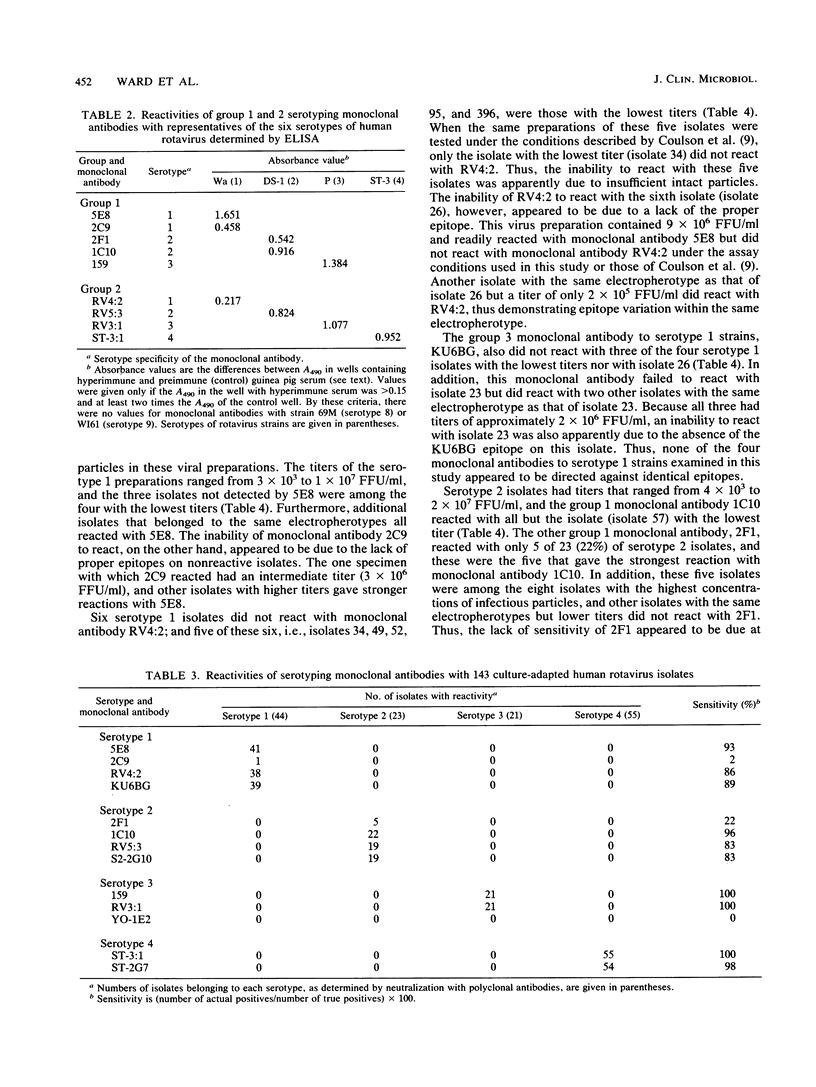
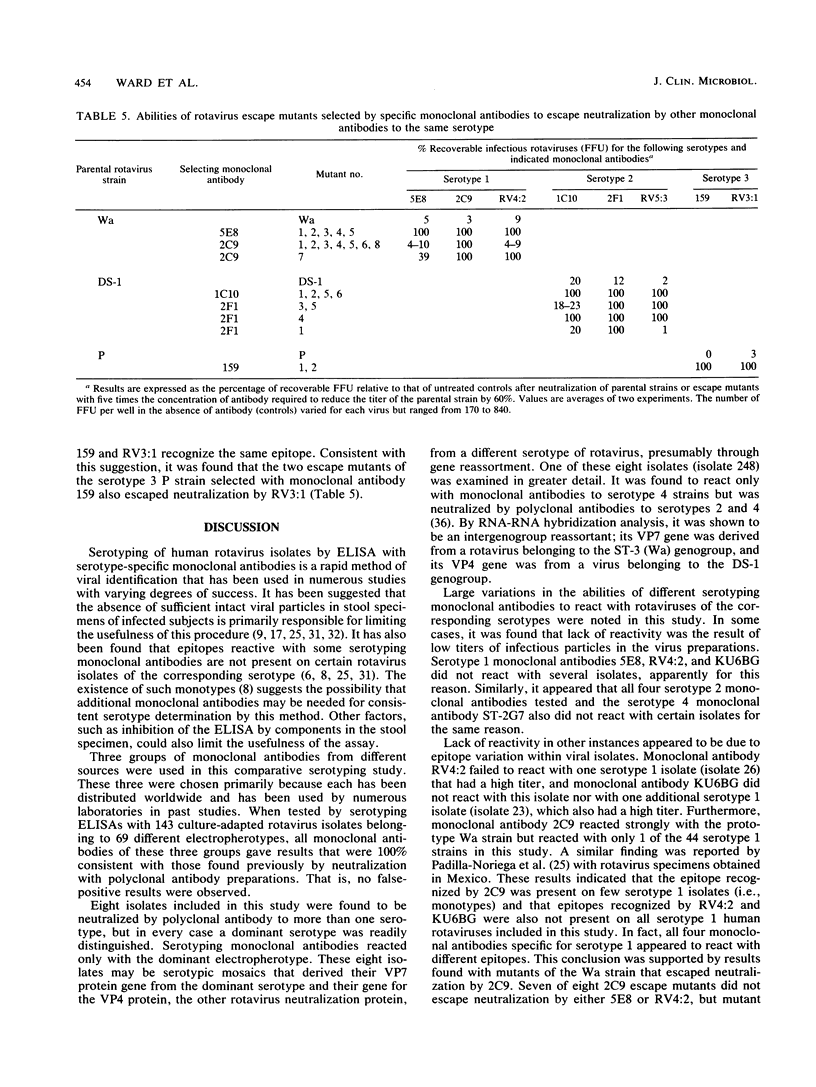
Abstract
Rotaviruses collected in Bangladesh during 1985 to 1986 were culture adapted and used in a comparative serotyping study with three groups of monoclonal antibodies, all of which reacted with the major neutralization protein (VP7) of serotype 1, 2, 3, or 4. The goals were to determine which monoclonal antibodies most accurately predicted the serotype and why large variations in serotyping efficiencies have occurred with these monoclonal antibodies in previous studies. The 143 rotavirus isolates used in this study belonged to 69 different electropherotypes; and 44, 23, 21, and 55 isolates were identified as serotype 1 through 4, respectively, by neutralization with serotype-specific hyperimmune antisera. Serotyping specificity by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibodies was 100% consistent with results found by neutralization with polyclonal antisera, but large differences were observed in the sensitivities of the different monoclonal antibodies. Monoclonal antibodies 5E8 (serotype 1), 1C10 (serotype 2), 159 (serotype 3), RV3:1 (serotype 3), ST-3:1 (serotype 4), and ST-2G7 (serotype 4) reacted with all the isolates of the corresponding serotype for which there were sufficient infectious particles. Monoclonal antibody 2F1 (serotype 2) was much less sensitive and reacted with only five serotype 2 isolates, but these were among those with the highest titers. Monoclonal antibodies RV4:2 (serotype 1), KU6BG (serotype 1), RV5:3 (serotype 2), and S2-2G10 (serotype 2), on the other hand, failed to react with between one and three isolates of the corresponding serotypes which had high titers, apparently because of epitope changes in these isolates. Effects of epitope variation were, however, most apparent with monoclonal antibodies 2C9 (serotype 1) and YO-1E2 (serotype 3), which reacted with one and no isolates of the corresponding serotypes, respectively. Cross-neutralization of escape mutants indicated that the serotype 1 monoclonal antibodies 5E8, 2C9, and RV4:2 reacted with different but probably overlapping epitopes, as did serotype 2 monoclonal antibodies 2F1, 1C10, and RV5:3, finding that were consistent with the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay data. Because of epitope variations between rotavirus strains, serotyping with several monoclonal antibodies directed at different epitopes may increase the sensitivity of the method.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed M. U., Taniguchi K., Kobayashi N., Urasawa T., Wakasugi F., Islam M., Shaikh H., Urasawa S. Characterization by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using subgroup- and serotype-specific monoclonal antibodies of human rotavirus obtained from diarrheic patients in Bangladesh. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1678–1681. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1678-1681.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beards G. M., Desselberger U., Flewett T. H. Temporal and geographical distributions of human rotavirus serotypes, 1983 to 1988. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2827–2833. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2827-2833.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein D. I., Kacica M. A., McNeal M. M., Schiff G. M., Ward R. L. Local and systemic antibody response to rotavirus WC3 vaccine in adult volunteers. Antiviral Res. 1989 Dec;12(5-6):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(89)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch C. J., Heath R. L., Gust I. D. Use of serotype-specific monoclonal antibodies to study the epidemiology of rotavirus infection. J Med Virol. 1988 Jan;24(1):45–53. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890240107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Unicomb L. E., Soenarto Y., Suwardji H., Ristanto, Barnes G. L. Rotavirus serotypes causing acute diarrhoea in hospitalized children in Yogyakarta, Indonesia during 1978-1979. Arch Virol. 1989;107(3-4):207–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01317917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. W., Mathan M. M., Mathew M., Martin R., Beards G. M., Mathan V. I. Rotavirus epidemiology in Vellore, south India: group, subgroup, serotype, and electrophoretype. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2410–2414. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2410-2414.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson B. S., Unicomb L. E., Pitson G. A., Bishop R. F. Simple and specific enzyme immunoassay using monoclonal antibodies for serotyping human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):509–515. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.509-515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson B. S. Variation in neutralization epitopes of human rotaviruses in relation to genomic RNA polymorphism. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90457-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagan R., Bar-David Y., Sarov B., Katz M., Kassis I., Greenberg D., Glass R. I., Margolis C. Z., Sarov I. Rotavirus diarrhea in Jewish and Bedouin children in the Negev region of Israel: epidemiology, clinical aspects and possible role of malnutrition in severity of illness. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1990 May;9(5):314–321. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199005000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman R. Perspective on the development and deployment of rotavirus vaccines. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Aug;6(8):704–710. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198708000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Perez-Schael I., Gonzalez M., Garcia D., Perez M., Daoud N., Cunto W., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Protection against severe rotavirus diarrhoea by rhesus rotavirus vaccine in Venezuelan infants. Lancet. 1987 Apr 18;1(8538):882–884. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92858-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Taniguchi K., Green K., Perez-Schael I., Garcia D., Sears J., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z. Relative frequencies of rotavirus serotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4 in Venezuelan infants with gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2092–2095. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2092-2095.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges-Courbot M. C., Beraud A. M., Beards G. M., Campbell A. D., Gonzalez J. P., Georges A. J., Flewett T. H. Subgroups, serotypes, and electrophoretypes of rotavirus isolated from children in Bangui, Central African Republic. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):668–671. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.668-671.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Sarasini A., Arista S., di Matteo A., Giovannelli L., Parea M., Halonen P. Prevalence of human rotavirus serotypes in some European countries 1981-1988. Scand J Infect Dis. 1990;22(1):5–10. doi: 10.3109/00365549009023112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Sarasini A., Coulson B. S., Parea M., Torsellini M., Arbustini E., Battaglia M. Comparative sensitivities of solid-phase immune electron microscopy and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serotyping of human rotavirus strains with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1383–1387. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1383-1387.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Sarasini A., di Matteo A., Parea M., Orsolini P., Battaglia M. Identification of two subtypes of serotype 4 human rotavirus by using VP7-specific neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1388–1392. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1388-1392.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsey N. A., Anderson E. L., Sears S. D., Steinhoff M., Wilson M., Belshe R. B., Midthun K., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Samorodin R. Human-rhesus reassortant rotavirus vaccines: safety and immunogenicity in adults, infants, and children. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1261–1267. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath R., Birch C., Gust I. Antigenic analysis of rotavirus isolates using monoclonal antibodies specific for human serotypes 1, 2, 3 and 4, and SA11. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2455–2466. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton D. R., Ward R. L. Effect of mutation in immunodominant neutralization epitopes on the antigenicity of rotavirus SA-11. J Gen Virol. 1985 Nov;66(Pt 11):2375–2381. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-11-2375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackow E. R., Shaw R. D., Matsui S. M., Vo P. T., Benfield D. A., Greenberg H. B. Characterization of homotypic and heterotypic VP7 neutralization sites of rhesus rotavirus. Virology. 1988 Aug;165(2):511–517. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90595-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S. M., Mackow E. R., Greenberg H. B. Molecular determinant of rotavirus neutralization and protection. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:181–214. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60585-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi T., Akatani K., Ikegami N., Katsushima N., Nakagomi O. Occurrence of changes in human rotavirus serotypes with concurrent changes in genomic RNA electropherotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2586–2592. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2586-2592.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padilla-Noriega L., Arias C. F., López S., Puerto F., Snodgrass D. R., Taniguchi K., Greenberg H. B. Diversity of rotavirus serotypes in Mexican infants with gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1114–1119. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1114-1119.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongsuwanne Y., Taniguchi K., Choonthanom M., Chiwakul M., Susansook T., Saguanwongse S., Jayavasu C., Urasawa S. Subgroup and serotype distributions of human, bovine, and porcine rotavirus in Thailand. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):1956–1960. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.1956-1960.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennels M. B., Losonsky G. A., Young A. E., Shindledecker C. L., Kapikian A. Z., Levine M. M. An efficacy trial of the rhesus rotavirus vaccine in Maryland. The Clinical Study Group. Am J Dis Child. 1990 May;144(5):601–604. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1990.02150290095037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Stoner-Ma D. L., Estes M. K., Greenberg H. B. Specific enzyme-linked immunoassay for rotavirus serotypes 1 and 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.286-291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Vo P. T., Offit P. A., Coulson B. S., Greenberg H. B. Antigenic mapping of the surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):434–451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa T., Morita Y., Greenberg H. B., Urasawa S. Direct serotyping of human rotavirus in stools by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using serotype 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4-specific monoclonal antibodies to VP7. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1159–1166. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unicomb L. E., Bishop R. F. Epidemiology of rotavirus strains infecting children throughout Australia during 1986-1987. A study of serotype and RNA electropherotype. Arch Virol. 1989;106(1-2):23–34. doi: 10.1007/BF01311035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unicomb L. E., Coulson B. S., Bishop R. F. Experience with an enzyme immunoassay for serotyping human group A rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):586–588. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.586-588.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa S., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K., Wakasugi F., Kobayashi N., Chiba S., Sakurada N., Morita M., Morita O., Tokieda M. Survey of human rotavirus serotypes in different locales in Japan by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):44–51. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa T., Urasawa S., Chiba Y., Taniguchi K., Kobayashi N., Mutanda L. N., Tukei P. M. Antigenic characterization of rotaviruses isolated in Kenya from 1982 to 1983. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1891–1896. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1891-1896.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Knowlton D. R., Pierce M. J. Efficiency of human rotavirus propagation in cell culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):748–753. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.748-753.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Nakagomi O., Knowlton D. R., McNeal M. M., Nakagomi T., Clemens J. D., Sack D. A., Schiff G. M. Evidence for natural reassortants of human rotaviruses belonging to different genogroups. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3219–3225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3219-3225.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



