Abstract
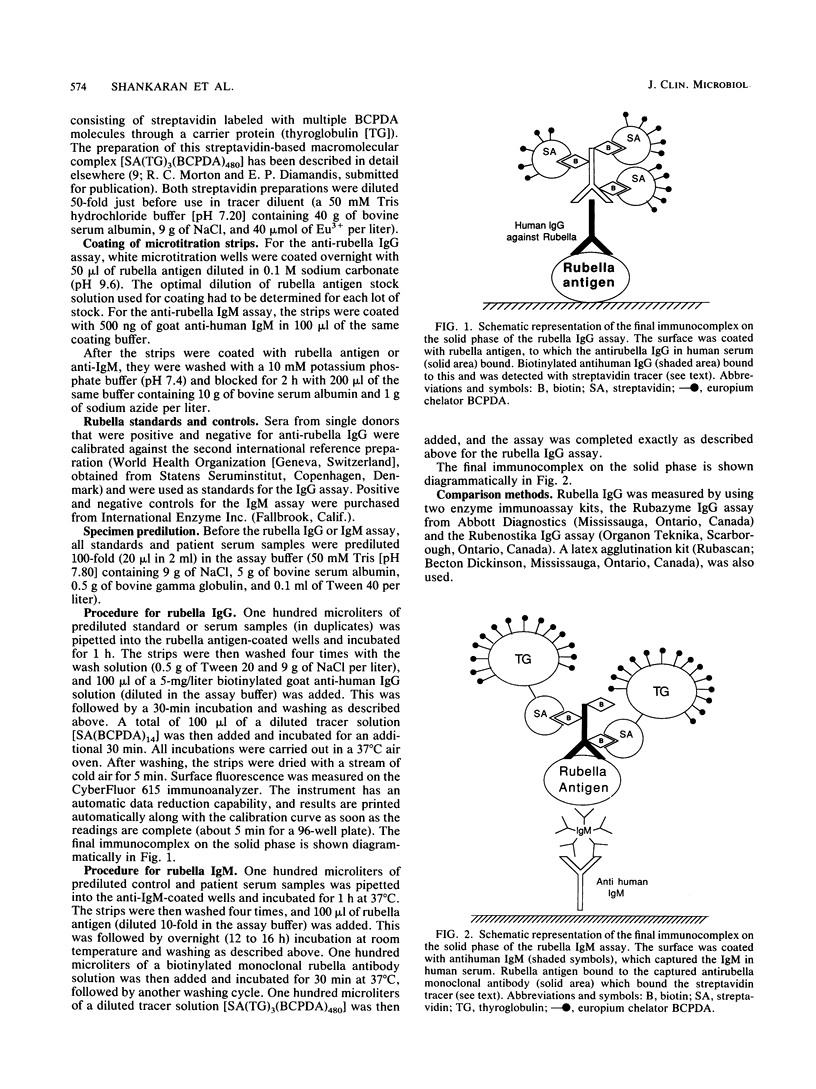
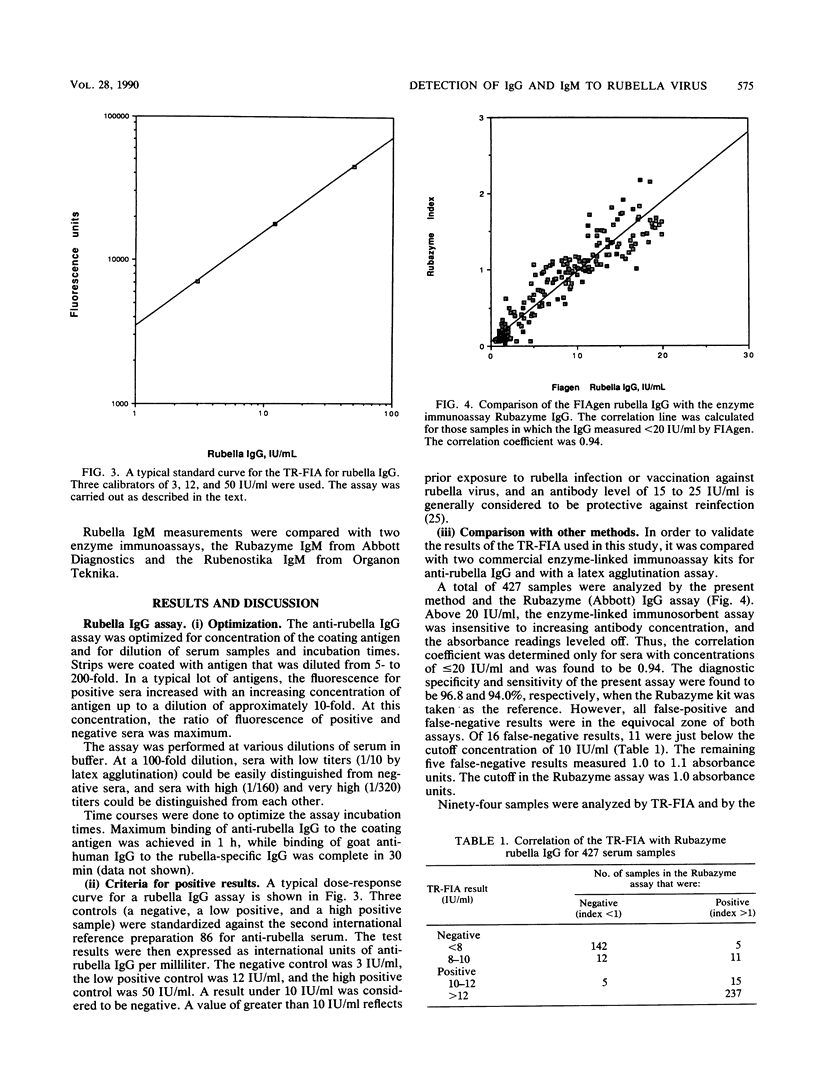
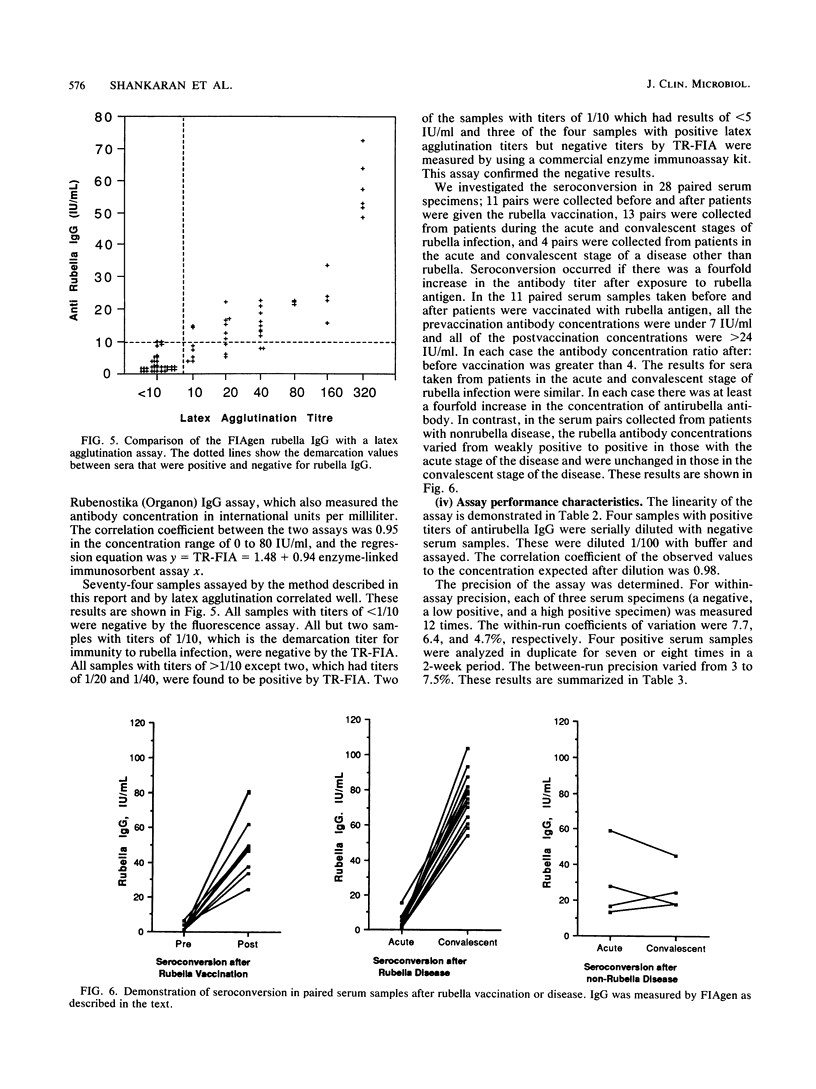
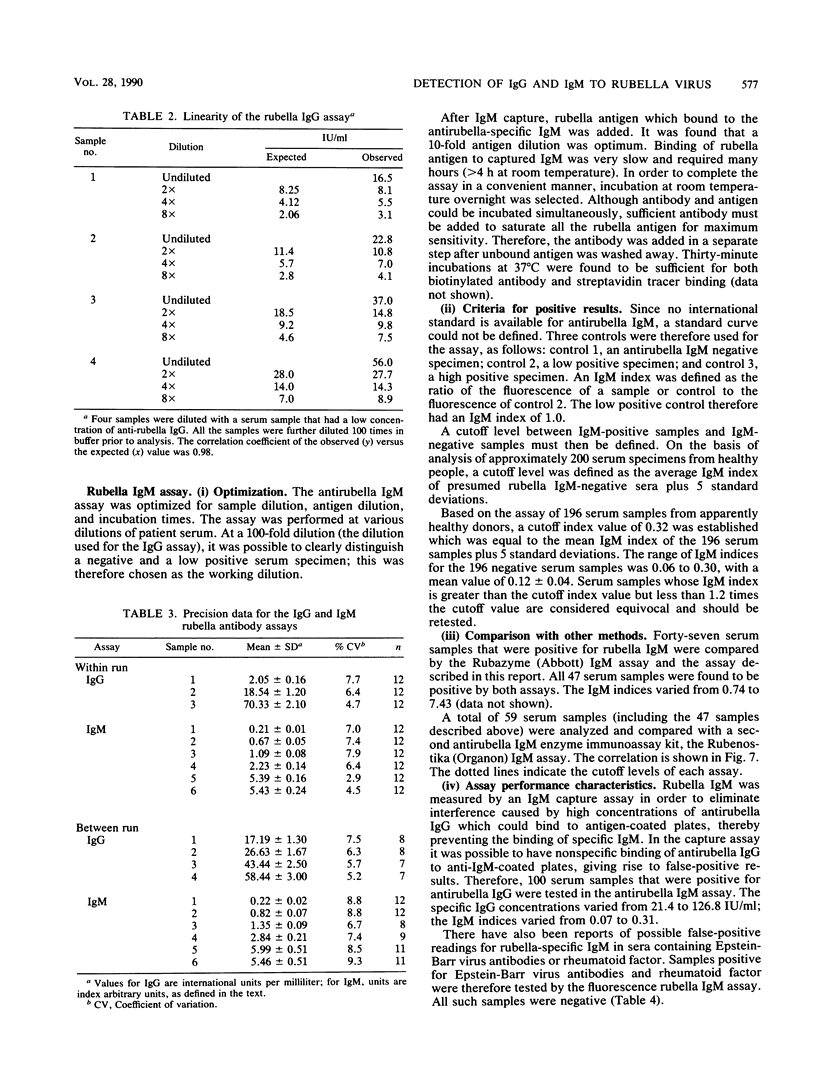
We describe new methods for the detection of immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM rubella-specific antibodies in serum. The IgG assay was based on a solid-phase rubella antigen immobilization approach, and the IgM assay was based on the IgM capture assay principle. Both assays used biotinylated antibodies (anti-human IgG and antirubella monoclonal antibody, respectively). The tracer system was based on streptavidin labeled with a fluorescent europium chelate. The final measurements were done by using time-resolved fluorescence. Both assays were thoroughly evaluated with clinical samples and compared successfully with established techniques. We anticipate that these assays are suitable for routine clinical use.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Best J. M., Palmer S. J., Morgan-Capner P., Hodgson J. A comparison of Rubazyme-M and MACRIA for the detection of rubella-specific IgM. J Virol Methods. 1984 Feb;8(1-2):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(84)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R., Doerr H. W., Geisen H. P., Hornig C., Huschka U., Munk K. Comparison of different methods for the detection of rubella-specific IgM antibodies. J Med Virol. 1981;8(3):207–214. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890080308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R., Hornig C., Sann G., Doerr H. W. Comparison of different methods for assessment of rubella infection and immunity. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1982 Sep;252(4):431–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantler S., Evans C. J. Selection and performance of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies in an IgM antibody capture enzyme immunoassay for rubella. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Feb 27;87(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary T. J., Cid A., Ellis B., Malkus H., Noto T., Halbert S., Castro A. A direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of antibodies for rubella virus in human sera. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1978 Feb;19(2):281–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper L. Z., Matters B., Rosenblum J. K., Krugman S. Experience with a modified rubella hemagglutination inhibition antibody test. JAMA. 1969 Jan 6;207(1):89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamandis E. P. Immunoassays with time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy: principles and applications. Clin Biochem. 1988 Jun;21(3):139–150. doi: 10.1016/0009-9120(88)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamandis E. P., Morton R. C., Reichstein E., Khosravi M. J. Multiple fluorescence labeling with europium chelators. Application to time-resolved fluoroimmunoassays. Anal Chem. 1989 Jan 1;61(1):48–53. doi: 10.1021/ac00176a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamandis E. P., Morton R. C. Time-resolved fluorescence using a europium chelate of 4,7-bis-(chlorosulfophenyl)-1,10-phenanthroline-2,9-dicarboxylic acid (BCPDA). Labeling procedures and applications in immunoassays. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Aug 9;112(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echevarria J. M., de Ory F., Najera R. Fluoroimmunoassay for detection of rubella-specific immunoglobulin M: comparison with indirect enzyme immunoassay and mu-chain capture. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):428–434. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.428-434.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evangelista R. A., Pollak A., Allore B., Templeton E. F., Morton R. C., Diamandis E. P. A new europium chelate for protein labelling and time-resolved fluorometric applications. Clin Biochem. 1988 Jun;21(3):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0009-9120(88)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravell M., Dorsett P. H., Gutenson O., Ley A. C. Detection of antibody to rubella virus by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136 (Suppl):S300–S303. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_2.s300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P., Meurman O., Lövgren T., Hemmilä I., Soini E. Detection of viral antigens by time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;104:133–146. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68949-9_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmilä I., Dakubu S., Mukkala V. M., Siitari H., Lövgren T. Europium as a label in time-resolved immunofluorometric assays. Anal Biochem. 1984 Mar;137(2):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmilä I. Fluoroimmunoassays and immunofluorometric assays. Clin Chem. 1985 Mar;31(3):359–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimo K. O., Meurman O. H., Halonen P. E., Ziola B. R., Viljanen M. K., Granfors K., Toivanen P. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of rubella virus immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;4(2):117–123. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.2.117-123.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennette E. H., Schmidt N. J., Magoffin R. L. The hemagglutination inhibition test for rubella: a comparison of its sensitivity to that of neutralization, complement fixation and fluorescent antibody tests for diagnosis of infection and determination of immunity status. J Immunol. 1967 Oct;99(4):785–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber H. Measurement of rubella antibody by hemagglutination inhibition. I. Variables affecting rubella hemagglutination. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):818–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber H. Measurement of rubella antibody by hemagglutination inhibition. II. Characteristics of an improved HAI test employing a new method for the removal of non-immunoglobulin HA inhibitors from serum. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):826–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurman O. H., Hemmilä I. A., Lövgren T. N., Halonen P. E. Time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay: a new test for rubella antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):920–925. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.920-925.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer P. P., Tedder R. S., Hamblig M. H., Shafi M. S., Burkhardt F., Schilt U. Antibody capture radioimmunoassay for anti-rubella IgM. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Apr;86(2):139–153. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400068856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siitari H., Hemmilä I., Soini E., Lövgren T., Koistinen V. Detection of hepatitis B surface antigen using time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):258–260. doi: 10.1038/301258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vejtorp M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for determination of rubella IgG antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1978 Dec;86B(6):387–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E. A simple method for detecting antibodies to rubella. Br J Exp Pathol. 1975 Aug;56(4):338–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


