Abstract
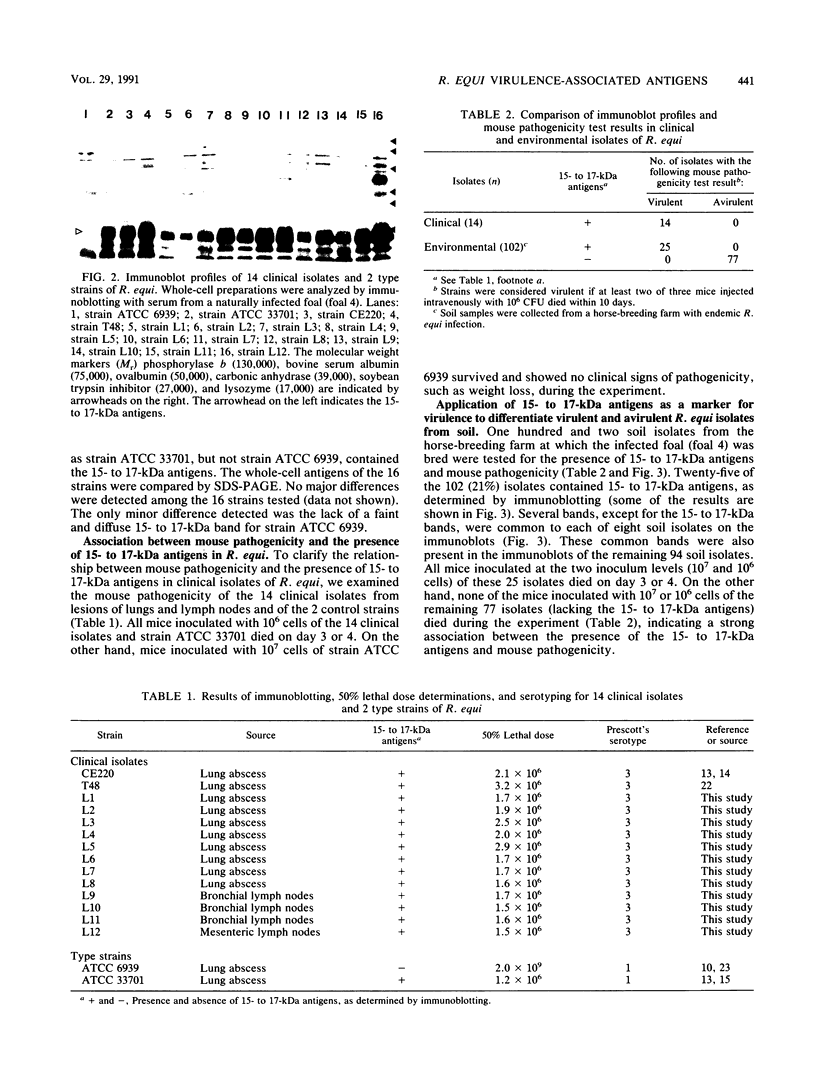
Antigens of Rhodococcus equi were analyzed by immunoblotting with naturally infected foal sera. Immunoblots of whole-cell antigen preparations of clinical isolates of R. equi revealed that major protein bands with molecular masses of 15 to 17 kDa were present in all clinical isolates tested and all isolates virulent for mice. In contrast, the 15- to 17-kDa antigens were not identified by immunoblotting in ATCC 6939, a type strain of R. equi that was avirulent for mice. Whole-cell antigens of 102 environmental isolates were investigated by immunoblotting and the mouse pathogenicity test. Twenty-five of these isolates were demonstrated to contain the 15- to 17-kDa antigens by immunoblotting and were virulent for mice. The remaining 77 environmental isolates lacked the 15- to 17-kDa antigens and were avirulent for mice. These data suggest that the diffuse 15- to 17-kDa proteins are virulence-associated antigens with immunogenicity in foals and that they may be useful in marking virulent R. equi contamination in the environment of a horse-breeding farm.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernheimer A. W., Linder R., Avigad L. S. Stepwise degradation of membrane sphingomyelin by corynebacterial phospholipases. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):123–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.123-131.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowles P. M., Woolcock J. B., Mutimer M. D. Experimental infection of mice with Rhodococcus equi: differences in virulence between strains. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Aug;14(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirino-Trejo J. M., Prescott J. F. Antibody response of horses to Rhodococcus equi antigens. Can J Vet Res. 1987 Jul;51(3):301–305. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirino-Trejo J. M., Prescott J. F. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of whole-cell preparations of Rhodococcus equi. Can J Vet Res. 1987 Jul;51(3):297–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger M. A., Kaeberle M. L., Roth J. A. Equine humoral immune response to Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Nov;45(11):2428–2430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hietala S. K., Ardans A. A., Sansome A. Detection of Corynebacterium equi-specific antibody in horses by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Jan;46(1):13–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens R. J., Fiske R. A., Renshaw H. W. Experimental subacute foal pneumonia induced by aerosol administration of Corynebacterium equi. Equine Vet J. 1982 Apr;14(2):111–116. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1982.tb02359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens R. J., Martens J. G., Fiske R. A., Hietala S. K. Rhodococcus equi foal pneumonia: protective effects of immune plasma in experimentally infected foals. Equine Vet J. 1989 Jul;21(4):249–255. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1989.tb02161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa M., Haritani M., Sugimoto C., Isayama Y. Virulence of Rhodococcus equi for mice. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1983 Oct;45(5):679–682. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.45.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa M., Kubo M., Sugimoto C., Isayama Y. Serogrouping of Rhodococcus equi. Microbiol Immunol. 1983;27(10):837–846. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1983.tb00648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F. Capsular serotypes of Corynebacterium equi. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Apr;45(2):130–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Coshan-Gauthier R., Barksdale L. Antibody to equi factor(s) in the diagnosis of Corynebacterium equi pneumonia of foals. Can J Comp Med. 1984 Oct;48(4):370–373. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Lastra M., Barksdale L. Equi factors in the identification of Corynebacterium equi Magnusson. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):988–990. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.988-990.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka B., Svastová A. Serodiagnostics of Corynebacterium (Rhodococcus) equi. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1985 Feb;32(2):137–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1985.tb01948.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Kawazu S., Tsubaki S. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of Corynebacterium (Rhodococcus) equi infection in foals. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Oct;46(10):2166–2170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Kawazu S., Tsubaki S. Humoral immune response of foals to experimental infection with Rhodococcus equi. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Aug;14(3):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Kawazu S., Tsubaki S. Immunoglobulin and specific antibody responses to Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi infection in foals as measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):943–947. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.943-947.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Michizoe T., Matsumura K., Nagai M., Sato H., Tsubaki S. Correlation of in vitro properties of Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi with virulence for mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1985;29(12):1175–1184. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1985.tb00907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Narita K., Ando K., Tsubaki S. Ecology of Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi in soil on a horse-breeding farm. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Jul;12(2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock J. B., Mutimer M. D. The capsules of Corynebacterium equi and Streptococcus equi. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Nov;109(1):127–130. doi: 10.1099/00221287-109-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagawa R., Honda E. Presence of pili in species of human and animal parasites and pathogens of the genuscorynebacterium. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1293–1295. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1293-1295.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]