Abstract
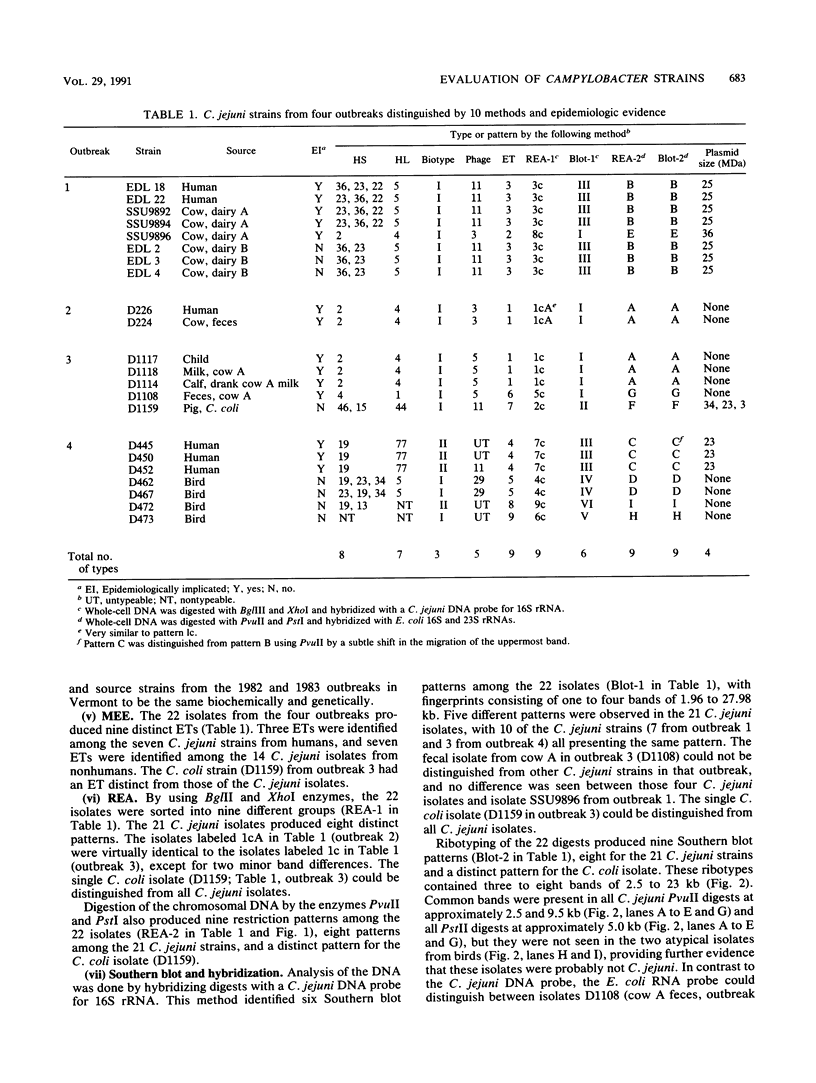
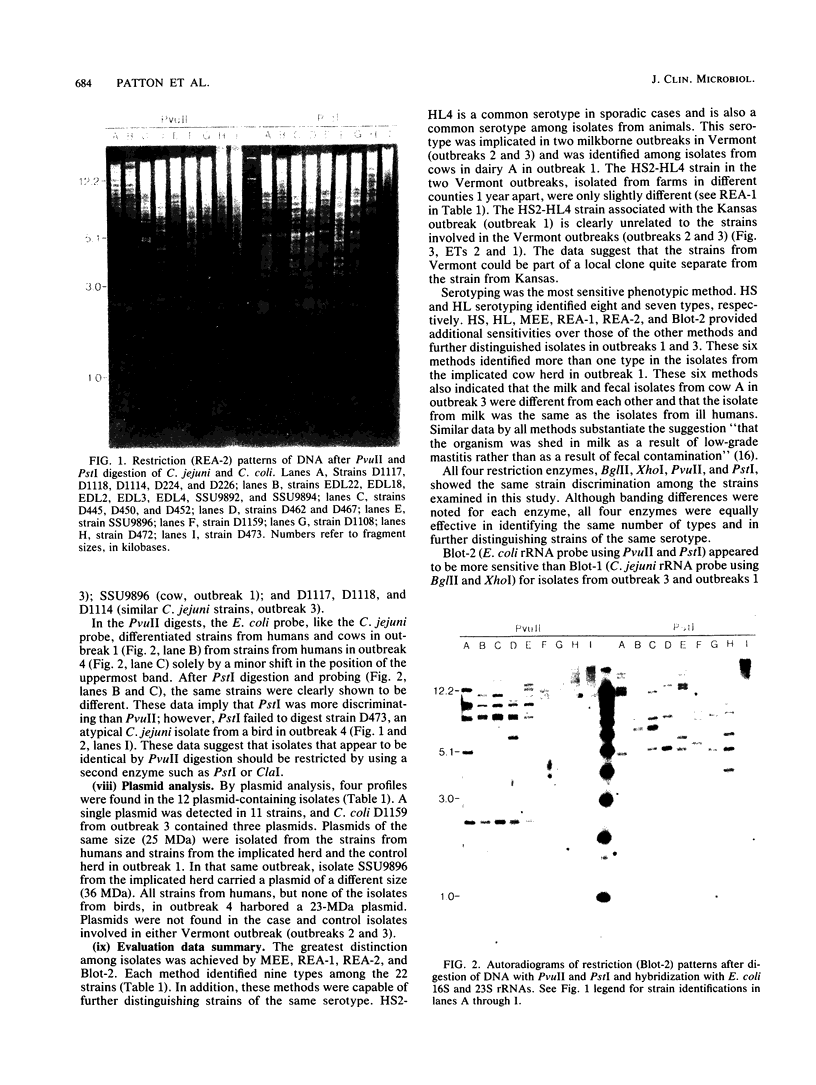
We compared four phenotypic and six genotypic methods for distinguishing Campylobacter jejuni strains from animals and humans involved in four epidemics. Based on a comparison with epidemiologic data, the methods that correctly identified all strains in three milkborne outbreaks and one waterborne outbreak were heat-stable and heat-labile serotyping; multilocus enzyme electrophoresis (MEE); DNA restriction endonuclease analysis with BglII, XhoI, PvuII, or PstI; and Southern blot and hybridization of PvuII- and PstI-digested DNA with Escherichia coli 16S and 23S rRNA (ribotyping). Biotyping, phage typing, plasmid analysis, and probing of BglII and XhoI DNA digests with C. jejuni 16S rRNA genes failed to correctly separate one or more strains. MEE, restriction endonuclease analysis, and ribotyping were the most sensitive methods and identified nine types among the 22 strains. These methods were also capable of further distinguishing strains within the same serotype. Data from MEE were also analyzed to calculate genetic relatedness among strains. Serotyping was the most discriminating phenotypic method, with eight and seven types distinguished by the heat-stable and heat-labile methods, respectively. MEE and ribotyping had several advantages over the other methods because they measure relatively stable and significant chromosomal differences and are applicable to other species and genera. These methods, however, are complex and not easily quantified; they are currently limited to specialized laboratories. When antisera are available, serotyping appears to be an effective and more practical approach to the identification of epidemic-related strains.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aeschbacher M., Piffaretti J. C. Population genetics of human and animal enteric Campylobacter strains. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1432–1437. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1432-1437.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altwegg M., Altwegg-Bissig R., Demarta A., Peduzzi R., Reeves M. W., Swaminathan B. Comparison of four typing methods for Aeromonas species. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1988 Jun;6(2):88–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Taylor D. N., Feldman R. A. Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections. Epidemiol Rev. 1983;5:157–176. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury W. C., Marko M. A., Hennessy J. N., Penner J. L. Occurrence of plasmid DNA in serologically defined strains of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):460–463. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.460-463.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury W. C., Pearson A. D., Marko M. A., Congi R. V., Penner J. L. Investigation of a Campylobacter jejuni outbreak by serotyping and chromosomal restriction endonuclease analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):342–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.342-346.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J., Garcia-Tornel S., Musser J. M., Selander R. K., Smith A. L. Molecular Epidemiology of multiply resistant Haemophilus influenzae type b in day care centers. J Infect Dis. 1987 Sep;156(3):483–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.3.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., Ross D. E. Restriction endonuclease analysis of Campylobacter strains with particular reference to Campylobacter fetus ss. fetus. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):117–124. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Nakahama C., Tobin J. O., Calarco K., Beer K. B., Joly J. R., Selander R. K. Paleoepidemiologic investigation of Legionnaires disease at Wadsworth Veterans Administration Hospital by using three typing methods for comparison of legionellae from clinical and environmental sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1121–1126. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1121-1126.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grajewski B. A., Kusek J. W., Gelfand H. M. Development of a bacteriophage typing system for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):13–18. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.13-18.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson P. J., Vogt R. L., Brondum J., Patton C. M. Isolation of Campylobacter jejuni from milk during an outbreak of campylobacteriosis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):789–789. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson D. N., Bolton F. J., Jones D. M., Sutcliffe E. M., Abbott J. D. Application of three typing schemes (Penner, Lior, Preston) to strains of Campylobacter spp. isolated from three outbreaks. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Apr;98(2):139–144. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800061847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaijser B., Sjögren E. Campylobacter strains in Sweden. Serotyping and correlation to clinical symptoms. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Aug;93(4):315–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Lassen J., Dommarsnes K., Kristiansen B. E., Caugant D. A., Ask E., Jahkola M. Comparison of epidemiological marker methods for identification of Salmonella typhimurium isolates from an outbreak caused by contaminated chocolate. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2019–2024. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2019-2024.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblatt A. N., Barrett T., Morris G. K., Tosh F. E. Epidemiologic and laboratory investigation of an outbreak of Campylobacter enteritis associated with raw milk. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Nov;122(5):884–889. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne-Roussel A., Courcoux P., Tompkins L. Gene disruption and replacement as a feasible approach for mutagenesis of Campylobacter jejuni. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1704–1708. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1704-1708.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. A., Patton C. M., Barrett T. J., Moss C. W. Differentiation of Campylobacter and Campylobacter-like organisms by cellular fatty acid composition. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):706–713. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.706-713.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind L., Sjögren E., Welinder-Olsson C., Kaijser B. Plasmids and serogroups in Campylobacter jejuni. APMIS. 1989 Dec;97(12):1097–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H. New, extended biotyping scheme for Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and "Campylobacter laridis". J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):636–640. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.636-640.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Patel A. Improved toluidine blue-DNA agar for detection of DNA hydrolysis by campylobacters. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):2030–2031. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.2030-2031.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Woodward D. L., Edgar J. A., Laroche L. J., Gill P. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.761-768.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moureau P., Derclaye I., Gregoire D., Janssen M., Cornelis G. R. Campylobacter species identification based on polymorphism of DNA encoding rRNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1514–1517. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1514-1517.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Borman P. A rapid biochemical method for purifying high molecular weight bacterial chromosomal DNA for restriction enzyme analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3631–3631. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton C. M., Barrett T. J., Morris G. K. Comparison of the Penner and Lior methods for serotyping Campylobacter spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):558–565. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.558-565.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Evins G. M., Heiba A. A., Plikaytis B. D., Farmer J. J., 3rd Clonal nature of Salmonella typhi and its genetic relatedness to other salmonellae as shown by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis, and proposal of Salmonella bongori comb. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):313–320. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.313-320.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks J. J., Lieb S., Baldy L. M., Berta S., Patton C. M., White M. C., Bigler W. J., Witte J. J. Epidemic campylobacteriosis associated with a community water supply. Am J Public Health. 1986 Apr;76(4):424–428. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.4.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Korhonen T. K., Väisänen-Rhen V., Williams P. H., Pattison P. E., Caugant D. A. Genetic relationships and clonal structure of strains of Escherichia coli causing neonatal septicemia and meningitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):213–222. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.213-222.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., McKinney R. M., Whittam T. S., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J., Nolte F. S., Pattison P. E. Genetic structure of populations of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1021–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1021-1037.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauxe R. V., Hargrett-Bean N., Patton C. M., Wachsmuth I. K. Campylobacter isolates in the United States, 1982-1986. MMWR CDC Surveill Summ. 1988 Jun;37(2):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Wachsmuth I. K., Shangkuan Y. H., Schmidt E. V., Barrett T. J., Schrader J. S., Scherach C. S., McGee H. B., Feldman R. A., Brenner D. J. Salmonellosis associated with marijuana: a multistate outbreak traced by plasmid fingerprinting. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 27;306(21):1249–1253. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205273062101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Williams S., Gordon K. P., Nolan C., Plorde J. J. Survey of plasmids and resistance factors in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):37–41. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Troup N. J., Woods T., Bibb W., McKinney R. M. Molecular epidemiology of Legionella species by restriction endonuclease and alloenzyme analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1875–1880. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1875-1880.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Troup N., Labigne-Roussel A., Cohen M. L. Cloned, random chromosomal sequences as probes to identify Salmonella species. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):156–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt R. L., Little A. A., Patton C. M., Barrett T. J., Orciari L. A. Serotyping and serology studies of campylobacteriosis associated with consumption of raw milk. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):998–1000. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.998-1000.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth K. Molecular epidemiology of bacterial infections: examples of methodology and of investigations of outbreaks. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):682–692. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Sokolow R., Morris G. K. Laboratory investigation of hemorrhagic colitis outbreaks associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):512–520. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.512-520.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]