Abstract
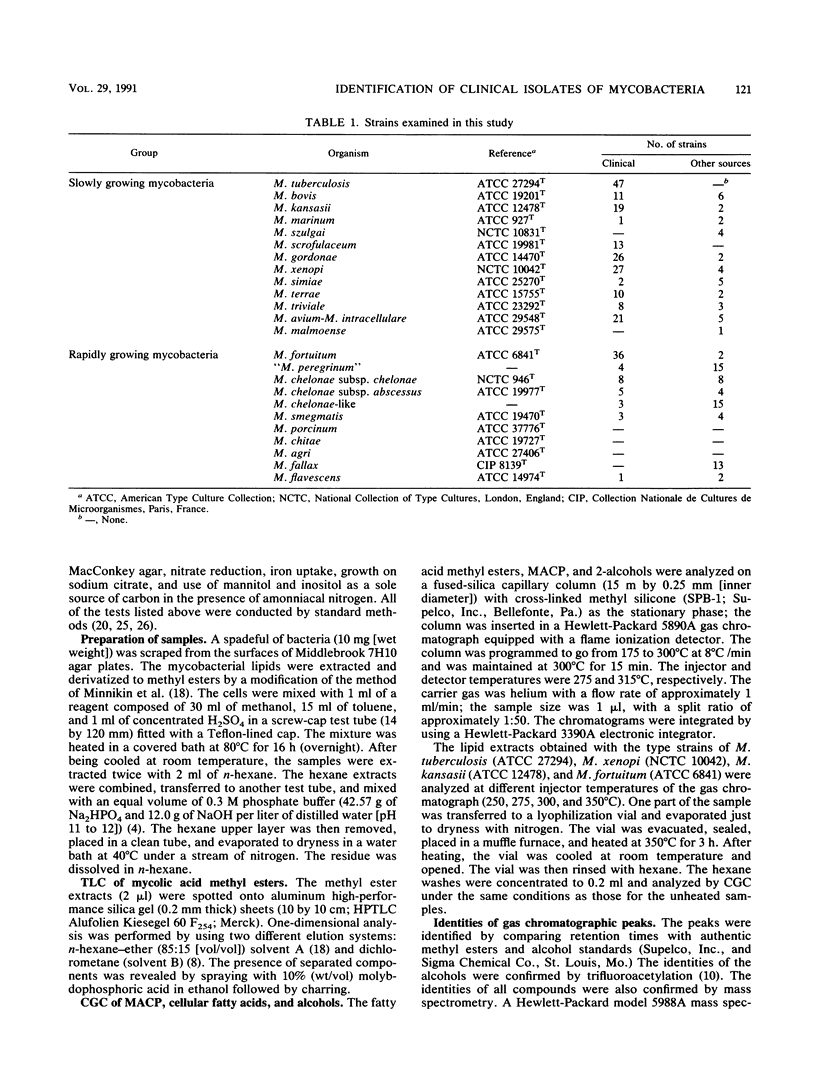
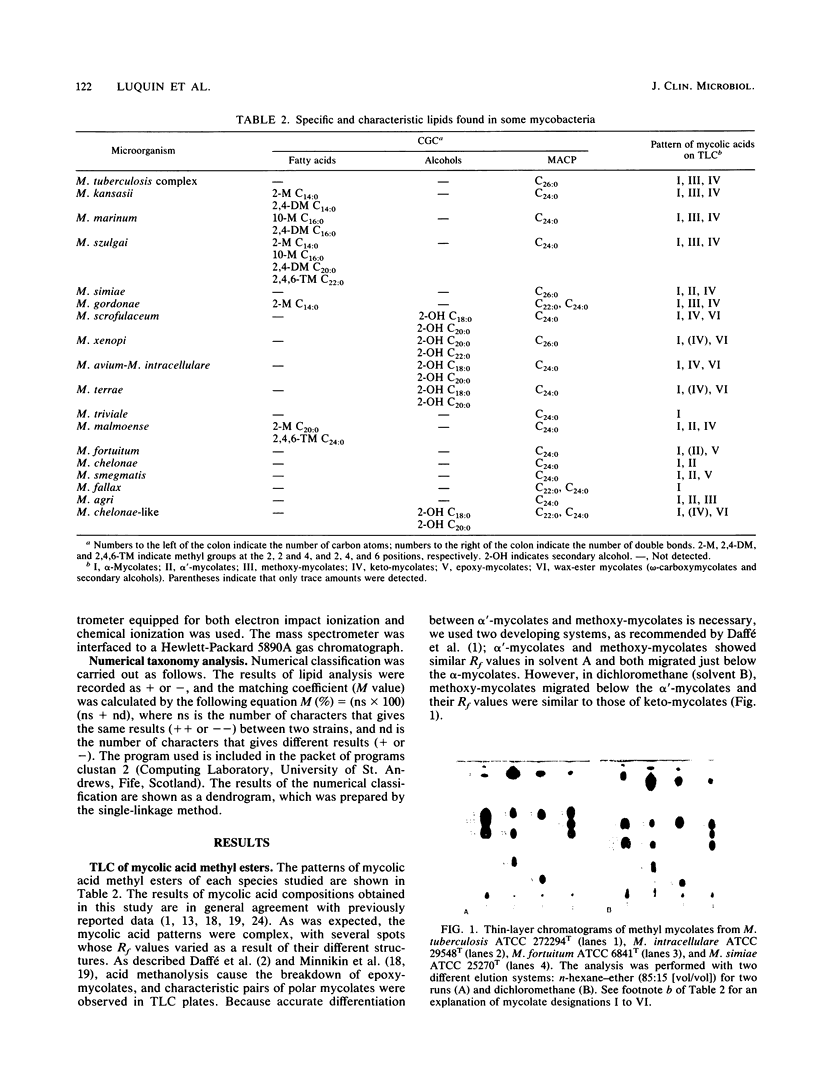
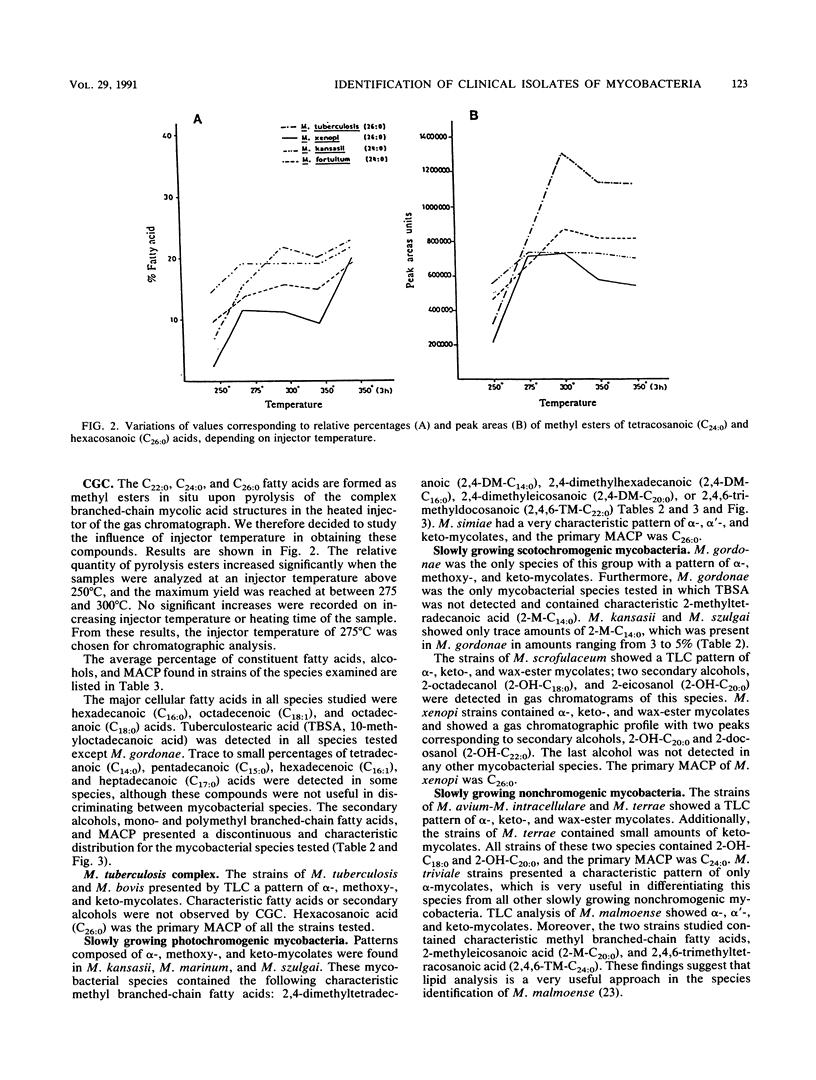
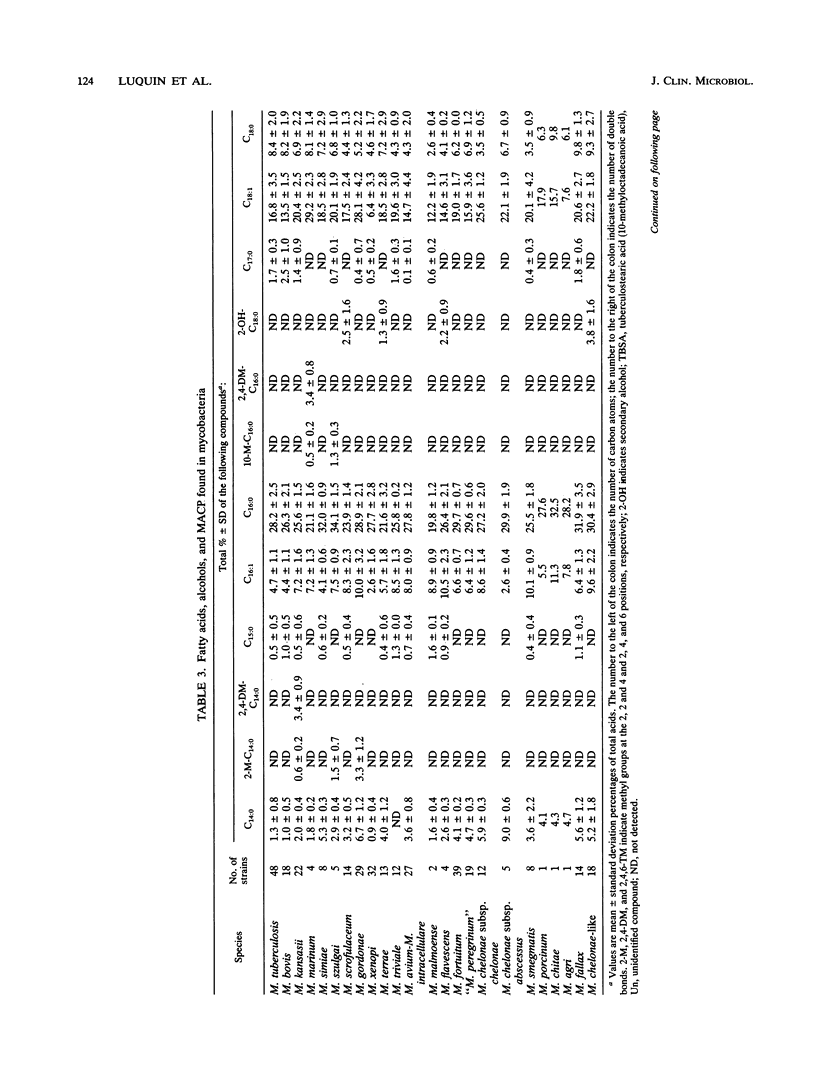
After experimental conditions were established, 366 strains of mycobacteria belonging to 23 different species were studied for fatty acids, secondary alcohols, and mycolic acid cleavage products by capillary gas-liquid chromatography. Additionally, the mycolic acid pattern was studied by thin-layer chromatography. Capillary gas-liquid chromatography allowed direct identification of the following Mycobacterium spp.: M. kansasii, M. marinum, M. szulgai, M. xenopi, M. malmoense, and M. gordonae. The patterns of mycolic acid methyl esters recorded for the test strains of M. chelonae and M. agri may be of value in the identification of these species. Moreover, the combined use of the two chromatographic techniques provided precise identification of the M. tuberculosis complex, M. simiae, M. fallax, M. triviale, and M. chelonae-like organisms. A minimal set of biochemical tests is usually required to obtain identification to the species level when chromatographic procedures alone are not sufficient. Under the reported experimental conditions, thin-layer chromatography and capillary gas-liquid chromatography are rapid and very useful techniques for the identification of mycobacteria.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daffé M., Lanéelle M. A., Asselineau C., Lévy-Frébault V., David H. Intérêt taxonomique des acides gras des mycobactéries: proposition d'une méthode d'analyse. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Sep-Oct;134B(2):241–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant G. O., Lambert M. A., Moss C. W. Gas-chromatographic analysis of mycolic acid cleavage products in mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):899–907. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.899-907.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins P. A. Lipid analysis for the identification of mycobacteria: an appraisal. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Sep-Oct;3(5):862–866. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.5.862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. A., Moss C. W., Silcox V. A., Good R. C. Analysis of mycolic acid cleavage products and cellular fatty acids of Mycobacterium species by capillary gas chromatography. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):731–736. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.731-736.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. Acidic methanolysis v. alkaline saponification in gas chromatographic characterization of mycobacteria: differentiation between Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare and Mycobacterium gastri. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Aug;91(4):235–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L., Jantzen E., Johnsson J. Gas chromatographic fatty acid profiles for characterisation of mycobacteria: an interlaboratory methodological evaluation. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;4(5):483–487. doi: 10.1007/BF02014429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L., Mårdh P. A. Gas chromatographic characterization of mycobacteria: analysis of fatty acids and trifluoroacetylated whole-cell methanolysates. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Feb;3(2):81–85. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.2.81-85.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechevalier M. P., Horan A. C., Lechevalier H. Lipid composition in the classification of nocardiae and mycobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):313–318. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.313-318.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy-Frébault V., Goh K. S., David H. L. Mycolic acid analysis for clinical identification of Mycobacterium avium and related mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):835–839. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.835-839.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayall B. C. Rapid identification of mycobacteria using gas liquid chromatography. Pathology. 1985 Jan;17(1):24–28. doi: 10.3109/00313028509063718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnikin D. E., Goodfellow M. Lipid composition in the classification and identification of acid-fast bacteria. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1980;8:189–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnikin D. E., Minnikin S. M., Parlett J. H., Goodfellow M., Magnusson M. Mycolic acid patterns of some species of Mycobacterium. Arch Microbiol. 1984 Oct;139(2-3):225–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00402005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdall P. A., Roberts G. D., Anhalt J. P. Identification of clinical isolates of mycobacteria with gas-liquid chromatography alone. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):506–514. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.506-514.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamura M. A review of the methods of identification and differentiation of mycobacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Sep-Oct;3(5):841–861. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.5.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valero-Guillén P. L., Pacheco F., Martín-Luengo F. Fatty acid composition and mycolic acid pattern of some chromogenic mycobacteria. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;59(2):113–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb03309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valero-Guillén P., Martín-Luengo F., Larsson L., Jimenez J., Juhlin I., Portaels F. Fatty and mycolic acids of Mycobacterium malmoense. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):153–154. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.153-154.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Swenson J. M., Silcox V. A., Good R. C., Tschen J. A., Stone M. S. Spectrum of disease due to rapidly growing mycobacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):657–679. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



