Abstract
Culture of blood is the most frequent means of diagnosing bacteremia. However, conventional blood culturing methods are slow in isolating bacteria. We developed a method for isolation of bacteria by centrifugation and filtration. Fresh human whole blood was inoculated with facultatively anaerobic and aerobic microorganisms (3 to 172 microorganisms per 5 ml). Seeded blood was then mixed with Ficoll-Hypaque (density, 1.149 +/- 0.002 g/ml) and centrifuged (386 x g) for 30 min at ambient temperature. The entire gradient (plasma, leukocytes, and Ficoll-Hypaque) was removed and filtered through a 0.22-micron membrane filter (Millipore). The filters were then placed on chocolate agar plates and incubated at 35 degrees C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. For each bacterium tested, approximately 35 to 100% of the viable microorganisms were recovered when compared with control cultures (pour plates of seeded blood). All bacteria produced isolated colonies on filters after overnight incubation (18 h). This procedure may prove to be a more rapid method for isolating bacteria from clinical blood samples than the blood culture bottle technique.
Full text
PDF
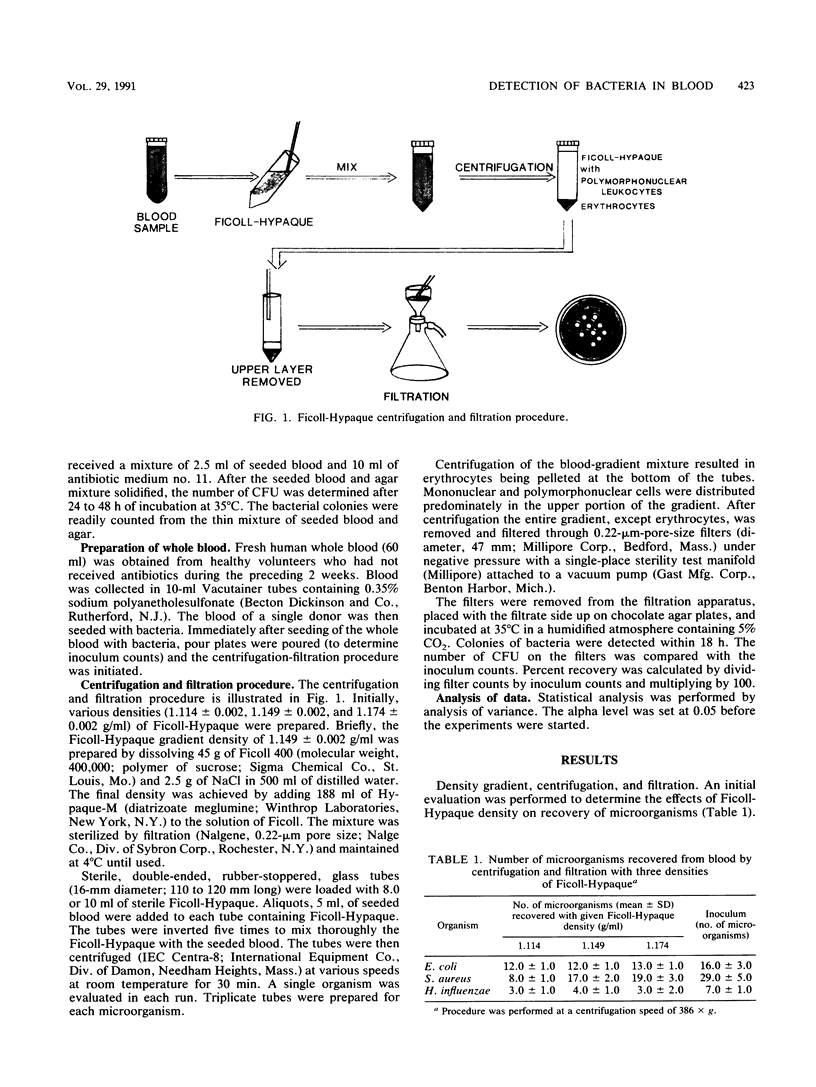

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dorn G. L., Haynes J. R., Burson G. G. Blood culture technique based on centrifugation: developmental phase. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Mar;3(3):251–257. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.3.251-257.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn G. L., Land G. A., Wilson G. E. Improved blood culture technique based on centrifugation: clinical evaluation. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):391–396. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.391-396.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn G. L., Smith K. New centrifugation blood culture device. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):52–54. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.52-54.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Komorowski R. A. Evaluation of the Sterifil lysis-filtration blood culture system. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):500–504. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.500-504.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry N. K., McLimans C. A., Wright A. J., Thompson R. L., Wilson W. R., Washington J. A., 2nd Microbiological and clinical evaluation of the isolator lysis-centrifugation blood culture tube. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):864–869. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.864-869.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlich M. B., Schell R. F., Francisco M., Le Frock J. L. Rapid detection of simulated bacteremia by centrifugation and filtration. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):99–102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.99-102.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmelreich C. A., Orlando M. F., Storch G. A. Comparison of the Oxoid Signal blood culture system with supplemented peptone broth in a pediatric hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1262–1265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1262-1265.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehn T. E. Bacteremia and fungemia in the immunocompromised patient. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;8(9):832–837. doi: 10.1007/BF02185856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Bone G., Phillips I. Comparison of radiometric and gas capture system for blood cultures. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jun;39(6):661–665. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.6.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberg R. E., Schell R. F., LeFrock J. L. Detection and quantitation of simulated anaerobic bacteremia by centrifugation and filtration. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):856–859. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.856-859.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Niles A. C., Heeren R. L., Curren M. M., James L. E., Hoppe-Bauer J. E. Comparative evaluation of the oxoid signal and Roche Septi-Chek blood culture systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2526–2530. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2526-2530.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer L. G., Reller L. B., Mirrett S. Controlled comparison of a new Becton Dickinson agar slant blood culture system with Roche Septi-Chek for the detection of bacteremia and fungemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2637–2639. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2637-2639.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer L., Reller B., Wang W. L., Mirrett S. Evaluation of modified trypticase soy broth versus supplemented peptone broth in the detection of bacteremia and fungemia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;7(3):384–387. doi: 10.1007/BF01962342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohner P., Auckenthaler R. Comparative evaluation of the BCB Roche and Oxoid Signal blood culture systems. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;8(2):150–153. doi: 10.1007/BF01963901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawhney D., Hinder S., Swaine D., Bridson E. Y. Novel method for detecting micro-organisms in blood cultures. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Nov;39(11):1259–1263. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.11.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan N. M., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Practical aerobic membrane filtration blood culture technique: clinical blood culture trial. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):37–43. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.37-43.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan N. M., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Practical aerobic membrane filtration blood culture technique: development of procedure. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):30–36. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.30-36.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trenholme G. M., Kaplan R. L., Karakusis P. H., Stine T., Fuhrer J., Landau W., Levin S. Clinical impact of rapid identification and susceptibility testing of bacterial blood culture isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1342–1345. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1342-1345.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd, Ilstrup D. M. Blood cultures: issues and controversies. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):792–802. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. P., Mirrett S., Reller L. B. Comparative evaluation of Oxoid Signal and BACTEC radiometric blood culture systems for the detection of bacteremia and fungemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):962–964. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.962-964.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Peterson D. L., Swan J. C., MacLowry J. D. Lysis-filtration blood culture versus conventional blood culture in a bacteremic rabbit model. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):74–77. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.74-77.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




