Abstract
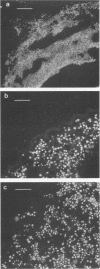
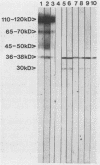
Three monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), designated 7C5, 7C9, and 5G8, against a cytoplasmic antigen of Cryptococcus neoformans were produced. MAbs 7C5 and 7C9 recognize culture filtrate antigen (exoantigen) of both encapsulated and nonencapsulated isolates of this pathogen, which suggests that they do not recognize capsular polysaccharide material. This is supported by immunofluorescence data which show reactivity of all 3 MAbs to cytoplasm and cell membranes only. MAb 7C9 also recognized C. neoformans var. gattii antigens but no other fungal pathogens tested in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, while 7C5 and 5G8 recognized antigens of the cross-reactive pathogen Trichosporon beigelii but did not recognize either C. neoformans var. gattii isolates or any other fungal antigens. By Western blot (immunoblot), 7C9 detected antigen at 110 to 120, 65 to 70, 45 to 50, and 36 to 38 kDa; in addition to the latter band, the other two MAbs recognized a band at approximately 30 kDa. All three MAbs were of the immunoglobulin G1 subclass. The two MAbs which are capable of reacting with noncapsular culture supernatant antigen have possible uses in serodiagnosis, particularly in AIDS patients infected with C. neoformans, since in this group the present latex agglutination test has some limitations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell C. K., Payne A. L., Teall A. J., Brownell A., Mackenzie D. W. Cryptococcal latex antigen test positive in patient with Trichosporon beigelii infection. Lancet. 1985 Jul 6;2(8445):43–44. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dismukes W. E. Cryptococcal meningitis in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):624–628. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan C. T. Specificity of the latex-cryptococcal antigen test. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Oct;58(4):358–364. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/58.5.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dromer F., Salamero J., Contrepois A., Carbon C., Yeni P. Production, characterization, and antibody specificity of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with Cryptococcus neoformans capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):742–748. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.742-748.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert T. F., Kozel T. R. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for Cryptococcus neoformans capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1895–1899. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1895-1899.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa J. I., Hamilton A. J., Bartholomew M. A., Harada T., Fenelon L., Hay R. J. Preparation of species-specific murine monoclonal antibodies against the yeast phase of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1766–1769. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1766-1769.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. S., Kaufman L., Koenig M. G. Diagnosis of cryptococcal meningitis. Value of immunologic detection of cryptococcal antigen. N Engl J Med. 1971 Aug 19;285(8):434–436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197108192850804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton A. J., Bartholomew M. A., Fenelon L. E., Figueroa J., Hay R. J. A murine monoclonal antibody exhibiting high species specificity for Histoplasma capsulatum var. capsulatum. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Feb;136(2):331–335. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-2-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper R. L., Perry E. V., Fainstein V. Diagnostic value of cryptococcal antigen in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with malignant disease. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):915–915. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox P. H., Jenkins D. 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APES): a new advance in section adhesion. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Oct;40(10):1256–1257. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.10.1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizels R. M., Burke J., Denham D. A. Phosphorylcholine-bearing antigens in filarial nematode parasites: analysis of somatic extracts, in-vitro secretions and infection sera from Brugia malayi and B. pahangi. Parasite Immunol. 1987 Jan;9(1):49–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1987.tb00488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew W. D., Sandrock A. W., Jr Cyclophosphamide treatment used to manipulate the immune response for the production of monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Jun 26;100(1-2):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Moorhead J. W. Regulation of cell-mediated immunity in cryptococcosis. I. Induction of specific afferent T suppressor cells by cryptococcal antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):276–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevost E., Newell R. Commercial cryptococcal latex kit: clinical evaluation in a medical center hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Nov;8(5):529–533. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.5.529-533.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read S. M., Northcote D. H. Minimization of variation in the response to different proteins of the Coomassie blue G dye-binding assay for protein. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;116(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]