Abstract
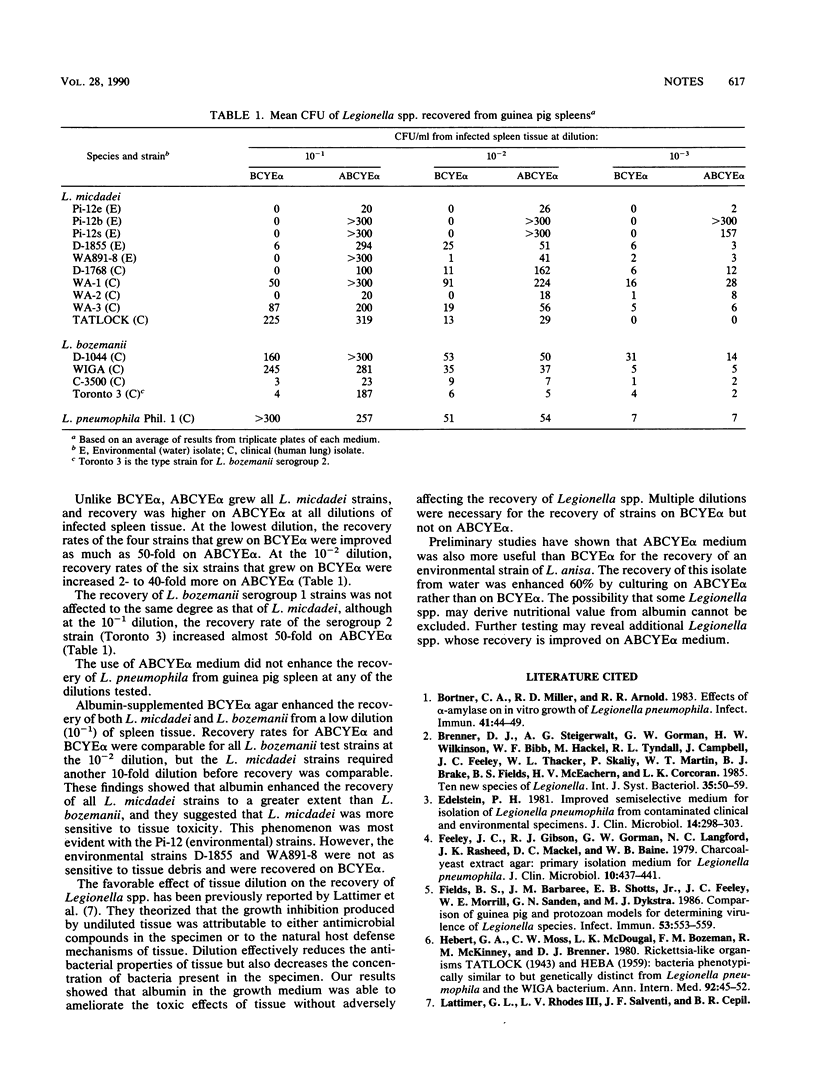
The recovery of Legionella micdadei and L. bozemanii serogroups 1 and 2 from infected guinea pig spleens was evaluated by using two culture media: buffered charcoal yeast extract agar with 0.1% alpha-ketoglutarate (BCYE alpha) and the same medium supplemented with 1% bovine serum albumin (ABCYE alpha). At the lowest dilution of spleen tissue (10(-1)), recovery of all strains of L. micdadei and L. bozemanii was more efficient on ABCYE alpha than on BCYE alpha. L. micdadei strains had higher recovery rates on ABCYE alpha after another 10-fold dilution, but recoveries of L. bozemanii were similar on both media. Recovery rates for most test strains were comparable on BCYE alpha and ABCYE alpha at the highest dilution (10(-3)) of tissue tested. The presence of albumin in BCYE alpha increased the recovery rate of L. micdadei more than that of L. bozemanii. The use of ABCYE alpha medium in place of BCYE alpha may improve the recovery of L. micdadei and L. bozemanii from clinical specimens. Preliminary studies indicate that this medium also enhances recovery of certain Legionella spp. from environmental samples.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bortner C. A., Miller R. D., Arnold R. R. Effects of alpha-amylase on in vitro growth of Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):44–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.44-49.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Improved semiselective medium for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from contaminated clinical and environmental specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):298–303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.298-303.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. S., Barbaree J. M., Shotts E. B., Jr, Feeley J. C., Morrill W. E., Sanden G. N., Dykstra M. J. Comparison of guinea pig and protozoan models for determining virulence of Legionella species. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):553–559. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.553-559.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Moss C. W., McDougal L. K., Bozeman F. M., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J. The rickettsia-like organisms TATLOCK (1943) and HEBA (1959): bacteria phenotypically similar to but genetically distinct from Legionella pneumophila and the WIGA bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jan;92(1):45–52. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D., Edwards M. L., Smith D. W. Changes in iron and transferrin levels and body temperature in experimental airborne legionellosis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):302–307. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Pasculle A. W., Dowling J. N., Pazin G. J., Sr, Puerzer M., Yee R. B., Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Hakala T. R. Opportunistic lung infection due to "Pittsburgh Pneumonia Agent". N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 1;301(18):953–958. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911013011801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Dowling J. N., Frola F. N., McDevitt D. A., Levi M. A. Antimicrobial therapy of experimental Legionella micdadei pneumonia in guinea pigs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Dec;28(6):730–734. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.6.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Cordes L. G., Myerowitz R. L., Patton C. M., Gorman G. W., Carmack C. L., Ezzell J. W., Dowling J. N. Pittsburgh pneumonia agent: direct isolation from human lung tissue. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):727–732. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaliy P., McEachern H. V. Survival of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium in water. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):662–663. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang P. W., Toma S., Moss C. W., Steigerwalt A. G., Cooligan T. G., Brenner D. J. Legionella bozemanii serogroup 2: a new etiological agent. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):30–33. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.30-33.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



