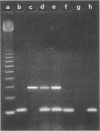
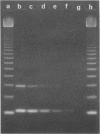
Abstract
A set of four synthetic oligonucleotide probes derived from sequences of the VT1 (Shiga-like toxin I [SLT-I]) and VT2 (SLT-II) genes were used in a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification procedure to detect these genes in some enteric pathogens. A total of 40 verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli strains and 43 isolates of other recognized enteric pathogens were studied. PCR amplification products identifying the VT1 and VT2 gene sequences were observed only in nucleic acid extracted from strains found to be VT positive in traditional tissue culture assays. Template nucleic acid extracted from other gram-negative bacteria was found to be negative with the exception of five isolates of Shigella dysenteriae type 1 in which good amplification with the VT1 probe was observed. The oligonucleotide probes clearly distinguished VT1 and VT2 strains of E. coli and did not give specific amplification with nucleic acid from VTe (a SLT-II variant)-producing E. coli. VT1 or VT2 genes or both were not detected in E. coli K-12 strain C600 or HB101 or in strains known to express other virulence factors, such as enterotoxins, adhesins, hemolysins, or unrelated cytotoxins. The sensitivity of the PCR procedure for detection of both VT1 and VT2 genes was determined to be 1 ng of total nucleic acid. Furthermore, the VT1 gene was easily detected when only 100 pg of nucleic acid was used as the template in the PCR procedure.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basta M., Karmali M., Lingwood C. Sensitive receptor-specified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Escherichia coli verocytotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1617–1622. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1617-1622.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderwood S. B., Auclair F., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Mekalanos J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the Shiga-like toxin genes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4364–4368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Taylor D. N., Seriwatana J., Brown J. E., Lexomboon U. Examination of colonies and stool blots for detection of enteropathogens by DNA hybridization with eight DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):331–334. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.331-334.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Gorbach S. L. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and serum antitoxin activity by the vascular permeability factor assay. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):731–735. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.731-735.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. K., Dalrymple J. M. Quantitative microtiter cytotoxicity assay for Shigella toxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):361–366. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.361-366.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H. A new heat-labile cytolethal distending toxin (CLDT) produced by Escherichia coli isolates from clinical material. Microb Pathog. 1988 Feb;4(2):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Meyer T. Evaluation of oligonucleotide probes for identification of shiga-like-toxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1180–1186. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1180-1186.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongmuang U., Honda T., Miwatani T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect Shiga toxin of Shigella dysenteriae and related toxins. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):115–118. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.115-118.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Xu J. G., Kaper J. B., Lior H., Prado V., Tall B., Nataro J., Karch H., Wachsmuth K. A DNA probe to identify enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli of O157:H7 and other serotypes that cause hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):175–182. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques L. R., Moore M. A., Wells J. G., Wachsmuth I. K., O'Brien A. D. Production of Shiga-like toxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):338–341. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Neill R. J. DNA probes for Shiga-like toxins I and II and for toxin-converting bacteriophages. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1292–1297. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1292-1297.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli after polymerase chain reaction amplification with a thermostable DNA polymerase. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):261–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.261-265.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Marques L. R., O'Brien A. D. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Shiga-like toxin II of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli and use of the monoclonal antibodies in a colony enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2127–2131. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2127-2131.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard D. R., Tyler S. D., Ng C. W., Rozee K. R. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) protocol for the specific detection of Chlamydia spp. Mol Cell Probes. 1989 Dec;3(4):383–389. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(89)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochetman G., Ou C. Y., Jones W. K. Polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1154–1157. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotland S. M., Rowe B., Smith H. R., Willshaw G. A., Gross R. J. Vero cytotoxin-producing strains of Escherichia coli from children with haemolytic uraemic syndrome and their detection by specific DNA probes. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Apr;25(4):237–243. doi: 10.1099/00222615-25-4-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speirs J. I., Stavric S., Konowalchuk J. Assay of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin with vero cells. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):617–622. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.617-622.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Jackson M. P., Sung L. M., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Cloning and sequencing of the genes for Shiga toxin from Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1116–1122. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1116-1122.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr P. I., Neill M. A., Clausen C. R., Newland J. W., Neill R. J., Moseley S. L. Genotypic variation in pathogenic Escherichia coli O157:H7 isolated from patients in Washington, 1984-1987. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):344–347. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Jackson M. P., Samuel J. E., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Cloning and sequencing of a Shiga-like toxin type II variant from Escherichia coli strain responsible for edema disease of swine. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4223–4230. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4223-4230.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Bevan I. S., Johnson M. A., Blomfield P. I., Bromidge T., Maitland N. J., Woodman C. B. The polymerase chain reaction: a new epidemiological tool for investigating cervical human papillomavirus infection. BMJ. 1989 Jan 7;298(6665):14–18. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6665.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]