Abstract
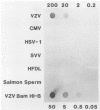
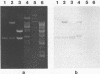
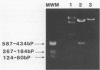
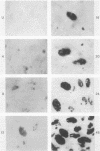
We describe a general method for the production of nonisotopic DNA and RNA probes for the detection of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) genome by in situ hybridization. VZV DNA was extracted from purified viral nucleocapsids, cleaved with restriction enzyme (RE) BamHI, and cloned into plasmid pBR322 by the standard vector insert procedure. We cloned over 85% of the VZV genome and obtained 18 recombinants. Plasmids containing the B, F, G, H, and J fragments of VZV DNA were labeled by the nick translation method with biotin-11-dUTP as the dTTP analog. Additionally, the B fragment was cleaved with RE AvaI, subcloned into the plasmid pGEM-4 transcription vector, and subsequently linearized with REs PstI and EcoRI. RNA was transcribed with T7 or SP6 polymerase, with a substitution of allylamine-UTP as the UTP analog, and labeled with epsilon-caproylamidobiotin-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester. The DNA and RNA probes were used under full-stringency conditions for in situ hybridization with alkaline phosphatase as the detector and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate-Nitro Blue Tetrazolium as the substrate. When tested under comparable conditions, the RNA probe was slightly more sensitive than was the DNA probe: both probes showed homology only with VZV-infected cells and clinical tissues and not with the other herpesviruses. Probes prepared from variable regions of the genome (fragments F and J) performed as well as did those from conserved regions (fragments B. G. and H). Biotinylated probes have distinct advantages over isotopic probes and retain their full potency for more than 2 years when stored properly.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigati D. J., Myerson D., Leary J. J., Spalholz B., Travis S. Z., Fong C. K., Hsiung G. D., Ward D. C. Detection of viral genomes in cultured cells and paraffin-embedded tissue sections using biotin-labeled hybridization probes. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):32–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90460-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croen K. D., Ostrove J. M., Dragovic L. J., Smialek J. E., Straus S. E. Latent herpes simplex virus in human trigeminal ganglia. Detection of an immediate early gene "anti-sense" transcript by in situ hybridization. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 3;317(23):1427–1432. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712033172302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croen K. D., Ostrove J. M., Dragovic L. J., Straus S. E. Patterns of gene expression and sites of latency in human nerve ganglia are different for varicella-zoster and herpes simplex viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9773–9777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbertson G., Grose C. Biotinylated and radioactive DNA probes for detection of varicella-zoster virus genome in infected human cells. Mol Cell Probes. 1988 Sep;2(3):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(88)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. Molecular cloning of the varicella-zoster virus genome and derivation of six restriction endonuclease maps. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1811–1814. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker J. R., Kudler L., Hyman R. W. Variation in the structure of varicella-zoster virus DNA. Intervirology. 1984;21(1):25–37. doi: 10.1159/000149500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld A. D., Schmidt N. J. Antigenic relationships among several simian varicella-like viruses and varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):807–812. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.807-812.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Dupuis K. W., Schmidt N. J. Rapid detection of herpes simplex virus DNA in human brain tissue by in situ hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):656–658. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.656-658.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Dupuis K. W., Schmidt N. J. Varicella-zoster viral glycoproteins analyzed with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):55–62. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.55-62.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Mahalingam R., Vafai A., Hurst J. W., Dupuis K. W. Monoclonal antibody to immediate early protein encoded by varicella-zoster virus gene 62. Virus Res. 1990 Jun;16(2):195–210. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Antisera to human cytomegalovirus produced in hamsters: reactivity in radioimmunoassay and other antibody assay systems. Infect Immun. 1976 Nov;14(5):1184–1190. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.5.1184-1190.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Solid phase radioimmunoassay for identification of Herpesvirus hominis types 1 and 2 from clinical materials. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):661–667. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.661-667.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Myoraku C. K., Gallo D. Serological reactivity of some monoclonal antibodies to varicella-zoster virus. Arch Virol. 1982;73(3-4):311–317. doi: 10.1007/BF01318084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Rozenman Y., Murray R., Devlin M., Vafai A. Detection of varicella-zoster virus nucleic acid in neurons of normal human thoracic ganglia. Ann Neurol. 1987 Sep;22(3):377–380. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Vafai A., Shtram Y., Becker Y., Devlin M., Wellish M. Varicella-zoster virus DNA in human sensory ganglia. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):478–480. doi: 10.1038/306478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. L., Oakes J. E. Simian varicella virus DNA shares homology with human varicella-zoster virus DNA. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbour D. A., Caunt A. E. The serological relationship of varicella-zoster virus to other primate herpesviruses. J Gen Virol. 1979 Nov;45(2):469–477. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-2-469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa Y., Yamamoto T., Yamanishi K., Takahashi M. Analysis of varicella-zoster virus DNAs of clinical isolates by endonuclease HpaI. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1817–1829. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R. W., Ecker J. R., Tenser R. B. Varicella-zoster virus RNA in human trigeminal ganglia. Lancet. 1983 Oct 8;2(8354):814–816. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90736-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Butler E. T., Roulland D., Chamberlin M. J. Bacteriophage SP6-specific RNA polymerase. II. Mapping of SP6 DNA and selective in vitro transcription. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5779–5788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koropchak C. M., Solem S. M., Diaz P. S., Arvin A. M. Investigation of varicella-zoster virus infection of lymphocytes by in situ hybridization. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2392–2395. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2392-2395.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. H., Dohner D. E., Wellinghoff W. J., Gelb L. D. Restriction endonuclease analysis of varicella-zoster vaccine virus and wild-type DNAs. J Med Virol. 1982;9(1):69–76. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall J. K., Myerson D., Beckmann A. M. Detection of viral DNA and RNA by in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Jan;34(1):33–38. doi: 10.1177/34.1.3001177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra L., Dohner D. E., Wellinghoff W. J., Gelb L. D. Physical maps of varicella-zoster virus DNA derived with 11 restriction enzymes. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):615–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.615-618.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Stanberry L. R., Edmond B. J. Varicella-zoster virus infection of strain 2 guinea pigs. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):106–113. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrove J. M., Reinhold W., Fan C. M., Zorn S., Hay J., Straus S. E. Transcription mapping of the varicella-zoster virus genome. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):600–606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.600-606.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer M. H., Ostrove J. M., Felser J. M., Straus S. E. Mapping of the varicella zoster virus deoxypyrimidine kinase gene and preliminary identification of its transcript. Virology. 1986 Feb;149(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Gallo D., Devlin V., Woodie J. D., Emmons R. W. Direct immunofluorescence staining for detection of herpes simplex and varicella-zoster virus antigens in vesicular lesions and certain tissue specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):651–655. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.651-655.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Improved yields of cell-free varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):709–715. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.709-715.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidlin M., Takiff H. E., Smith H. A., Hay J., Straus S. E. Detection of varicella-zoster virus by dot-blot hybridization using a molecularly cloned viral DNA probe. J Med Virol. 1984;13(1):53–61. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890130107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G. B., Cook M. L., Feldman L. T. RNA complementary to a herpesvirus alpha gene mRNA is prominent in latently infected neurons. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2434993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus S. E., Aulakh H. S., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J., Casey T. A., Vande Woude G. F., Owens J., Smith H. A. Structure of varicella-zoster virus DNA. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):516–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.516-525.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus S. E., Hay J., Smith H., Owens J. Genome differences among varicella-zoster virus isolates. J Gen Virol. 1983 May;64(Pt 5):1031–1041. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-5-1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus S. E., Owens J., Ruyechan W. T., Takiff H. E., Casey T. A., Vande Woude G. F., Hay J. Molecular cloning and physical mapping of varicella-zoster virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):993–997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vafai A., Wellish M., Gilden D. H. Expression of varicella-zoster virus in blood mononuclear cells of patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2767–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vafai A., Wellish M., Gilden D. Polypeptides encoded by varicella-zoster virus unique short sequences. Virus Res. 1986 Jul;5(1):67–76. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonsover A., Leventon-Kriss S., Langer A., Smetana Z., Zaizov R., Potaznick D., Cohen I. J., Gotlieb-Stematsky T. Detection of varicella-zoster virus in lymphocytes by DNA hybridization. J Med Virol. 1987 Jan;21(1):57–66. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890210108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H. Nucleic acids or immunoglobulins: which are the molecular probes of the future? Mol Cell Probes. 1988 Jun;2(2):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(88)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Morton D. H., Stanton L. W., Neff B. J. Restriction endonuclease analysis of the DNA from varicella-zoster virus: stability of the DNA after passage in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jul;55(Pt 1):207–211. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-1-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]