Abstract
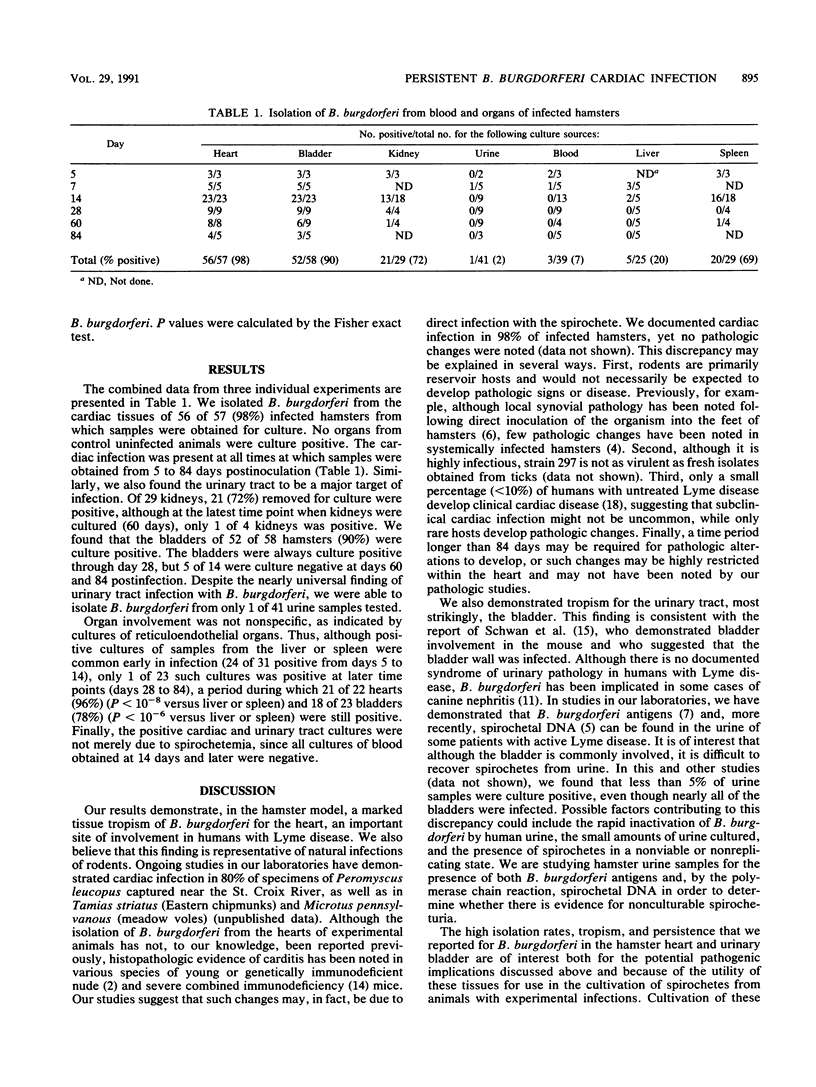
The heart can be severely affected in humans with Lyme disease, causing conduction defects and, rarely, heart failure. Although immunodeficient and young mice may develop cardiac lesions, cultivation of Borrelia burgdorferi from cardiac tissues of experimentally infected animals has not been reported previously. We infected Syrian hamsters with B. burgdorferi 297 and found a marked tropism of the spirochete for myocardial and urinary tract tissues. Fifty-six of 57 hearts (98%) and 52 of 58 bladders (90%) were culture positive. The cardiac infection was persistent and could be documented in 21 of 22 hearts (96%) cultured from days 28 to 84 postinfection. The urinary tract was also a site of persistent infection in most animals, with 18 of 23 bladders (78%) being culture positive from days 28 to 84. The persistence of spirochetes was specific for the heart and bladder, as indicated by negative cultures of specimens from the liver and spleen, in which only 1 of 23 cultures was positive from days 28 to 84. Because of the high isolation rates, tropism, and persistence that we found for B. burgdorferi in the hamster heart and bladder, these sites will be useful and important for the cultivation of spirochetes in experimental studies that evaluate the efficacies both of candidate vaccines in preventing infection and of antibiotics in eradicating organisms from privileged sites. In addition, the clear demonstration of persistent cardiac infection with B. burgdorferi may provide a useful model for studying the pathogenesis of cardiac Lyme disease.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Beck D. S., Hansen G. M., Terwilliger G. A., Moody K. D. Lyme borreliosis in selected strains and ages of laboratory mice. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):133–138. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Gage K. L. Susceptibility of the hispid cotton rat (Sigmodon hispidus) to the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Nov;37(3):624–628. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.37.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H., Johnson R. C. The histopathology of experimentally infected hamsters with the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1986 Feb;181(2):263–269. doi: 10.3181/00379727-181-42251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. L., Jurkovich P., Kramber J. M., Johnson R. C. Molecular detection of persistent Borrelia burgdorferi in the urine of patients with active Lyme disease. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):269–278. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.269-278.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hejka A., Schmitz J. L., England D. M., Callister S. M., Schell R. F. Histopathology of Lyme arthritis in LSH hamsters. Am J Pathol. 1989 May;134(5):1113–1123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde F. W., Johnson R. C., White T. J., Shelburne C. E. Detection of antigens in urine of mice and humans infected with Borrelia burgdorferi, etiologic agent of Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):58–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.58-61.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M., Duray P. H. Experimental infection of the hamster with Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:258–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M. In vitro and in vivo susceptibility of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, to four antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):164–167. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Schreier A. B., Ficke C. M. Clinical and serologic studies of canine borreliosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1987 Nov 1;191(9):1089–1094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus L. C., Steere A. C., Duray P. H., Anderson A. E., Mahoney E. B. Fatal pancarditis in a patient with coexistent Lyme disease and babesiosis. Demonstration of spirochetes in the myocardium. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Sep;103(3):374–376. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-3-374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznick J. W., Braunstein D. B., Walsh R. L., Smith C. R., Wolfson P. M., Gierke L. W., Gorelkin L., Chandler F. W. Lyme carditis. Electrophysiologic and histopathologic study. Am J Med. 1986 Nov;81(5):923–927. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90370-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Museteanu C., Zimmer G., Mossmann H., Simon M. M. The severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) mouse. A laboratory model for the analysis of Lyme arthritis and carditis. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1427–1432. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Schrumpf M. E., Karstens R. H. The urinary bladder, a consistent source of Borrelia burgdorferi in experimentally infected white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus). J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):893–895. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.893-895.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinsky R. J., Piesman J. Ear punch biopsy method for detection and isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi from rodents. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1723–1727. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1723-1727.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek G., Klein J., Bittner R., Glogar D. Isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi from the myocardium of a patient with longstanding cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 25;322(4):249–252. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199001253220407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Batsford W. P., Weinberg M., Alexander J., Berger H. J., Wolfson S., Malawista S. E. Lyme carditis: cardiac abnormalities of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jul;93(1):8–16. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-1-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


