Abstract
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has many potential applications in the field of nucleic acid diagnostics. In particular, it has been successfully applied to the detection of pathogens present in low copy numbers such as the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Here we describe a time-resolved fluorescence-based hybridization assay which, combined with the PCR, offers an extremely sensitive method for the detection of nucleic acids. In this assay format, the PCR is run by standard procedures and the subsequent hybridization reaction is carried out in solution by using two oligonucleotide probes, one biotinylated and one labeled with europium (Eu3+). The sandwich hybrids are then collected onto a streptavidin-coated microtitration well, and the bound Eu3+ is measured in a time-resolved fluorometer. This assay is rapid, user friendly, and quantitative and lends itself to automation. The application of this assay to the detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is described.
Full text
PDF

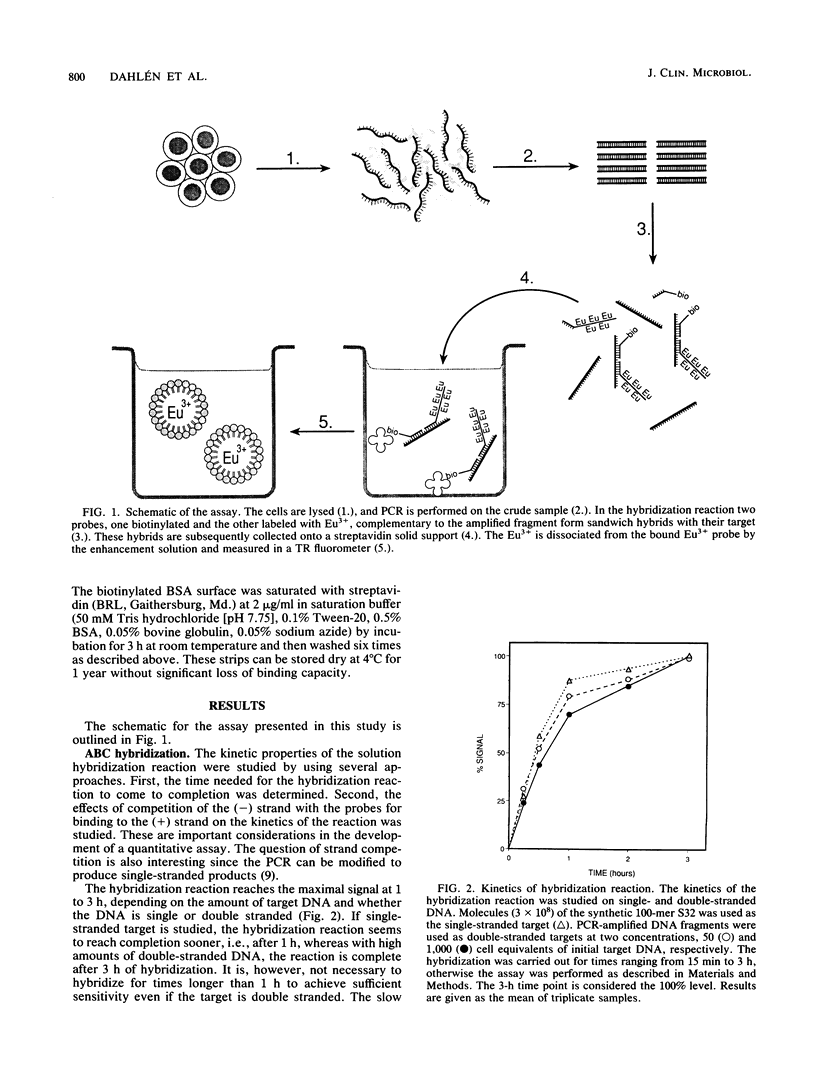
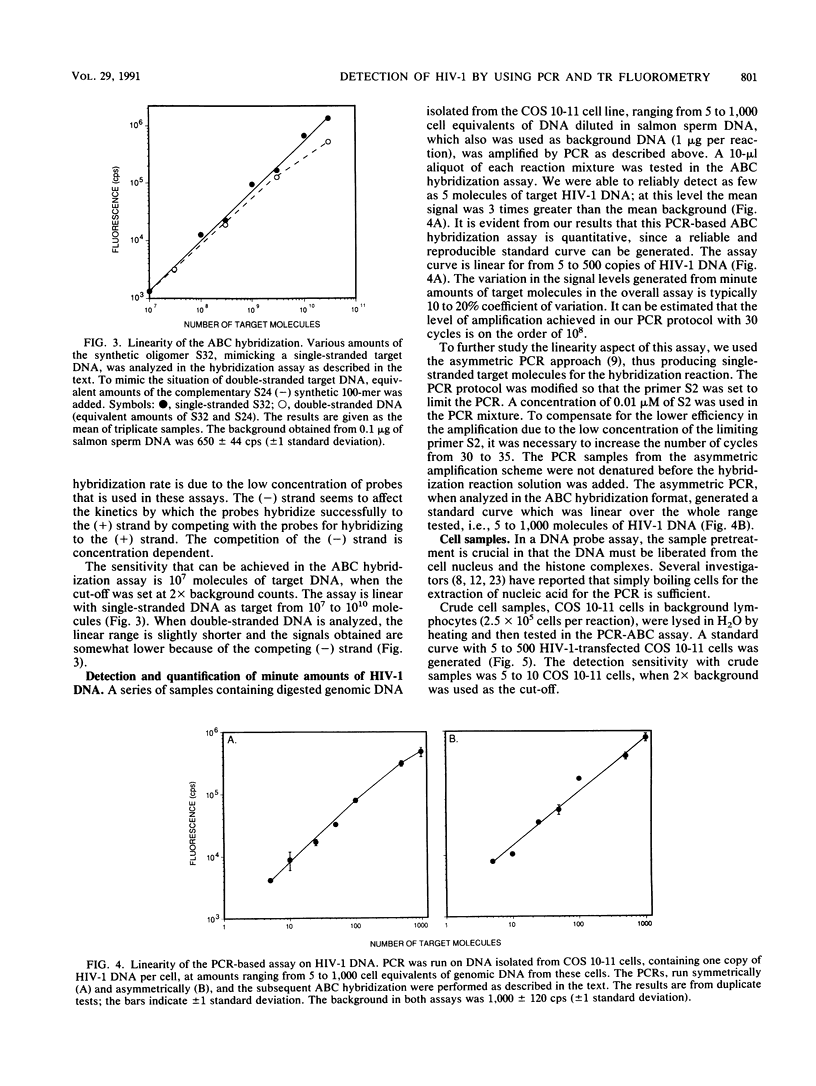
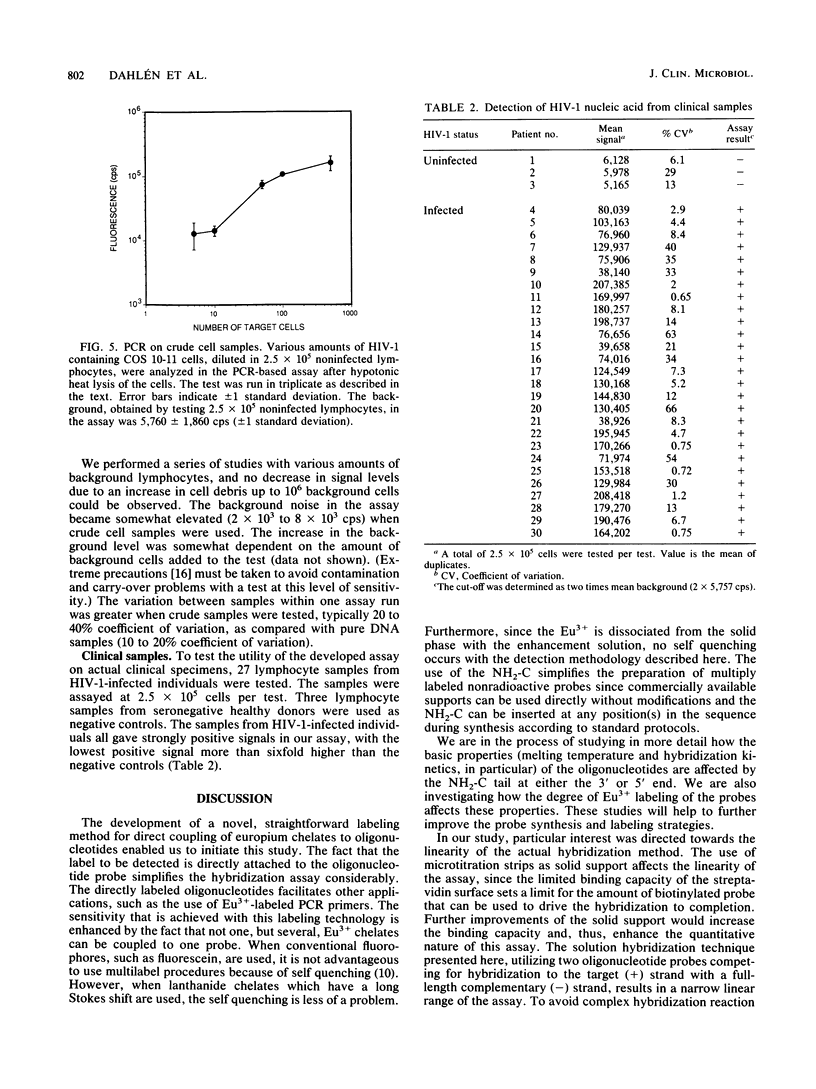


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chamberlain J. S., Gibbs R. A., Ranier J. E., Nguyen P. N., Caskey C. T. Deletion screening of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus via multiplex DNA amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11141–11156. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chehab F. F., Kan Y. W. Detection of specific DNA sequences by fluorescence amplification: a color complementation assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9178–9182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlén P., Hurskainen P., Lövgren T., Hyypiä T. Time-resolved fluorometry for the identification of viral DNA in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2434–2436. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2434-2436.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlén P., Syvänen A. C., Hurskainen P., Kwiatkowski M., Sund C., Ylikoski J., Söderlund H., Lövgren T. Sensitive detection of genes by sandwich hybridization and time-resolved fluorometry. Mol Cell Probes. 1987 Jun;1(2):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(87)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Huang W. M., Woo S. L. Screening for phenylketonuria mutations by DNA amplification with the polymerase chain reaction. Lancet. 1988 Mar 5;1(8584):497–499. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91295-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embury S. H., Scharf S. J., Saiki R. K., Gholson M. A., Golbus M., Arnheim N., Erlich H. A. Rapid prenatal diagnosis of sickle cell anemia by a new method of DNA analysis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Mar 12;316(11):656–661. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198703123161103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferre F., Garduno F. Preparation of crude cell extract suitable for amplification of RNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2141–2141. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haralambidis J., Angus K., Pownall S., Duncan L., Chai M., Tregear G. W. The preparation of polyamide-oligonucleotide probes containing multiple non-radioactive labels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):501–505. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Moudgil T., Alam M. Quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in the blood of infected persons. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 14;321(24):1621–1625. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912143212401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Neumann R., Keyte J. Amplification of human minisatellites by the polymerase chain reaction: towards DNA fingerprinting of single cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):10953–10971. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.10953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Smith D. B., Foote S. J., Samaras N., Peterson M. G. Colorimetric detection of specific DNA segments amplified by polymerase chain reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2423–2427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwoh D. Y., Davis G. R., Whitfield K. M., Chappelle H. L., DiMichele L. J., Gingeras T. R. Transcription-based amplification system and detection of amplified human immunodeficiency virus type 1 with a bead-based sandwich hybridization format. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1173–1177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Higuchi R. Avoiding false positives with PCR. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):237–238. doi: 10.1038/339237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oser A., Roth W. K., Valet G. Sensitive non-radioactive dot-blot hybridization using DNA probes labelled with chelate group substituted psoralen and quantitative detection by europium ion fluorescence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1181–1196. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang S., Koyanagi Y., Miles S., Wiley C., Vinters H. V., Chen I. S. High levels of unintegrated HIV-1 DNA in brain tissue of AIDS dementia patients. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):85–89. doi: 10.1038/343085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Walsh P. S., Levenson C. H., Erlich H. A. Genetic analysis of amplified DNA with immobilized sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6230–6234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Doyle M. V., Mark D. F. Quantitation of mRNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9717–9721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D. Y., Wallace R. B. The ligation amplification reaction (LAR)--amplification of specific DNA sequences using sequential rounds of template-dependent ligation. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):560–569. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90280-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



