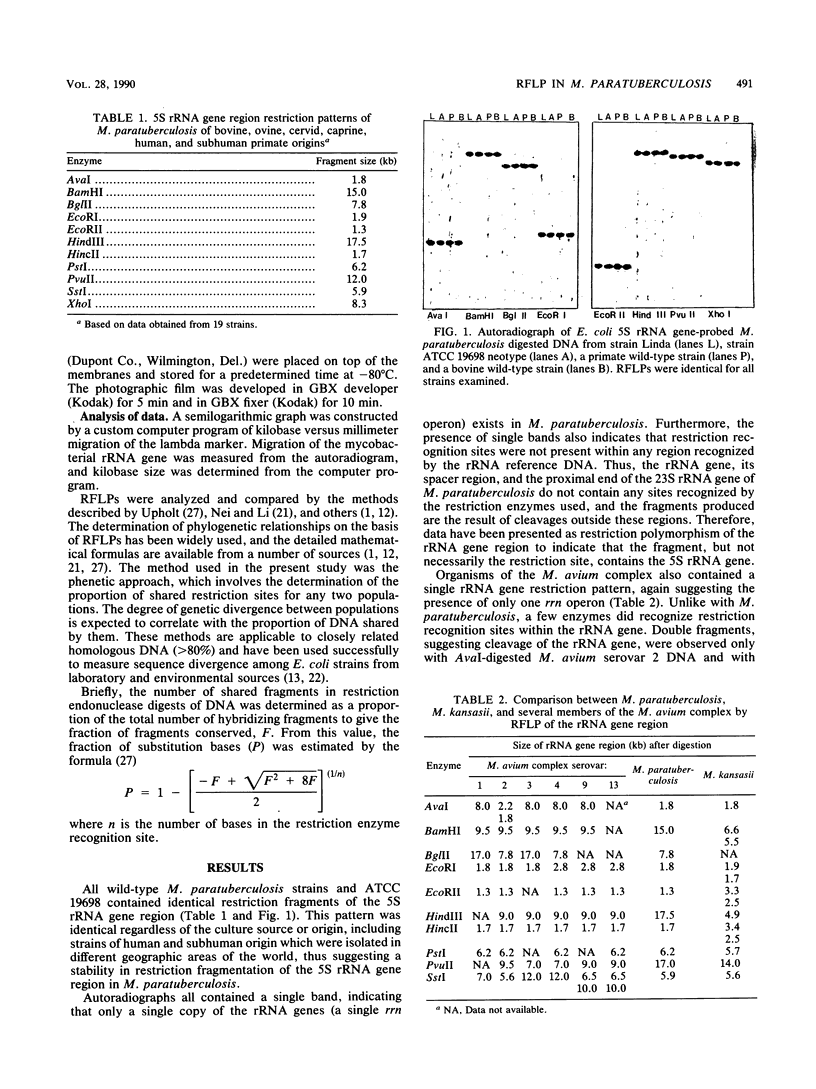
- McClure H. M., Chiodini R. J., Anderson D. C., Swenson R. B., Thayer W. R., Coutu J. A. Mycobacterium paratuberculosis infection in a colony of stumptail macaques (Macaca arctoides). J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):1011–1019. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Chiodini R. J., Hermon-Taylor J. Determination of genome size and DNA homology between an unclassified Mycobacterium species isolated from patients with Crohn's disease and other mycobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jan;133(1):211–214. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-1-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Chiodini R., Hermon-Taylor J. Crohn's disease-isolated mycobacteria are identical to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, as determined by DNA probes that distinguish between mycobacterial species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):796–801. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.796-801.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5269–5273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. P., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequences of trpA of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: an evolutionary comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5244–5248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorel M. F. Review of the occurrence of mycobactin dependence among mycobacteria species. Ann Rech Vet. 1984;15(3):405–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upholt W. B. Estimation of DNA sequence divergence from comparison of restriction endonuclease digests. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1257–1265. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne L. G. The "atypical" mycobacteria: recognition and disease association. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;12(3):185–222. doi: 10.3109/10408418509104429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipple D. L., Kapke P. A., Andrews R. E., Jr Analysis of restriction endonuclease fragment patterns of DNA from Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Vet Microbiol. 1989 Feb;19(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(89)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]