Abstract
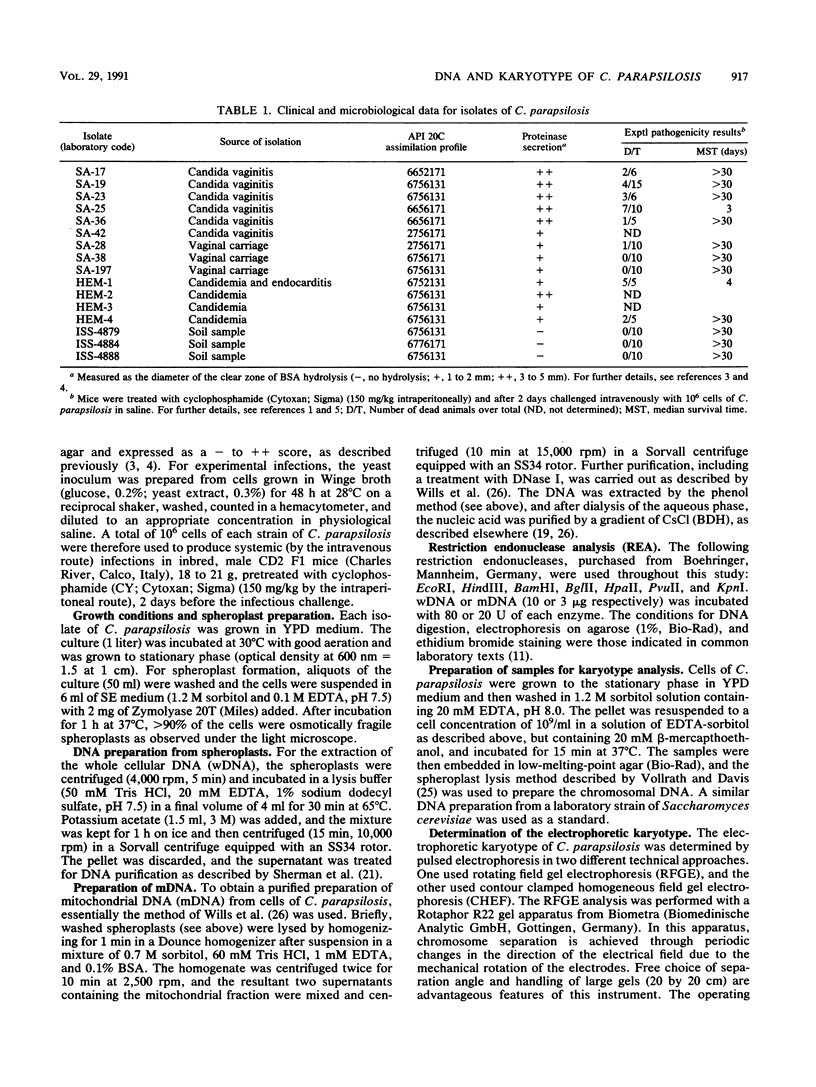
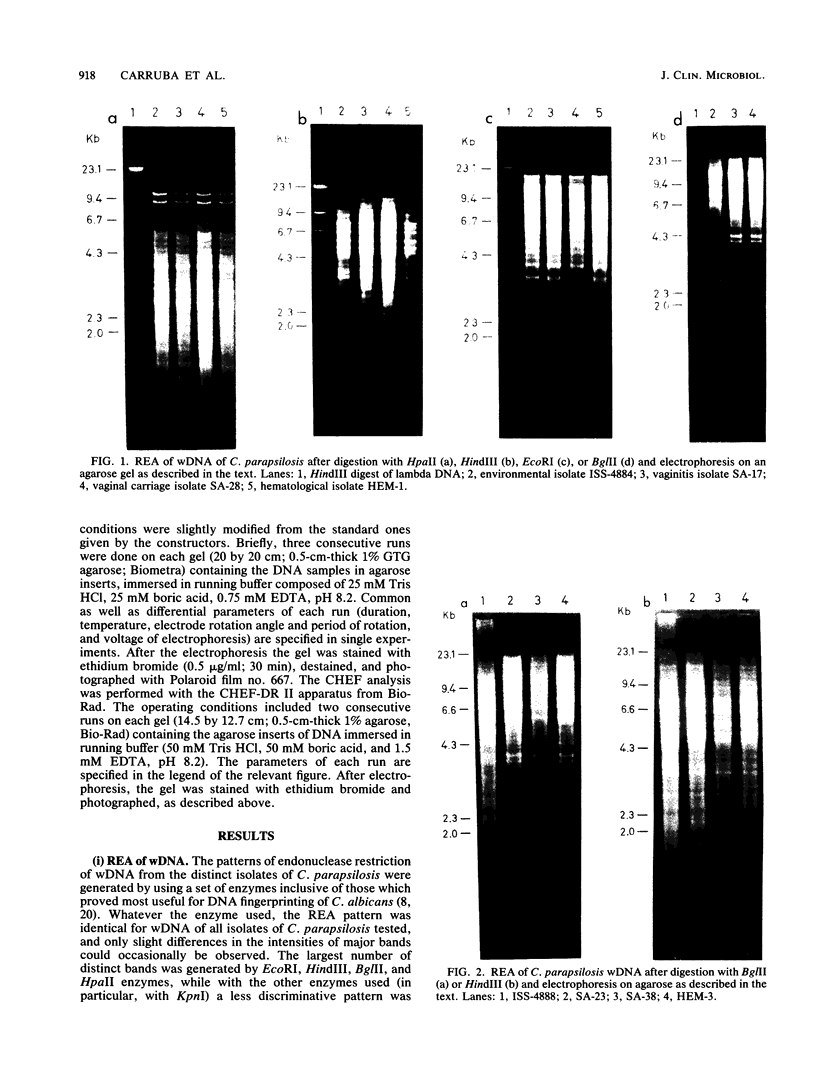
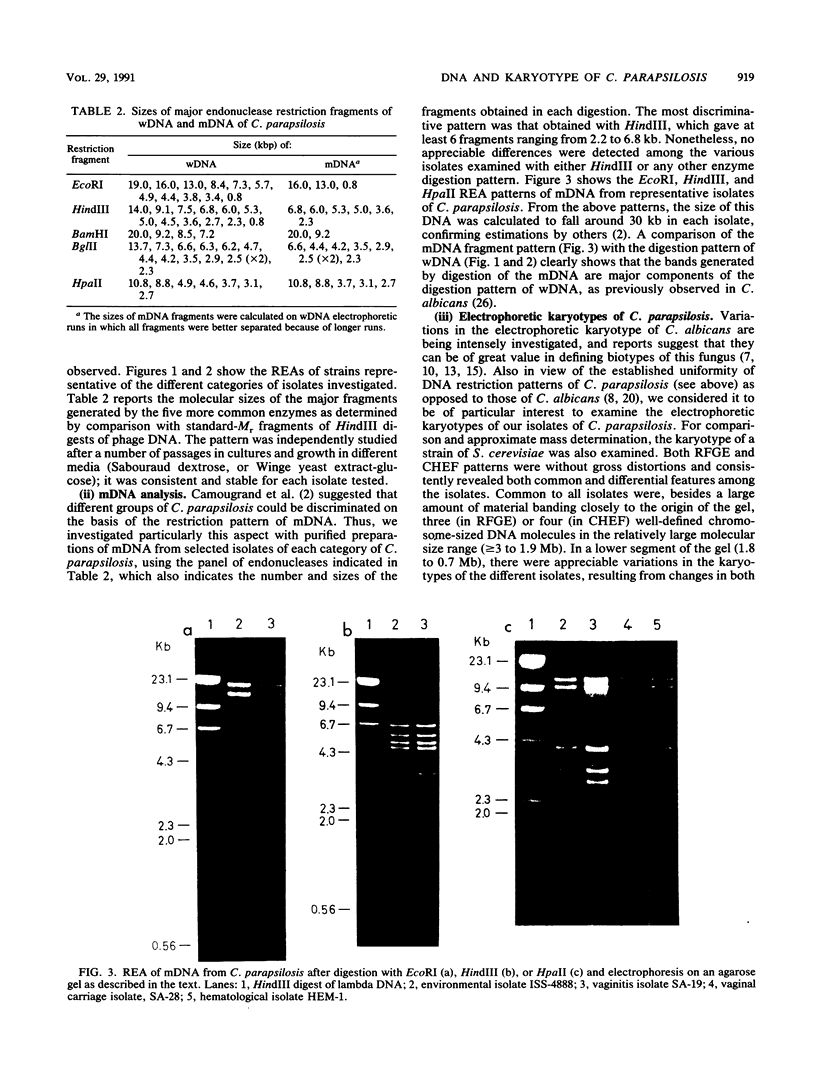
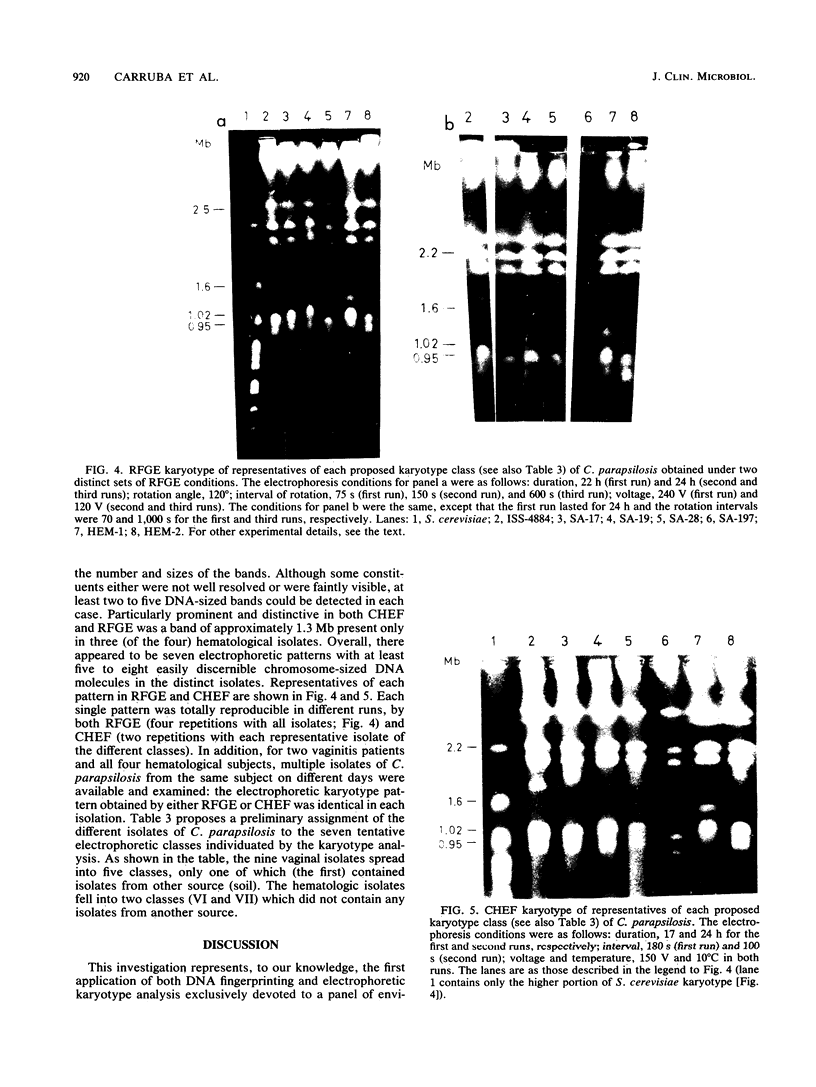
The endonuclease restriction pattern (DNA fingerprinting) and the electrophoretic karyotype of 16 Candida parapsilosis isolates from environmental and clinical sources were investigated. DNA from both whole cells and separated mitochondria was digested with enzymes, including EcoRI, BamHI, KpnI, BglII, HpaII, PvuII, and HindIII. Regardless of their source and pathogenic properties, all isolates showed a uniform, reproducible, and overlapping whole-cell DNA fingerprinting with each endonuclease digest. Mitochondrial DNA fragments were, in all cases, major contributors to the total cellular DNA restriction pattern. In contrast, the electrophoretic karyotype generated by rotating field gel electrophoresis (RFGE) or contour clamped homogeneous field electrophoresis (CHEF) showed a remarkable polymorphism among the isolates. This polymorphism concerned the smaller molecular size section of the karyotype (range, 1.8 to 0.7 Mb), where at least two to five chromosomal bands could be consistently detected by both RFGE and CHEF. Larger (greater than or equal to 3.0 to 1.9 Mb) chromosome-sized DNA bands (four in CHEF and three in RFGE) were quite distinct and common to all isolates. Thus, seven karyotype classes could be defined, on the basis of both the number and size of putative chromosomes. The three categories of isolates (soil, vaginal, and hematological) were not randomly distributed among the seven classes. In particular, the four hematological isolates had a karyotype pattern which was clearly distinct from that shown by the three environmental isolates, and of the nine vaginal isolates only one shared a class with isolates from another source (soil). Although tentative, the classification was totally consistent with the independent and reproducible results obtained by the two pulse-field electrophoretic techniques employed. It is suggested that the electrophoretic analysis of the karyotype might be particularly useful for epidemiological and pathogenicity studies on biotypes of C. parapsilosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bistoni F., Vecchiarelli A., Cenci E., Sbaraglia G., Perito S., Cassone A. A comparison of experimental pathogenicity of Candida species in cyclophosphamide-immunodepressed mice. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(5):409–418. doi: 10.1080/00362178485380661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camougrand N., Mila B., Velours G., Lazowska J., Guérin M. Discrimination between different groups of Candida parapsilosis by mitochondrial DNA restriction analysis. Curr Genet. 1988 May;13(5):445–449. doi: 10.1007/BF00365667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bernardis F., Agatensi L., Ross I. K., Emerson G. W., Lorenzini R., Sullivan P. A., Cassone A. Evidence for a role for secreted aspartate proteinase of Candida albicans in vulvovaginal candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1276–1283. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bernardis F., Lorenzini R., Verticchio R., Agatensi L., Cassone A. Isolation, acid proteinase secretion, and experimental pathogenicity of Candida parapsilosis from outpatients with vaginitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2598–2603. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2598-2603.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komshian S. V., Uwaydah A. K., Sobel J. D., Crane L. R. Fungemia caused by Candida species and Torulopsis glabrata in the hospitalized patient: frequency, characteristics, and evaluation of factors influencing outcome. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):379–390. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.3.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasker B. A., Carle G. F., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Comparison of the separation of Candida albicans chromosome-sized DNA by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3783–3793. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., D'Souza T. M., Magee P. T. Strain and species identification by restriction fragment length polymorphisms in the ribosomal DNA repeat of Candida species. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1639–1643. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1639-1643.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., Koltin Y., Gorman J. A., Magee P. T. Assignment of cloned genes to the seven electrophoretically separated Candida albicans chromosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4721–4726. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., Magee P. T. Electrophoretic karyotypes and chromosome numbers in Candida species. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Feb;133(2):425–430. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-2-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martino P., Meloni G., Cassone A. Candidal endocarditis and treatment with fluconazole and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Jun 15;112(12):966–967. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-12-966_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz W. G., Connelly C., Hieter P. Variation of electrophoretic karyotypes among clinical isolates of Candida albicans. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):842–845. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.842-845.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier-Carpentier F., Kiehn T. E., Armstrong D. Fungemia in the immunocompromised host. Changing patterns, antigenemia, high mortality. Am J Med. 1981 Sep;71(3):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monod M., Porchet S., Baudraz-Rosselet F., Frenk E. The identification of pathogenic yeast strains by electrophoretic analysis of their chromosomes. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Jun;32(2):123–129. doi: 10.1099/00222615-32-2-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Candida albicans proteinase as a virulence factor in the pathogenesis of Candida infections. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Dec;260(4):539–542. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., McManus E. J., Riggsby W. S., Jones J. M. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism in Candida albicans. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):214–215. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouffe J. F., Brown D. G., Silva J., Jr, Eck T., Stricof R. L., Fekety F. R., Jr Nosocomial outbreak of Candida parapsilosis fungemia related to intravenous infusions. Arch Intern Med. 1977 Dec;137(12):1686–1689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggsby W. S., Torres-Bauza L. J., Wills J. W., Townes T. M. DNA content, kinetic complexity, and the ploidy question in Candida albicans. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;2(7):853–862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.7.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Stevens D. A. Application of DNA typing methods to epidemiology and taxonomy of Candida species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):675–679. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.675-679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staib F., Mishra S. K., Tompak B., Grosse G., Abel T., Blisse A., Folkens U., Fröhlich B. Pathogenic yeast-like fungi in meat products. Zentralbl Bakteriol A. 1980;248(3):422–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staib F. Proteolysis and pathogenicity of Candida albicans strains. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1969 May 28;37(4):345–348. doi: 10.1007/BF02129881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Resolution of DNA molecules greater than 5 megabases by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7865–7876. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Lasker B. A., Sirotkin K., Riggsby W. S. Repetitive DNA of Candida albicans: nuclear and mitochondrial components. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):918–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.918-924.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bernardis F., Morelli L., Ceddia T., Lorenzini R., Cassone A. Experimental pathogenicity and acid proteinase secretion of vaginal isolates of Candida parapsilosis. J Med Vet Mycol. 1990;28(2):125–137. doi: 10.1080/02681219080000171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]