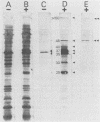
Abstract
Antibodies against Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:3 were measured by crossed immunoelectrophoresis (XIE) using whole-cell sonic extract as antigen and by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) using either purified lipopolysaccharide or whole formalinized cells expressing virulence plasmid-encoded surface antigens (pYV+ cells). The results were compared with those obtained with the standard tube agglutination method. Sera from three groups of people were examined by using these assays. The first group consisted of healthy blood donors, the second consisted of patients with recent infection due to microorganisms other than Y. enterocolitica O:3, and the third consisted of patients with recent Y. enterocolitica O:3 infection. Sera from the last group were also obtained at regular intervals for 12 months postinfection. Results obtained with XIE and the ELISAs were in good agreement with those obtained with tube agglutination. Variation, diagnostic sensitivity, and diagnostic specificity were satisfactory for all the assays studied. However, the lipopolysaccharide ELISA was less laborious than tube agglutination and XIE and carried a somewhat greater diagnostic specificity than the pYV+ ELISA. XIE and the pYV+ ELISA, on the other hand, also had advantages. XIE enabled simultaneous examination of the individual antibody response against a wide range of chromosome-encoded antigens, and the pYV+ ELISA enabled detection of specific pYV antibodies when sera were adsorbed with formalinized pYV-cured Y. enterocolitica O:3 cells prior to the assay.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bissett M. L., Powers C., Abbott S. L., Janda J. M. Epidemiologic investigations of Yersinia enterocolitica and related species: sources, frequency, and serogroup distribution. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):910–912. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.910-912.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitzan M., Häck H. J., Mauff G. Yersinia enterocolitica serodiagnosis: a dual role of specific IgA. Evaluation of microagglutination and ELISA. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Dec;267(2):194–205. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J., Sheehan D. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: guidelines for serologic diagnosis of human infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5(5):898–906. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.5.898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundle D. R., Gidney M. A., Perry M. B., Duncan J. R., Cherwonogrodzky J. W. Serological confirmation of Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 O-antigens by monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):389–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.389-393.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson H. E., Hurvell B., Lindberg A. A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for titration of antibodies against Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Jun;84(3):168–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G. R., Biot T., Lambert de Rouvroit C., Michiels T., Mulder B., Sluiters C., Sory M. P., Van Bouchaute M., Vanooteghem J. C. The Yersinia yop regulon. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1455–1459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glimcher L. H., Kruisbeek A. M., Paul W. E., Green I. Functional activity of a transformed thymic epithelial cell line. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Jan;17(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Jalkanen S., von Essen R., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Isomäki O., Pekkola-Heino K., Merilahti-Palo R., Saario R., Isomäki H., Toivanen A. Yersinia antigens in synovial-fluid cells from patients with reactive arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 26;320(4):216–221. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901263200404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Ståhlberg T. H., Toivanen A. Comparison of bacteria with and without plasmid-encoded proteins as antigens for measurement of immunoglobulin M, G, and A antibodies to Yersinia enterocolitica by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):583–585. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.583-585.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K. Measurement of immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgG, and IgA antibodies against Yersinia enterocolitica by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: persistence of serum antibodies during disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):336–341. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.336-341.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Toivanen A. IgA-anti-yersinia antibodies in yersinia triggered reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Jul;45(7):561–565. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.7.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Viljanen M. K., Toivanen A. Measurement of immunoglobulin M, immunoglobulin G, and immunoglobulin A antibodies against Yersinia enterocolitica by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: comparison of lipopolysaccharide and whole bacterium as antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):6–14. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.6-14.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gripenberg M., Nissinen A., Väisänen E., Linder E. Demonstration of antibodies against Yersinia enterocolitica lipopolysaccharide in human sera by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):279–284. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.279-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., KUPFERBERG L. L., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. III. Effects of calcium ions on the growth of virulent and avirulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1959 Mar;77(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.3.317-321.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasin M., Rottem S., Razin S. The outer membrane of Proteus mirabilis. I. Isolation and characterization of the outer and cytoplasmic membrane fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 14;375(3):381–394. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Schröder J., Ulrich M. Analysis of the class-specific immune response to Yersinia enterocolitica virulence-associated antigens in oro-gastrically infected rabbits. Microb Pathog. 1988 Dec;5(6):437–447. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindersson P., Knudsen J. D., Axelsen N. H. Cloning and expression of treponema pallidum common antigen (Tp-4) in Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):587–596. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Axelsen N. H. Identification and quantitation of precipitins against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis by means of crossed immunoelectrophoresis with intermediate gel. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Jun;81(3):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Heesemann J., Lehtonen O. P., Granfors K., Toivanen A. Avidity of antibodies against released proteins of Yersinia spp: comparison of patients with or without reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Dec;48(12):1003–1006. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.12.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Ståhlberg T. H., Granfors K., Kuusisto P., Toivanen A. Serological cross-reactions against Yersinia enterocolitica in patients infected with other arthritis-associated microbes. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1990 Jan-Feb;8(1):5–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. H., Hartzen S. H., Parm M. The determination of specific IgA-antibodies to Yersinia enterocolitica and their role in enteric infections and their complications. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Oct;93(5):331–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. H. The spectrum of clinical manifestations of infections with Yersinia enterocolitica and their pathogenesis. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:257–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paerregaard A., Espersen F., Baek L., Høiby N. Crossed immuno-electrophoretic analysis of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype 0:3 antigens. APMIS. 1988 Apr;96(4):306–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paerregaard A., Espersen F., Hannover Larsen J., Høiby N. Adhesion of Yersinia enterocolitica to human epithelial cell lines and to rabbit and human small intestinal tissue. APMIS. 1990 Jan;98(1):53–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paerregaard A., Espersen F., Høiby N. Cross-reactions between Yersinia enterocolitica serogroup 0:3 and other serogroups of the same species, as well as thirty-four other bacterial species. APMIS. 1988 Apr;96(4):315–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoerner C., Wartenberg K., Röllinghoff M. Differentiation of serological responses to Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O9 and Brucella species by immunoblot or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using whole bacteria and Yersinia outer membrane proteins. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1570–1574. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1570-1574.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand G. H., Pedersen S. S., Tilling R., Brown M. R., Høiby N. Use of immunoblot detection of serum antibodies in the diagnosis of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in cystic fibrosis. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Nov;27(3):169–177. doi: 10.1099/00222615-27-3-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M. Expression of antigens encoded by the virulence plasmid of Yersinia enterocolitica under different growth conditions. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):183–190. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.183-190.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M., Poikonen K. Experimental intestinal infection of rats by Yersinia enterocolitica 0:3. A follow-up study with specific antibodies to the virulence plasmid specified antigens. Scand J Infect Dis. 1986;18(4):355–364. doi: 10.3109/00365548609032347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sory M. P., Cornelis G. Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 as a potential live oral carrier for protective antigens. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jun;4(6):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ståhlberg T. H., Granfors K., Pekkola-Heino K., Soppi E., Toivanen A. Immunoblotting analysis of human IgM, IgG and IgA response to chromosomally coded antigens of Yersinia enterocolitica 0:3. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1987 Apr;95(2):71–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1987.tb00011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ståhlberg T. H., Heesemann J., Granfors K., Toivanen A. Immunoblot analysis of IgM, IgG, and IgA responses to plasmid encoded released proteins of Yersinia enterocolitica in patients with or without yersinia triggered reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Jul;48(7):577–581. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.7.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Brubaker R. R. Roles of V antigen in promoting virulence and immunity in yersiniae. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2226–2230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartenberg K., Knapp W., Ahamed N. M., Widemann C., Mayer H. Temperature-dependent changes in the sugar and fatty acid composition of lipopolysaccharides from Yersinia enterocolitica strains. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Feb;253(4):523–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel B. E., Heesemann J., Wenzel K. W., Scriba P. C. Antibodies to plasmid-encoded proteins of enteropathogenic Yersinia in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease. Lancet. 1988 Jan 2;1(8575-6):56–56. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winblad S., Niléhn B., Sternby N. H. Yersinia enterocolitica (Pasteurella x) in human enteric infections. Br Med J. 1966 Dec 3;2(5526):1363–1366. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5526.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Koning J., Heesemann J., Hoogkamp-Korstanje J. A., Festen J. J., Houtman P. M., van Oijen P. L. Yersinia in intestinal biopsy specimens from patients with seronegative spondyloarthropathy: correlation with specific serum IgA antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jan;159(1):109–112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]