Abstract
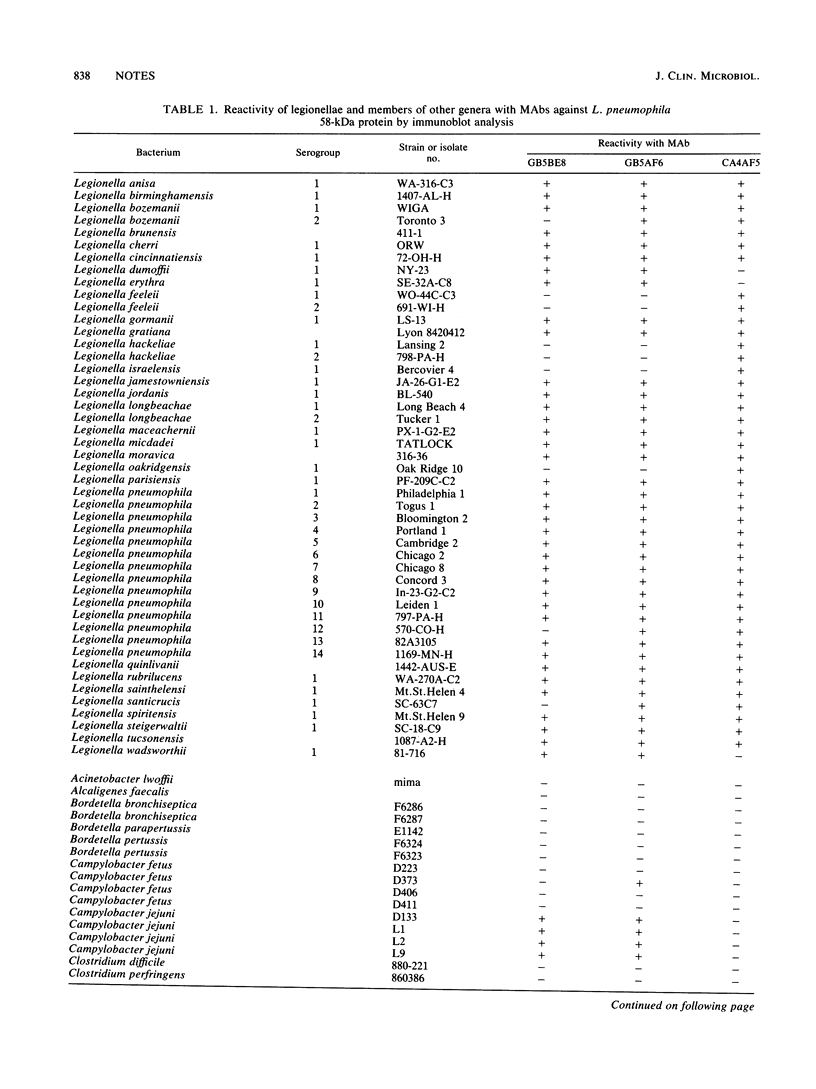
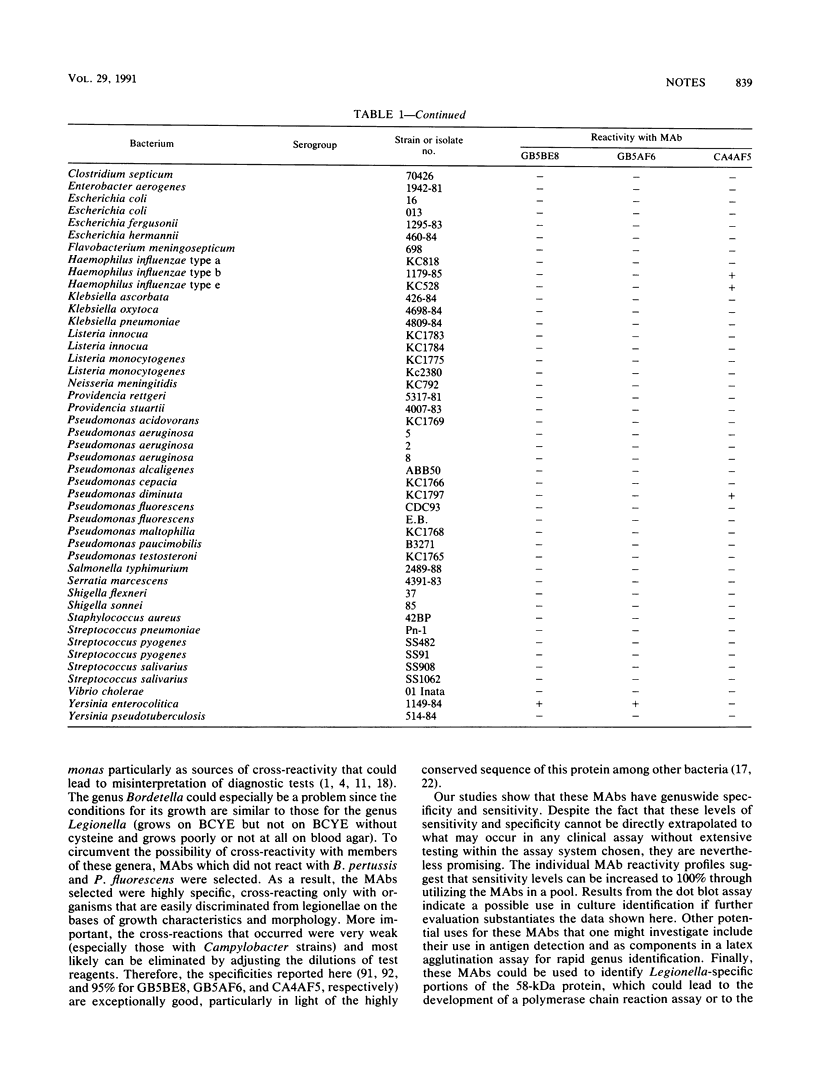
Three monoclonal antibodies against the Legionella pneumophila 58-kDa protein were produced. By using immunoblot analysis, the percentages of reactivity against 47 serogroups of Legionella representing 29 species were determined to be 80.9, 87.2, and 95.6 for monoclonal antibodies GB5BE8, GB5AF6, and CA4AF5, respectively. Specificities obtained from testing 63 heterologous organisms representing 22 genera and 46 species were 90.7, 92.2, and 95.3% for monoclonal antibodies GB5BE8, GB5AF6, and CA4AF5, respectively. No single heterologous strain was reactive with all three monoclonal antibodies. These monoclonal antibodies successfully identified all 10 clinical isolates of Legionella examined in a dot blot assay and should be excellent reagents for use in genuswide diagnostic immunoassays.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson R. F., Malcolm G. B., Pine L., Harrell W. K. Factors influencing the reactivity of Legionella antigens in immunofluorescence tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):909–917. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.909-917.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein N., Marmet D., Surgot M., Nowicki M., Meugnier H., Fleurette J., Ageron E., Grimont F., Grimont P. A., Thacker W. L. Legionella gratiana sp. nov. isolated from French spa water. Res Microbiol. 1989 Oct;140(8):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlone G. M., Plikaytis B. B., Arko R. J. Immune serum to protein molecular weight standards for calibrating Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):89–91. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry W. B., Pittman B., Harris P. P., Hebert G. A., Thomason B. M., Thacker L., Weaver R. E. Detection of Legionnaires disease bacteria by direct immunofluorescent staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):329–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.329-338.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. T., Espersen F., Høiby N., Cho S. N., Friis-Møller A., Reif J. S. Cross-reactions between Legionella pneumophila (serogroup 1) and twenty-eight other bacterial species, including other members of the family Legionellaceae. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1441–1456. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1441-1456.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Butler C. A., Quinn F. D. Cloning and temperature-dependent expression in Escherichia coli of a Legionella pneumophila gene coding for a genus-common 60-kilodalton antigen. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1731–1739. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1731-1739.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lema M. W., Brown A., Butler C. A., Hoffman P. S. Heat-shock response in Legionella pneumophila. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Oct;34(10):1148–1153. doi: 10.1139/m88-202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrison L. H., Bibb W. F., Cherry W. B., Thacker L. Determination of antigenic relationships among legionellae and non-legionellae by direct fluorescent-antibody and immunodiffusion tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):332–337. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.332-337.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pau C. P., Plikaytis B. B., Carlone G. M., Warner I. M. Purification, partial characterization, and seroreactivity of a genuswide 60-kilodalton Legionella protein antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):67–71. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.67-71.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plikaytis B. B., Carlone G. M., Pau C. P., Wilkinson H. W. Purified 60-kilodalton Legionella protein antigen with Legionella-specific and nonspecific epitopes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2080–2084. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2080-2084.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plikaytis B. D., Carlone G. M., Plikaytis B. B. Numerical analysis of normalized whole-cell protein profiles after sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Sep;132(9):2653–2660. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-9-2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. S., O'Connor S. P., Holloway B. P., Plikaytis B. B., Carlone G. M., Mayer L. W. Nucleotide sequence of htpB, the Legionella pneumophila gene encoding the 58-kilodalton (kDa) common antigen, formerly designated the 60-kDa common antigen. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):3154–3157. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.3154-3157.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. S., Plikaytis B. B., Wilkinson H. W. Immunologic response of patients with legionellosis against major protein-containing antigens of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 as shown by immunoblot analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):92–99. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.92-99.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis 65-kilodalton antigen is a heat shock protein which corresponds to common antigen and to the Escherichia coli GroEL protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):446–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.446-451.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Edelstein P. H., Goldstein L. C., Sturge J. C., Plorde J. J. Comparison of cross-staining reactions by Pseudomonas spp. and fluorescein-labeled polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies directed against Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):647–649. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.647-649.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Hancock K., Simons A. R. Calibration of prestained protein molecular weight standards for use in the "Western" or enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot techniques. Anal Biochem. 1984 Dec;143(2):304–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90667-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Peralta J. M., Simons A. R. Enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot techniques (EITB) for studying the specificities of antigens and antibodies separated by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:377–391. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C. A heat shock operon in Coxiella burnetti produces a major antigen homologous to a protein in both mycobacteria and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1227–1234. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1227-1234.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Sampson J. S., Plikaytis B. B. Evaluation of a commercial gene probe for identification of Legionella cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):217–220. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.217-220.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]