Abstract
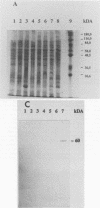
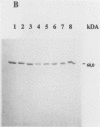
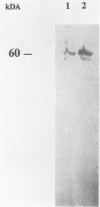
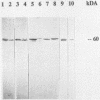
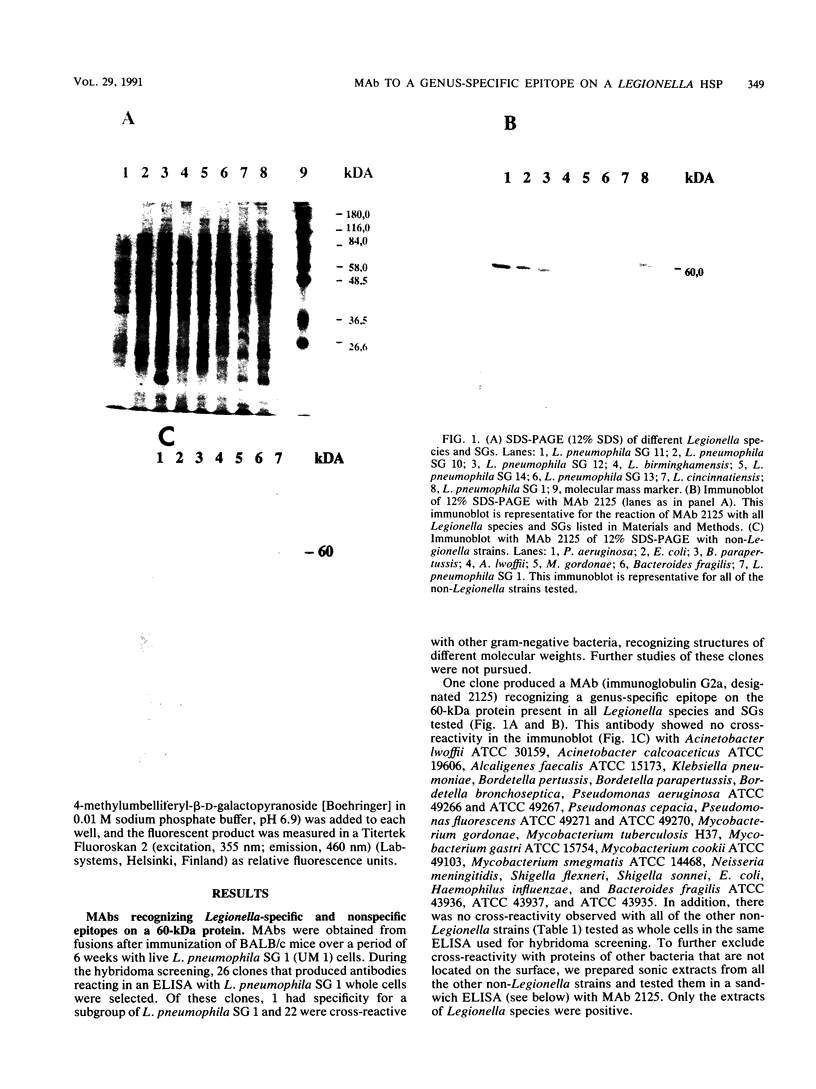
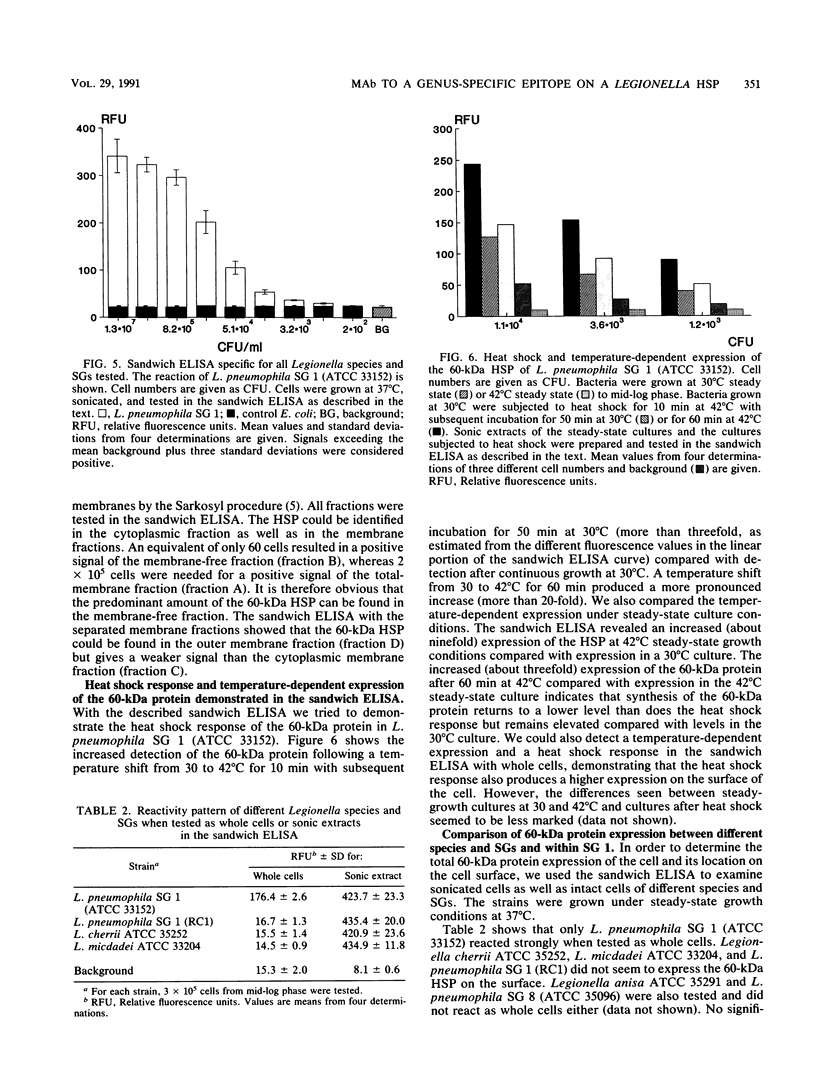
A monoclonal antibody (MAb) immunoglobulin G2a (2125) was produced against a 60-kDa Legionella heat shock protein (HSP), recognizing a unique epitope common to all species of the genus Legionella. The antibody reacted in the immunoblot with 59 Legionella species and serogroups that were tested and showed no cross-reactivity with other bacteria, including Acinetobacter spp., Bordetella spp., Pseudomonas spp., Mycobacterium spp., and Escherichia coli. Two other MAbs (2122 and 2130) reacted with the 60-kDa Legionella protein as well but showed different cross-reactivities with other gram-negative bacteria in the same molecular mass range. The genus-specific MAb 2125 as well as the cross-reacting MAbs 2122 and 2130 were shown to be reactive with the expressed protein of the cloned gene of the 60-kDa HSP of Legionella micdadei and Legionella pneumophila. These antibodies demonstrate that Legionella-specific and nonspecific epitopes are present on this protein. A sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in which the genus-specific MAb is used both as a capture antibody and as a biotinylated second antibody has been established. With this test it is possible to detect Legionella whole cells, sonicated cells, and cell fractions containing the 60-kDa HSP. The main part of the 60-kDa HSP is found in the cytoplasmic fraction. The sandwich ELISA can be used to demonstrate the increased expression of the 60-kDa protein in Legionella cells following heat shock as well as marked differences in the detection of the 60-kDa HSP on whole cells of different Legionella strains. The high specificity and sensitivity of the sandwich ELISA for sonicated cells might be very useful to screen on a genus level for Legionella cells or the 60-kDa antigen in environmental isolates or body fluids of patients.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bangsborg J. M., Collins M. T., Høiby N., Hindersson P. Cloning and expression of the Legionella micdadei "common antigen" in Escherichia coli. APMIS. 1989 Jan;97(1):14–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best M. G., Stout J. E., Yu V. L., Muder R. R. Tatlockia micdadei (Pittsburgh pneumonia agent) growth kinetics may explain its infrequent isolation from water and the low prevalence of Pittsburgh pneumonia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1521–1522. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1521-1522.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindle R. J., Bryant T. N., Draper P. W. Taxonomic investigation of Legionella pneumophila using monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):536–539. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.536-539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R., Deubel U., Hadding U., Bitter-Suermann D. Identification of functionally relevant determinants on the complement component C3 with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2042–2050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler C. A., Street E. D., Hatch T. P., Hoffman P. S. Disulfide-bonded outer membrane proteins in the genus Legionella. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):14–18. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.14-18.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. T., Espersen F., Høiby N., Cho S. N., Friis-Møller A., Reif J. S. Cross-reactions between Legionella pneumophila (serogroup 1) and twenty-eight other bacterial species, including other members of the family Legionellaceae. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1441–1456. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1441-1456.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruyn J., Bosmans R., Turneer M., Weckx M., Nyabenda J., Van Vooren J. P., Falmagne P., Wiker H. G., Harboe M. Purification, partial characterization, and identification of a skin-reactive protein antigen of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):245–252. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.245-252.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Edelstein M. A. Evaluation of the Merifluor-Legionella immunofluorescent reagent for identifying and detecting 21 Legionella species. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2455–2458. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2455-2458.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis T. P., Miller R. A., Young D. B., Khanolkar S. R., Buchanan T. M. Immunochemical characterization of a protein associated with Mycobacterium leprae cell wall. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.371-377.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith M. E., Lindquist D. S., Benson R. F., Thacker W. L., Brenner D. J., Wilkinson H. W. First isolation of Legionella gormanii from human disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):380–381. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.380-381.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K., Bangsborg J. M., Fjordvang H., Pedersen N. S., Hindersson P. Immunochemical characterization of and isolation of the gene for a Borrelia burgdorferi immunodominant 60-kilodalton antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2047–2053. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2047-2053.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Butler C. A., Quinn F. D. Cloning and temperature-dependent expression in Escherichia coli of a Legionella pneumophila gene coding for a genus-common 60-kilodalton antigen. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1731–1739. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1731-1739.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly J. R., Déry P., Gauvreau L., Coté L., Trépanier C. Legionnaires' disease caused by Legionella dumoffii in distilled water. CMAJ. 1986 Dec 1;135(11):1274–1277. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaijser B. Immunological studies of an antigen common to many gram-negative bacteria with special reference to E. coli. Characterization and biological significance. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;48(1):72–81. doi: 10.1159/000231293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Heat shock proteins and the immune response. Immunol Today. 1990 Apr;11(4):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90050-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lema M. W., Brown A., Butler C. A., Hoffman P. S. Heat-shock response in Legionella pneumophila. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Oct;34(10):1148–1153. doi: 10.1139/m88-202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist D. S., Nygaard G., Thacker W. L., Benson R. F., Brenner D. J., Wilkinson H. W. Thirteenth serogroup of Legionella pneumophila isolated from patients with pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):586–587. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.586-587.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pau C. P., Plikaytis B. B., Carlone G. M., Warner I. M. Purification, partial characterization, and seroreactivity of a genuswide 60-kilodalton Legionella protein antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):67–71. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.67-71.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters H., Jürs M., Jann B., Jann K., Timmis K. N., Bitter-Suermann D. Monoclonal antibodies to enterobacterial common antigen and to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide outer core: demonstration of an antigenic determinant shared by enterobacterial common antigen and E. coli K5 capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):459–466. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.459-466.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plikaytis B. B., Carlone G. M., Pau C. P., Wilkinson H. W. Purified 60-kilodalton Legionella protein antigen with Legionella-specific and nonspecific epitopes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2080–2084. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2080-2084.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Thomason B. M., Brake B. J., Thacker L., Wilkinson H. W., Kuritsky J. N. Legionella pneumonia in the United States: the distribution of serogroups and species causing human illness. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):819–819. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. S., Plikaytis B. B., Wilkinson H. W. Immunologic response of patients with legionellosis against major protein-containing antigens of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 as shown by immunoblot analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):92–99. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.92-99.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis 65-kilodalton antigen is a heat shock protein which corresponds to common antigen and to the Escherichia coli GroEL protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):446–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.446-451.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Hertz J. B., Høiby N., Jensen K., Mansa B., Samra Z. An antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. I. The isolation of a 'common antigen' from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Jun;88(3):143–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang P. W., Toma S., MacMillan L. G. Legionella oakridgensis: laboratory diagnosis of a human infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):462–463. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.462-463.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker W. L., Wilkinson H. W., Plikaytis B. B., Steigerwalt A. G., Mayberry W. R., Moss C. W., Brenner D. J. Second serogroup of Legionella feeleii strains isolated from humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.1-4.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Thacker W. L., Brenner D. J., Ryan K. J. Fatal Legionella maceachernii pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1055–1055. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1055-.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Thacker W. L., Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J., Ampel N. M., Wing E. J. Second serogroup of Legionella hackeliae isolated from a patient with pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):488–489. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.488-489.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Leister F. J., Whitcomb L. S., Santosham M. Enzyme immunoassays for the detection of bacterial antigens utilizing biotin-labeled antibody and peroxidase biotin--avidin complex. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 11;56(3):319–327. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(83)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]