Abstract
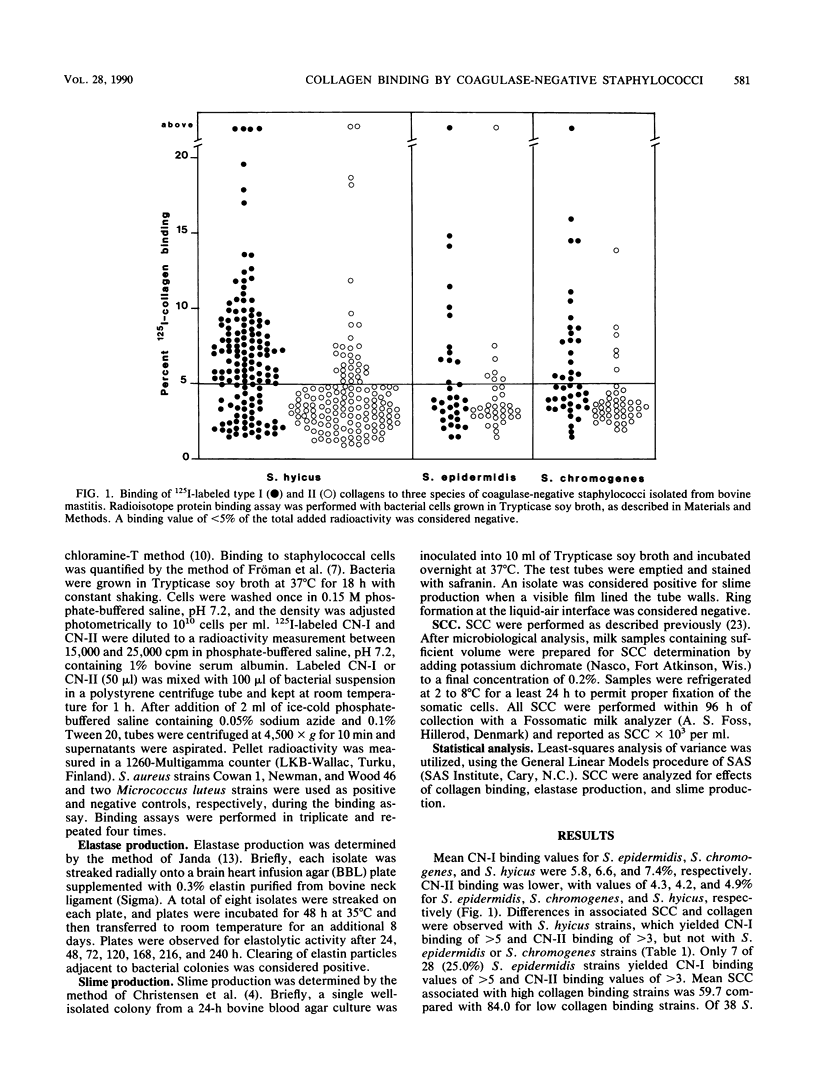
Collagen binding, elastase production, slime production, and associated somatic cell counts were determined with 160 strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from bovine intramammary infections. Mean binding values for type I and II collagen with Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. chromogenes, and S. hyicus strains were 5.8, 6.6, and 7.4 and 4.3, 4.2, and 4.9%, respectively. Eleven of 28 (39.3%) S. epidermidis, 1 of 38 (2.6%) S. chromogenes, and 1 of 94 (1.1%) S. hyicus strains were elastase positive. Slime production was noted with 12 (42.9%) S. epidermidis, 1 (2.6%) S. chromogenes, and 11 (11.7%) S. hyicus strains. No differences in somatic cell counts were observed with type I or type II collagen binding, elastase production, or slime production with S. epidermidis or S. chromogenes. However, somatic cell counts associated with S. hyicus strains with collagen type I binding affinities of greater than 5 and type II binding affinities of greater than 3 were 320.7 x 10(3) compared with 163.9 x 10(3) for strains with lower binding affinities.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bramley A. J., Dodd F. H. Reviews of the progress of dairy science: mastitis control--progress and prospects. J Dairy Res. 1984 Aug;51(3):481–512. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900023797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Parisi J. T., Bisno A. L., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Characterization of clinically significant strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):258–269. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.258-269.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., De Keyser H. Prevalence of different species of coagulase-negative staphylococci on teats and in milk samples from dairy cows. J Dairy Res. 1980 Feb;47(1):155–158. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900020999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Derycke J. Staphylococcus hyicus in cattle. Res Vet Sci. 1979 May;26(3):356–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröman G., Switalski L. M., Faris A., Wadström T., Hök M. Binding of Escherichia coli to fibronectin. A mechanism of tissue adherence. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14899–14905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Hancock G. A. Synergistic hemolysis exhibited by species of staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):409–415. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.409-415.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishak M. A., Gröschel D. H., Mandell G. L., Wenzel R. P. Association of slime with pathogenicity of coagulase-negative staphylococci causing nosocomial septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1025–1029. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1025-1029.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M. Elastolytic activity among staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):945–946. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.945-946.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. M., Pearson R. E., Clabaugh G. A., Heald C. W. Relationships between somatic cell counts and milk production. J Dairy Sci. 1984 Aug;67(8):1823–1831. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(84)81510-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamo W., Fröman G., Wadström T. Interaction of sub-epithelial connective tissue components with Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci from bovine mastitis. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Oct;18(2):163–176. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miedzobrodzki J., Naidu A. S., Watts J. L., Ciborowski P., Palm K., Wadström T. Effect of milk on fibronectin and collagen type I binding to Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from bovine mastitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):540–544. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.540-544.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidu A. S., Ekstrand J., Wadström T. Binding of type-I and type-II collagens to Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from patients with toxic shock syndrome compared to other staphylococcal infections. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1989 Mar;1(4):219–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb02386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson S. C., Paape M. J., Harmon R. J., Ziv G. Mammary leukocyte response to drug therapy. J Dairy Sci. 1986 Jun;69(6):1733–1742. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(86)80592-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poutrel B., Rainard P. Predicting the probability of quarter infection (by major pathogens) from somatic cell concentration. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Jul;43(7):1296–1299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T. Molecular aspects on pathogenesis of wound and foreign body infections due to staphylococci. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Aug;266(1-2):191–211. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts J. L. Etiological agents of bovine mastitis. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Jan;16(1):41–66. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts J. L., Nickerson S. C. A comparison of the STAPH-Ident and STAPH-Trac systems to conventional methods in the identification of staphylococci isolated from bovine udders. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Jul;12(2):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts J. L., Owens W. E. Synergistic hemolysis associated with coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from bovine mammary glands. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2037–2039. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2037-2039.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


