Abstract
Candida species are an important cause of infection in immunocompromised hosts and the leading cause of nosocomial fungal infections. Study of the epidemiology of Candida infection has been difficult because of lack of a reliable typing system. We describe a typing system utilizing contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields (CHEF), which is a modified version of pulsed-field gradient gel electrophoresis, and compared it with restriction enzyme analysis (REA) of genomic DNA. The study was done with 35 Candida albicans clinical isolates from separate patients. CHEF and REA were performed on each isolate, and the patterns were compared. The REA procedure revealed 17 strain types while the CHEF procedure was able to distinguish 23 strain types of C. albicans. The CHEF technique yields unique patterns of chromosomal bands that can be used to distinguish clinical isolates and demonstrates greater sensitivity than REA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allardet-Servent A., Bouziges N., Carles-Nurit M. J., Bourg G., Gouby A., Ramuz M. Use of low-frequency-cleavage restriction endonucleases for DNA analysis in epidemiological investigations of nosocomial bacterial infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2057–2061. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2057-2061.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Bolivar R., Fainstein V. Infectious complications in leukemic patients. Semin Hematol. 1982 Jul;19(3):193–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P. Candidiasis in cancer patients. Am J Med. 1984 Oct 30;77(4D):13–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bross J., Talbot G. H., Maislin G., Hurwitz S., Strom B. L. Risk factors for nosocomial candidemia: a case-control study in adults without leukemia. Am J Med. 1989 Dec;87(6):614–620. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80392-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Odds F. C., Lee W., Webster C., Williams J. D. Outbreak of systemic Candida albicans in intensive care unit caused by cross infection. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Mar 9;290(6470):746–748. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6470.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung L. L., Hudson J. B. Development of DNA probes for Candida albicans. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;10(3):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(88)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childress C. M., Holder I. A., Neely A. N. Modifications of a Candida albicans biotyping system. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1392–1394. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1392-1394.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer D. R., Eccleshall R., Marmur J. Isolation of yeast DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:39–44. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60950-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E., Glee P. M., Horn H. L. Candida albicans- and Candida stellatoidea-specific DNA fragment. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1720–1724. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1720-1724.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I., Engleberg N. C. Applied molecular genetics: new tools for microbiologists and clinicians. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):416–430. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox B. C., Mobley H. L., Wade J. C. The use of a DNA probe for epidemiological studies of candidiasis in immunocompromised hosts. J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):488–494. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum M. A. Mechanisms potentiating Candida infections. A review. Mycoses. 1988 Nov;31(11):543–557. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1988.tb04408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannini S. H., Schittini M., Keithly J. S., Warburton P. W., Cantor C. R., Van der Ploeg L. H. Karyotype analysis of Leishmania species and its use in classification and clinical diagnosis. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):762–765. doi: 10.1126/science.3961502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glee P. M., Russell P. J., Welsch J. A., Pratt J. C., Cutler J. E. Methods for DNA extraction from Candida albicans. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jul;164(1):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90387-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy D. A., Bell J. I., Long E. O., Lindsten T., McDevitt H. O. Mapping of the class II region of the human major histocompatibility complex by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):453–455. doi: 10.1038/323453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann C. S., Merz W. G. Electrophoretic karyotypes of Torulopsis glabrata. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2165–2168. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2165-2168.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komshian S. V., Uwaydah A. K., Sobel J. D., Crane L. R. Fungemia caused by Candida species and Torulopsis glabrata in the hospitalized patient: frequency, characteristics, and evaluation of factors influencing outcome. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):379–390. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.3.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Burnie J., Matthews R. Fingerprinting Candida albicans. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Nov 6;93(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90186-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., D'Souza T. M., Magee P. T. Strain and species identification by restriction fragment length polymorphisms in the ribosomal DNA repeat of Candida species. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1639–1643. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1639-1643.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., Koltin Y., Gorman J. A., Magee P. T. Assignment of cloned genes to the seven electrophoretically separated Candida albicans chromosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4721–4726. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee P. T., Rikkerink E. H., Magee B. B. Methods for the genetics and molecular biology of Candida albicans. Anal Biochem. 1988 Dec;175(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maksymiuk A. W., Thongprasert S., Hopfer R., Luna M., Fainstein V., Bodey G. P. Systemic candidiasis in cancer patients. Am J Med. 1984 Oct 30;77(4D):20–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
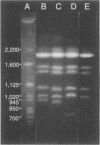
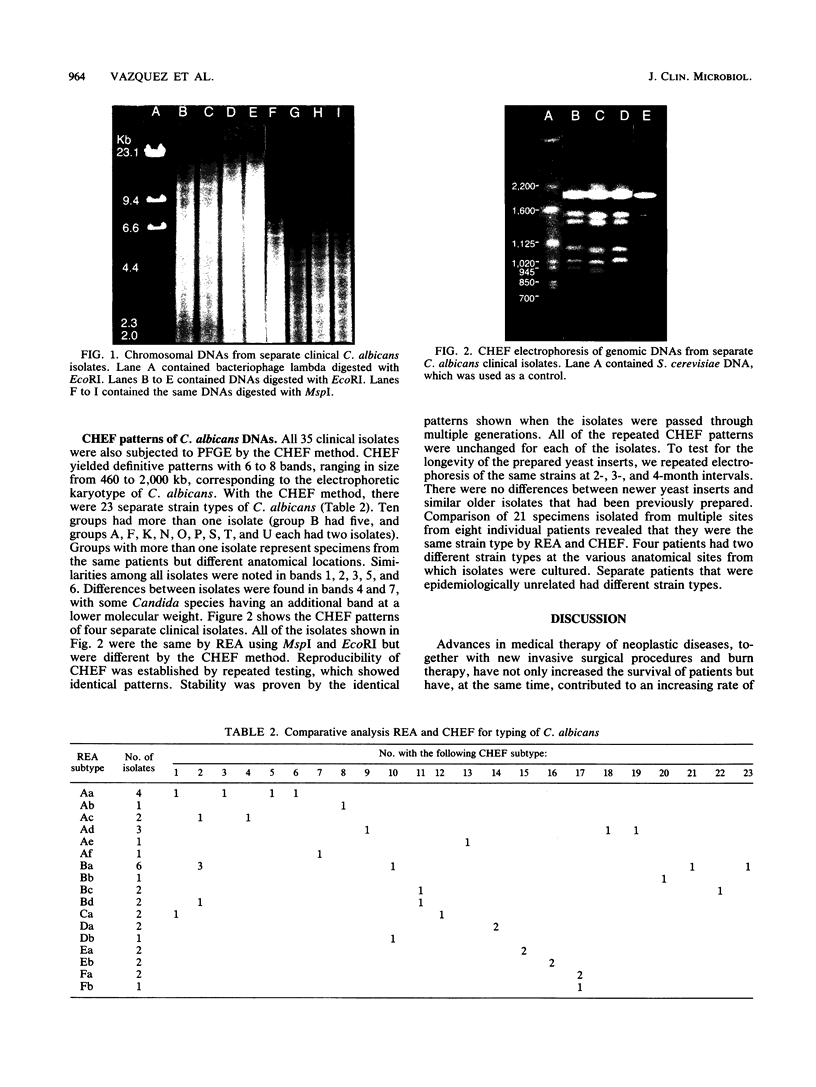
- Merz W. G., Connelly C., Hieter P. Variation of electrophoretic karyotypes among clinical isolates of Candida albicans. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):842–845. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.842-845.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monod M., Porchet S., Baudraz-Rosselet F., Frenk E. The identification of pathogenic yeast strains by electrophoretic analysis of their chromosomes. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Jun;32(2):123–129. doi: 10.1099/00222615-32-2-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petes T. D., Hereford L. M., Skryabin K. G. Characterization of two types of yeast ribosomal DNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):295–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.295-305.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A. Infection control: opportunistic fungal infections--the increasing importance of Candida species. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1989 Jun;10(6):270–273. doi: 10.1086/646021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phongpaichit S., Mackenzie D. W., Fraser C. Strain differentiation of Candida albicans by morphotyping. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Oct;99(2):421–428. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonelli L., Archibusacci C., Sestito M., Morace G. Killer system: a simple method for differentiating Candida albicans strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):774–780. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.774-780.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggsby W. S., Torres-Bauza L. J., Wills J. W., Townes T. M. DNA content, kinetic complexity, and the ploidy question in Candida albicans. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;2(7):853–862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.7.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Román M. C., Linares Sicilia M. J. Preliminary investigation of Candida albicans biovars. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):430–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.430-431.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Stevens D. A. A Candida albicans dispersed, repeated gene family and its epidemiologic applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1452–1456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Stevens D. A. Application of DNA typing methods to epidemiology and taxonomy of Candida species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):675–679. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.675-679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Matsumoto T., Niwa O., Klco S., Fan J. B., Yanagida M., Cantor C. R. An electrophoretic karyotype for Schizosaccharomyces pombe by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4481–4489. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell R. G., Hermans I. F., Wilkins R. J., Corner B. E. Chromosomal variations in Candida albicans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3625–3625. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Vazquez J. Candidemia and systemic candidiasis. Semin Respir Infect. 1990 Jun;5(2):123–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Bauzá L. J., Riggsby W. S. Protoplasts from yeast and mycelial forms of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Aug;119(2):341–349. doi: 10.1099/00221287-119-2-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Smits M., Ponnudurai T., Vermeulen A., Meuwissen J. H., Langsley G. Chromosome-sized DNA molecules of Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1985 Aug 16;229(4714):658–661. doi: 10.1126/science.3895435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. W., Speller D. C., Day J. K., Farrell A. J. Resistogram method for differentiation of strains of Candida albicans. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;46(3):571–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb00857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. W. Typing of Candida albicans. J Hosp Infect. 1984 Sep;5(3):244–252. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(84)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wey S. B., Mori M., Pfaller M. A., Woolson R. F., Wenzel R. P. Hospital-acquired candidemia. The attributable mortality and excess length of stay. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Dec;148(12):2642–2645. doi: 10.1001/archinte.148.12.2642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson M. I., Samaranayake L. P., MacFarlane T. W. A new simple method for biotyping Candida albicans. Microbios. 1987;51(208-209):159–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Lasker B. A., Sirotkin K., Riggsby W. S. Repetitive DNA of Candida albicans: nuclear and mitochondrial components. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):918–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.918-924.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]