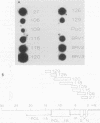
Abstract
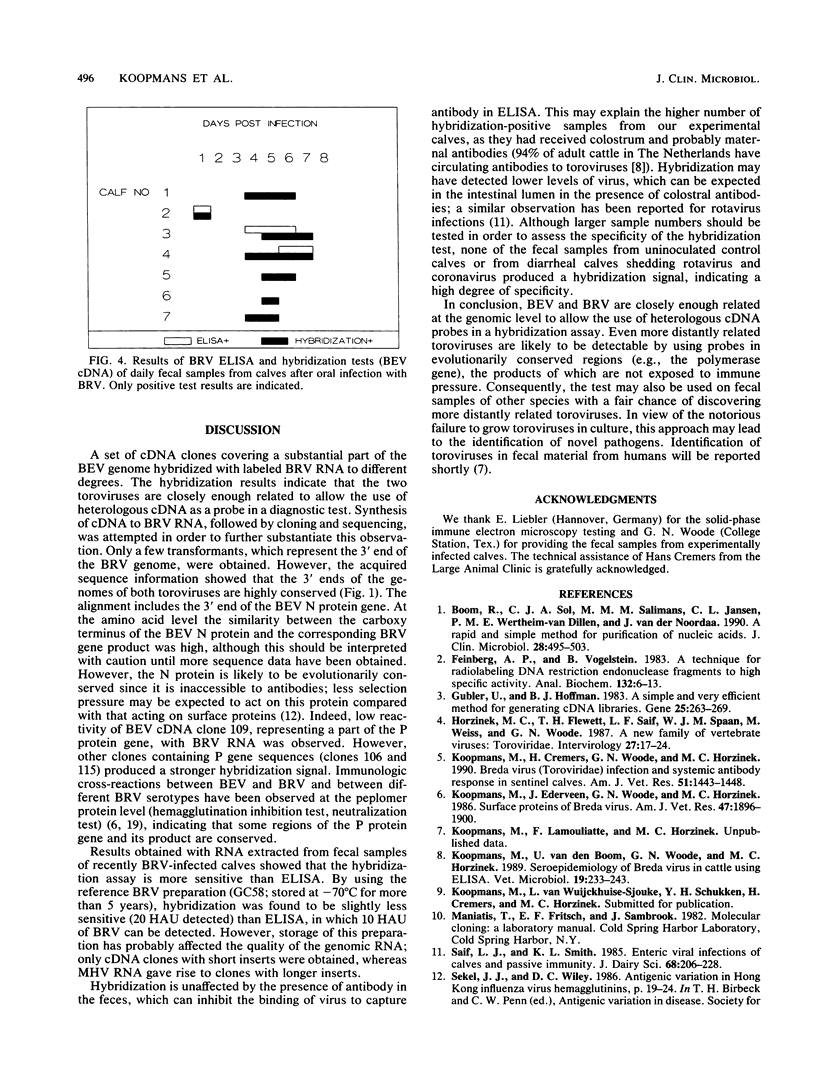
A genomic cDNA library of RNA from Breda virus (BRV), a bovine torovirus, was prepared. The nucleotide sequence of the 3' end of the genome was found to be highly conserved (93% identical) between BRV and Berne virus, the torovirus prototype. Cross-hybridization experiments were performed to select Berne virus cDNA clones for use as probes in a dot hybridization assay; the objective was to detect heterologous torovirus RNA in fecal material. A rapid RNA extraction method was employed to make the test applicable for routine diagnosis. Samples from calves after experimental and natural infection with BRV were assayed to establish the sensitivity and specificity of the test and to compare the test with the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for antigen detection. For this purpose, 53 samples from seven infected calves were tested with both methods. In the ELISA, BRV was detected in six fecal samples from three inoculated calves. By use of the hybridization test, 16 samples from seven calves reacted positively. With one exception, only postinoculation samples were found positive in hybridization. No signal was seen in feces from uninoculated calves or from calves infected with rotavirus or coronavirus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boom R., Sol C. J., Salimans M. M., Jansen C. L., Wertheim-van Dillen P. M., van der Noordaa J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.495-503.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horzinek M. C., Flewett T. H., Saif L. J., Spaan W. J., Weiss M., Woode G. N. A new family of vertebrate viruses: Toroviridae. Intervirology. 1987;27(1):17–24. doi: 10.1159/000149710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopmans M., Cremers H., Woode G., Horzinek M. C. Breda virus (Toroviridae) infection and systemic antibody response in sentinel calves. Am J Vet Res. 1990 Sep;51(9):1443–1448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopmans M., Ederveen J., Woode G. N., Horzinek M. C. Surface proteins of Breda virus. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Sep;47(9):1896–1900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopmans M., van den Boom U., Woode G., Horzinek M. C. Seroepidemiology of Breda virus in cattle using ELISA. Vet Microbiol. 1989 Mar;19(3):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(89)90069-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Smith K. L. Enteric viral infections of calves and passive immunity. J Dairy Sci. 1985 Jan;68(1):206–228. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(85)80813-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijder E. J., Ederveen J., Spaan W. J., Weiss M., Horzinek M. C. Characterization of Berne virus genomic and messenger RNAs. J Gen Virol. 1988 Sep;69(Pt 9):2135–2144. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-9-2135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijder E. J., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. A 3'-coterminal nested set of independently transcribed mRNAs is generated during Berne virus replication. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):331–338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.331-338.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijder E. J., den Boon J. A., Bredenbeek P. J., Horzinek M. C., Rijnbrand R., Spaan W. J. The carboxyl-terminal part of the putative Berne virus polymerase is expressed by ribosomal frameshifting and contains sequence motifs which indicate that toro- and coronaviruses are evolutionarily related. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4535–4542. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijder E. J., den Boon J. A., Spaan W. J., Verjans G. M., Horzinek M. C. Identification and primary structure of the gene encoding the Berne virus nucleocapsid protein. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3363–3370. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W. J., Rottier P. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Isolation and identification of virus-specific mRNAs in cells infected with mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-A59). Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):424–434. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90449-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M., Steck F., Horzinek M. C. Purification and partial characterization of a new enveloped RNA virus (Berne virus). J Gen Virol. 1983 Sep;64(Pt 9):1849–1858. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-9-1849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Reed D. E., Runnels P. L., Herrig M. A., Hill H. T. Studies with an unclassified virus isolated from diarrheic calves. Vet Microbiol. 1982 Jul;7(3):221–240. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(82)90036-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Saif L. J., Quesada M., Winand N. J., Pohlenz J. F., Gourley N. K. Comparative studies on three isolates of Breda virus of calves. Am J Vet Res. 1985 May;46(5):1003–1010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Berlo M. F., Rottier P. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Intracellular equine arteritis virus (EAV)-specific RNAs contain common sequences. Virology. 1986 Jul 30;152(2):492–496. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90154-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]