Abstract
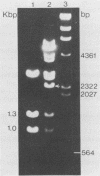
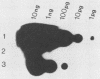
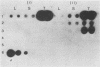
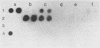
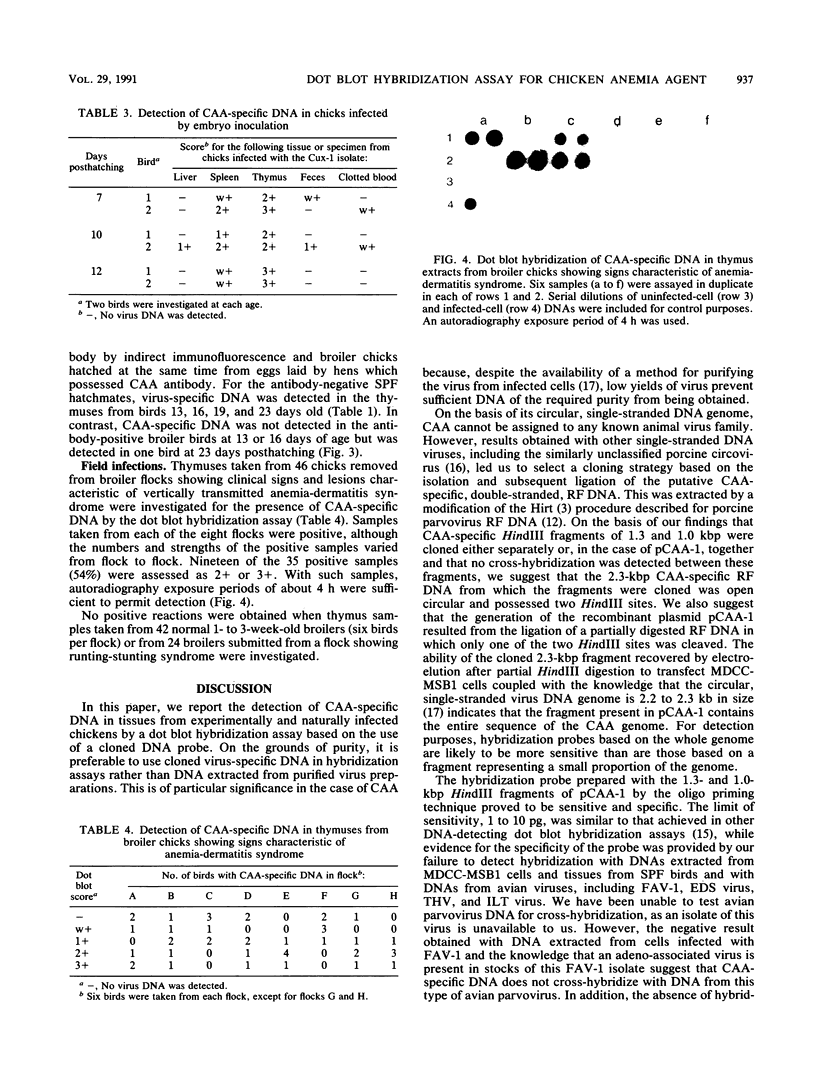
A dot blot hybridization assay capable of detecting chicken anemia agent (CAA)-specific DNA in tissues from infected birds has been developed. The assay uses a 32P-labeled DNA probe prepared from cloned CAA-specific fragments representing the entire virus genome and has a sensitivity limit of between and 1 and 10 pg. DNAs from CAA isolates originating in the Federal Republic of Germany, Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Australia were detected. Investigation of specimens from experimentally infected chicks indicated that virus-specific DNA was detected in the tissues of birds from 5 through 42 days after infection and that greater amounts were usually detected in the thymus than in the spleen, liver, feces, or blood. Tissues from specific-pathogen-free and broiler chicks which had become infected at an older age through contact with experimentally infected anemic chicks also contained CAA-specific DNA detectable by the assay. Thymuses from 1- to 2-week-old chicks from eight commercial broiler flocks which had been showing clinical signs characteristic of anemia-dermatitis syndrome were found positive by the hybridization technique, but thymuses from chicks obtained from broiler flocks which did not show such signs were found negative. Of the 35 positive samples (from 46 samples tested), 19 (54%) contained virus-specific DNA in sufficiently great amounts to permit 4-h autoradiography exposures and sample throughput times of 2 days. When compared with virus isolation, the CAA dot blot hybridization assay is time- and labor-saving.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Connor T. J., McNeilly F., Spackman D. Chicken anemia agent in the United States: isolation of the virus and detection of antibody in broiler breeder flocks. Avian Dis. 1989 Oct-Dec;33(4):691–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Mackie D. P., Pollock D. A., McNair J., Todd D., Mawhinney K. A., Connor T. J., McNeilly F. Production and preliminary characterization of monoclonal antibodies to chicken anemia agent. Avian Dis. 1990 Apr-Jun;34(2):352–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor T. W., Joo H. S., Collett M. S. Porcine parvovirus DNA: characterization of the genomic and replicative form DNA of two virus isolates. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Danna K. J. Efficient infection of monkey cells with DNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7575–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C. Diagnostic deoxyribonucleic acid probes for infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):82–101. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischer I., Buhk H. J. Viral DNA from cells infected with porcine circovirus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Nov;270(1-2):280–287. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80164-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd D., Creelan J. L., Mackie D. P., Rixon F., McNulty M. S. Purification and biochemical characterization of chicken anaemia agent. J Gen Virol. 1990 Apr;71(Pt 4):819–823. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-4-819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuasa N., Taniguchi T., Imada T., Hihara H. Distribution of chicken anemia agent (CAA) and detection of neutralizing antibody in chicks experimentally inoculated with CAA. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1983 Fall;23(3):78–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]