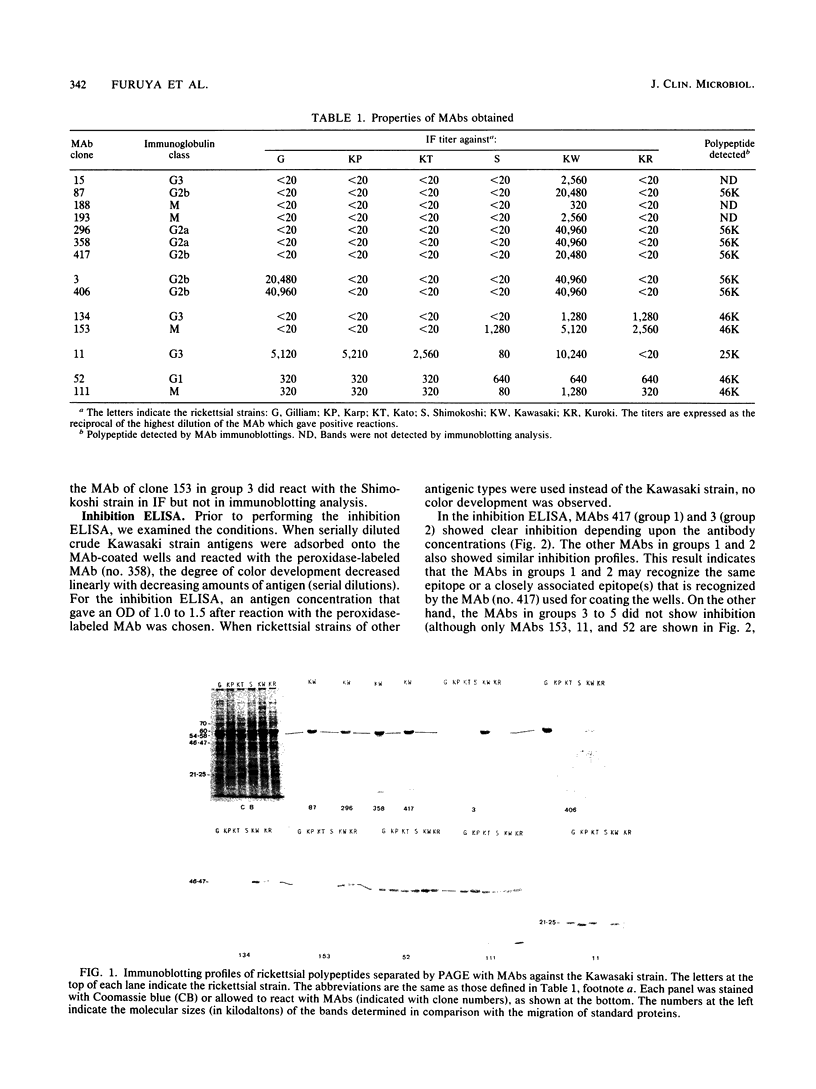
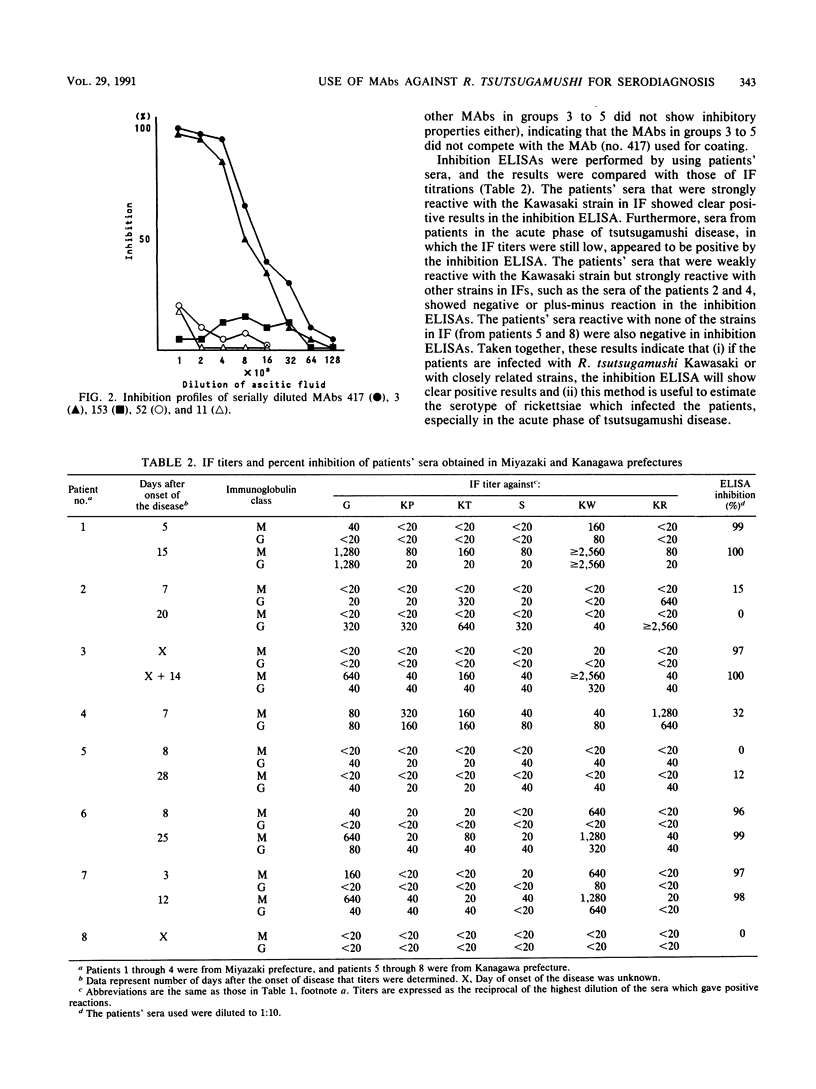
Abstract
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) against Rickettsia tsutsugamushi Kawasaki were prepared. The crossreactivity tests of the MAbs performed by using antigenically distinct strains of R. tsutsugamushi in immunofluorescence and immunoblotting analyses indicated that the Kawasaki strain contains a strain-specific epitope and also contains a common epitope on the 56-kDa polypeptide cross-reactive with the Gilliam strain, group- and subgroup-specific epitopes on the 46-kDa polypeptide, and a subgroup-specific epitope on the 25-kDa polypeptide. By using the strain-specific MAb for serodiagnosis of tsutsugamushi disease (or scrub typhus fever), we have established a method which was designated the inhibition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The principle of the method is to measure the percentage of inhibition of antigen absorption on a MAb-coated plate by antibody-positive sample sera which were mixed with the antigen suspension. The advantages of this test for practical use are that (i) crude antigen can be used, i.e., purification of the antigen is not required; (ii) the test is more sensitive than immunofluorescence; (iii) the final judgment of plus or minus is clear-cut; and (iv) rickettsial antigenic types in the patients can be distinguished by this test.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eisemann C. S., Osterman J. V. Identification of strain-specific and group-reactive antigenic determinants on the Karp, Gilliam and Kato strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Nov;34(6):1173–1178. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya Y., Inoue M., Yoshihara N. Use of monoclonal antibodies in the assay of hepatitis B core antigen and antibody. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1984 Aug;37(4):151–159. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.37.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. Identification and partial characterization of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi major protein immunogens. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):603–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.603-609.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies D. H., Cieplinski W., Dharmgrongartama B., Gefter M. L., Morrison S. L., Kelly T., Scharff M. D. Regulation of immunoglobulin expression in mouse myeloma cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):781–791. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Tanaka H., Blas B. L., Noseñas J. S., Tokawa T., Ohsawa S. Evaluation of ELISA with ABTS, 2-2'-azino-di-(3-ethylbenzthiazoline sulfonic acid), as the substrate of peroxidase and its application to the diagnosis of schistosomiasis. Jpn J Exp Med. 1984 Jun;54(3):131–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata M., Yoshida Y., Osono M., Ohashi N., Oyanagi M., Urakami H., Tamura A., Nogami S., Tanaka H., Kawamura A., Jr Production and characterization of monoclonal strain-specific antibodies against prototype strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(7):599–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi N., Tamura A., Suto T. Immunoblotting analysis of anti-rickettsial antibodies produced in patients of Tsutsugamushi disease. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(11):1085–1092. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Ohashi N., Urakami H., Takahashi K., Oyanagi M. Analysis of polypeptide composition and antigenic components of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):671–675. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.671-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Takahashi K., Tsuruhara T., Urakami H., Miyamura S., Sekikawa H., Kenmotsu M., Shibata M., Abe S., Nezu H. Isolation of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi antigenically different from Kato, Karp, and Gilliam strains from patients. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(8):873–882. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Urakami H., Tsuruhara T. Purification of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi by Percoll density gradient centrifugation. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(4):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urakami H., Yamamoto S., Tsuruhara T., Ohashi N., Tamura A. Serodiagnosis of scrub typhus with antigens immobilized on nitrocellulose sheet. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1841–1846. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1841-1846.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Kawabata N., Ooura K., Murata M., Minamishima Y. [Antigenic types of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi isolated from patients with tsutsugamushi fever and their distribution in Miyazaki Prefecture]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1989 Feb;63(2):109–117. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.63.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Kawabata N., Tamura A., Urakami H., Ohashi N., Murata M., Yoshida Y., Kawamura A., Jr Immunological properties of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi, Kawasaki strain, isolated from a patient in Kyushu. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(7):611–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




