Abstract
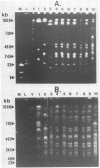
Ten Legionella pneumophila strains isolated from different sources were analyzed according to their restriction fragment patterns obtained by cleavage of genomic DNA with NotI and SfiI and separation by pulsed field electrophoresis. Three L. pneumophila isolates from a nosocomial outbreak in Lübeck (Germany) and three other L. pneumophila strains independently isolated from a water tap located in the care unit where the patients were hospitalized exhibited identical restriction fragment profiles. Therefore, we concluded that these environmental specimens were the source of the Legionnaires disease. Another two isolates from patients and two strains from the environment, all unrelated to the outbreak described, showed different cleavage patterns.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender L., Ott M., Marre R., Hacker J. Genome analysis of Legionella ssp. by orthogonal field alternation gel electrophoresis (OFAGE). FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Nov;60(3):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90313-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson R. F., Thacker W. L., Wilkinson H. W., Fallon R. J., Brenner D. J. Legionella pneumophila serogroup 14 isolated from patients with fatal pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):382–382. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.382-.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan J. W., Ashworth L. A. The relationship between the serogroup antigen and lipopolysaccharide of Legionella pneumophila. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Feb;96(1):39–48. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Improved semiselective medium for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from contaminated clinical and environmental specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):298–303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.298-303.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly J. R., Chen Y. Y., Ramsay D. Serogrouping and subtyping of Legionella pneumophila with monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1040–1046. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1040-1046.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher W. E., Plouffe J. F., Para M. F. Plasmid profiles of clinical and environmental isolates of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1422–1423. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1422-1423.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M., Hollis R., Johnson W., Massanari R. M., Helms C., Wenzel R., Hall N., Moyer N., Joly J. The application of molecular and immunologic techniques to study the epidemiology of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Jul-Aug;12(4):295–302. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(89)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro C. D., Burge S. H., Palmer S. R., Tobin J. O., Watkins I. D. Legionella pneumophila in a hospital water system following a nosocomial outbreak: prevalence, monoclonal antibody subgrouping and effect of control measures. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Jun;98(3):253–262. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800062002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Troup N. J., Woods T., Bibb W., McKinney R. M. Molecular epidemiology of Legionella species by restriction endonuclease and alloenzyme analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1875–1880. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1875-1880.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr Legionnaires disease: historical perspective. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):60–81. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ketel R. J. Similar DNA restriction endonuclease profiles in strains of Legionella pneumophila from different serogroups. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1838–1841. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1838-1841.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ketel R. J., de Wever B. Genetic typing in a cluster of Legionella pneumophila infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):1105–1107. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.1105-1107.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]