Abstract
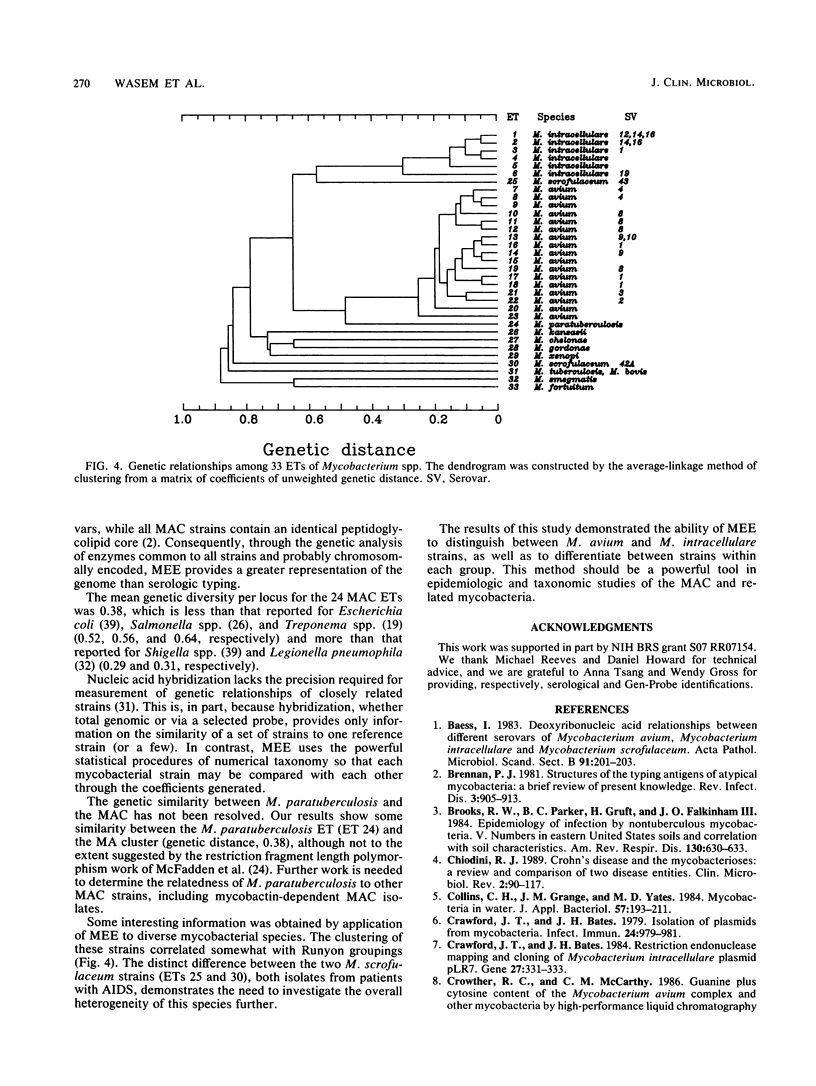
Multilocus enzyme electrophoresis analysis was used to evaluate the Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC), M. paratuberculosis, and nine other mycobacterial species. The average number of alleles per locus was 2.8 for the 35 MAC and 2 M. paratuberculosis strains which represented 24 electrophoretic types (ETs) and two distinct groups. The M. avium group was resolved into 17 ETs and contained the M. paratuberculosis ET. The M. intracellulare group consisted of six ETs. There was complete agreement between Gen-Probe identification and group placement by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. The mean genetic diversity per locus for the 24 MAC ETs was 0.38. This procedure subdivided some serovars and, if implemented, should prove to be a powerful epidemiologic tool for the MAC. Eleven additional ETs were formed after the data for the other mycobacterial species were pooled with those for the MAC.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baess I. Deoxyribonucleic acid relationships between different serovars of Mycobacterium avium, Mycobacterium intracellulare and Mycobacterium scrofulaceum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Jun;91(3):201–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P. J. Structures of the typing antigens of atypical mycobacteria: a brief review of present knowledge. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Sep-Oct;3(5):905–913. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.5.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks R. W., Parker B. C., Gruft H., Falkinham J. O., 3rd Epidemiology of infection by nontuberculous mycobacteria. V. Numbers in eastern United States soils and correlation with soil characteristics. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;130(4):630–633. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.4.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J. Crohn's disease and the mycobacterioses: a review and comparison of two disease entities. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):90–117. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. H., Grange J. M., Yates M. D. Mycobacteria in water. J Appl Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;57(2):193–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1984.tb01384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. T., Bates J. H. Isolation of plasmids from mycobacteria. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):979–981. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.979-981.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. T., Bates J. H. Restriction endonuclease mapping and cloning of Mycobacterium intracellulare plasmid pLR7. Gene. 1984 Mar;27(3):331–333. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkinham J. O., 3rd Arylsulfatase activity of Mycobacterium avium, M. intracellulare, and M. scrofulaceum. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;40(1):66–70. doi: 10.1099/00207713-40-1-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good R. C. Opportunistic pathogens in the genus Mycobacterium. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:347–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good R. C., Snider D. E., Jr Isolation of nontuberculous mycobacteria in the United States, 1980. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):829–833. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange J. M., Yates M. D., Boughton E. The avian tubercle bacillus and its relatives. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 May;68(5):411–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb02892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruft H., Loder A., Osterhout M., Parker B. D., Falkinham J. O., 3rd Postulated sources of Mycobacterium intracellulare and Mycobacterium scrofulaceum infection: isolation of mycobacteria from estuaries and ocean waters. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Dec;120(6):1385–1388. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.6.1385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins C. C., Gold J. W., Whimbey E., Kiehn T. E., Brannon P., Cammarata R., Brown A. E., Armstrong D. Mycobacterium avium complex infections in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Aug;105(2):184–188. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-2-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lygren S. T., Closs O., Bercouvier H., Wayne L. G. Catalases, peroxidases, and superoxide dismutases in Mycobacterium leprae and other mycobacteria studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):666–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.666-672.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lymbery A. J., Hampson D. J., Hopkins R. M., Combs B., Mhoma J. R. Multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for identification and typing of Treponema hyodysenteriae and related spirochaetes. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Mar;22(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90127-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy C. M., Taylor M. A., Dennis M. W. Maximum growth rate of Mycobacterium avium in continuous culture or chronically infected BALB/c mice. Microbios. 1987;52(211):97–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy C. M. Utilization of nitrate or nitrite as single nitrogen source by Mycobacterium avium. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):263–267. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.263-267.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy C., Ashbaugh P. Factors that affect the cell cycle of Mycobacterium avium. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Sep-Oct;3(5):914–925. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.5.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClatchy J. K. The seroagglutination test in the study of nontuberculous mycobacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Sep-Oct;3(5):867–870. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.5.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Thompson J., Chiodini R., Hermon-Taylor J. The use of DNA probes identifying restriction-fragment-length polymorphisms to examine the Mycobacterium avium complex. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Nov;1(3):283–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb01934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Anz W. Sources of Mycobacterium avium complex infection resulting in human diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Dec;116(6):1057–1064. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.6.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Evins G. M., Heiba A. A., Plikaytis B. D., Farmer J. J., 3rd Clonal nature of Salmonella typhi and its genetic relatedness to other salmonellae as shown by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis, and proposal of Salmonella bongori comb. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):313–320. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.313-320.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Tomioka H., Sato K., Tasaka H., Dawson D. J. Identification of various serovar strains of Mycobacterium avium complex by using DNA probes specific for Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium intracellulare. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1694–1697. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1694-1697.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Tomioka H., Sato K., Tasaka H., Tsukamura M., Kuze F., Asano K. Identification and partial characterization of Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium intracellulare by using DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):994–997. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.994-997.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., McKinney R. M., Whittam T. S., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J., Nolte F. S., Pattison P. E. Genetic structure of populations of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1021–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1021-1037.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Musser J. M., Caugant D. A., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Population genetics of pathogenic bacteria. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jul;3(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne L. G. The "atypical" mycobacteria: recognition and disease association. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;12(3):185–222. doi: 10.3109/10408418509104429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Ochman H., Selander R. K. Multilocus genetic structure in natural populations of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1751–1755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury W., Spencer A. K., Stahman M. A. An improved procedure using ferricyanide for detecting catalase isozymes. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90375-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakrus M. A., Good R. C. Geographic distribution, frequency, and specimen source of Mycobacterium avium complex serotypes isolated from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):926–929. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.926-929.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



