Abstract
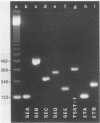
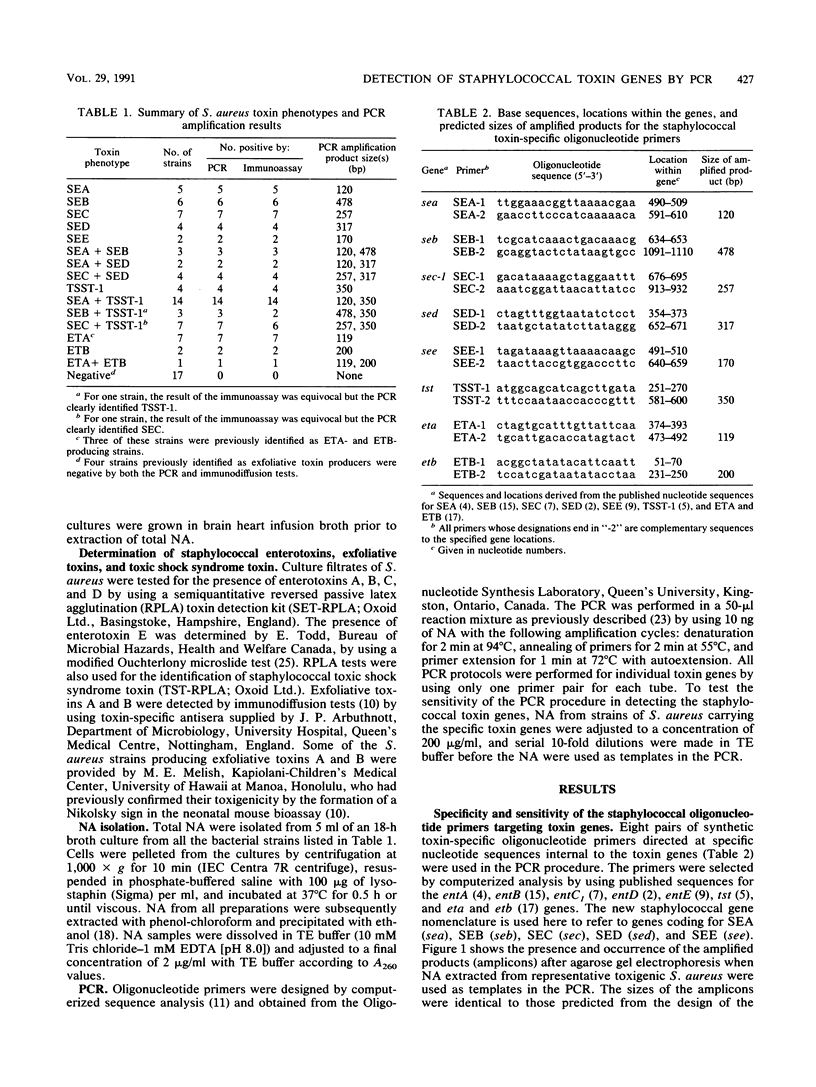
Eight pairs of synthetic oligonucleotide primers were used in a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) protocol to detect genes for staphylococcal enterotoxins A to E, exfoliative toxins A and B, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 in Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from clinical specimens and contaminated foods. Primers were targeted to internal regions of the toxin genes, and amplification fragments were detected after the PCR by agarose gel electrophoresis. Unequivocal discrimination of toxin genes was obtained by the PCR by using nucleic acids extracted from 88 strains of S. aureus whose toxigenicity was established biologically and immunologically. In immunological assays, two strains of S. aureus produced equivocal results for production of enterotoxin C or toxic shock syndrome toxin 1, giving an overall concordance between phenotypic and genotypic identification of 97.7%. Primer specificity was established in the PCR by using nucleic acids from known toxin-producing bacterial pathogens and from nontoxigenic S. aureus. Strains of Streptococcus spp., including some producers of pyrogenic exotoxin A carrying the speA gene, were negative by the PCR designed to detect staphylococcal toxins. The detection limits were established for all the staphylococcal toxin genes within their respective PCR protocols. The identification of staphylococcal toxin genes in strains of S. aureus by the PCR offers a very specific, sensitive, relatively rapid, and inexpensive alternative to traditional immunological assays which depend on adequate gene expression for reliability and sensitivity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayles K. W., Iandolo J. J. Genetic and molecular analyses of the gene encoding staphylococcal enterotoxin D. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4799–4806. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4799-4806.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Mekalanos J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the type A staphylococcal enterotoxin gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):34–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.34-41.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomster-Hautamaa D. A., Kreiswirth B. N., Kornblum J. S., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M. The nucleotide and partial amino acid sequence of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15783–15786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Kreiswirth B. N., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M. Analysis of toxic shock syndrome isolates producing staphylococcal enterotoxins B and C1 with use of southern hybridization and immunologic assays. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11 (Suppl 1):S75–S82. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_1.s75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Schlievert P. M. Nucleotide sequence of the staphylococcal enterotoxin C1 gene and relatedness to other pyrogenic toxins. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):15–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00329830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Weckbach L., Harth G., Haidaris C. Distribution and expression of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene among Staphylococcus aureus isolates of toxic shock syndrome and non-toxic shock syndrome origin. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11 (Suppl 1):S90–S95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_1.s90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch J. L., Soltis M. T., Betley M. J. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the type E staphylococcal enterotoxin gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2954–2960. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2954-2960.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iandolo J. J. Genetic analysis of extracellular toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:375–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. P., L'Italien J. J., Schlievert P. M. Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type A (scarlet fever toxin) is related to Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 May;203(2):354–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00333979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. L., Khan S. A. Nucleotide sequence of the enterotoxin B gene from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):29–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.29-33.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M. A., Miller L., Walker J. A., Boulnois G. J. Nucleotide sequence of the streptolysin O (SLO) gene: structural homologies between SLO and other membrane-damaging, thiol-activated toxins. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3228–3232. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3228-3232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Schmidt J. J., Johnson-Winegar A. D., Spero L., Iandolo J. J. Sequence determination and comparison of the exfoliative toxin A and toxin B genes from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3904–3909. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3904-3909.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):705–711. doi: 10.1126/science.2185544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill R. J., Fanning G. R., Delahoz F., Wolff R., Gemski P. Oligonucleotide probes for detection and differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus strains containing genes for enterotoxins A, B, and C and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1514–1518. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1514-1518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Heuvelman K. J., Wernars K. Synthetic enterotoxin B DNA probes for detection of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):531–533. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.531-533.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli after polymerase chain reaction amplification with a thermostable DNA polymerase. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):261–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.261-265.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard D. R., Johnson W. M., Lior H., Tyler S. D., Rozee K. R. Rapid and specific detection of verotoxin genes in Escherichia coli by the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):540–545. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.540-545.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifai S., Barbancon V., Prevost G., Piemont Y. Synthetic exfoliative toxin A and B DNA probes for detection of toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):504–506. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.504-506.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins R., Gould S., Bergdoll M. Detecting the enterotoxigenicity of Staphylococcus aureus strains. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):946–950. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.946-950.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochetman G., Ou C. Y., Jones W. K. Polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1154–1157. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- See R. H., Chow A. W. Microbiology of toxic shock syndrome: overview. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11 (Suppl 1):S55–S60. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_1.s55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Razdan M., Kuntsmann G., Aschenbach J. M., Evenson M. L., Bergdoll M. S. Detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and radioimmunoassays: comparison of monoclonal and polyclonal antibody systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):885–890. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.885-890.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. A., Allen R. L., Falmagne P., Johnson M. K., Boulnois G. J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and complete nucleotide sequence of the gene for pneumolysin, the sulfhydryl-activated toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1184–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1184-1189.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks C. R., Ferretti J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the type A streptococcal exotoxin (erythrogenic toxin) gene from Streptococcus pyogenes bacteriophage T12. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):144–150. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.144-150.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Azavedo J. C., Arbuthnott J. P. Assays for epidermolytic toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Methods Enzymol. 1988;165:333–338. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)65049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]