Abstract
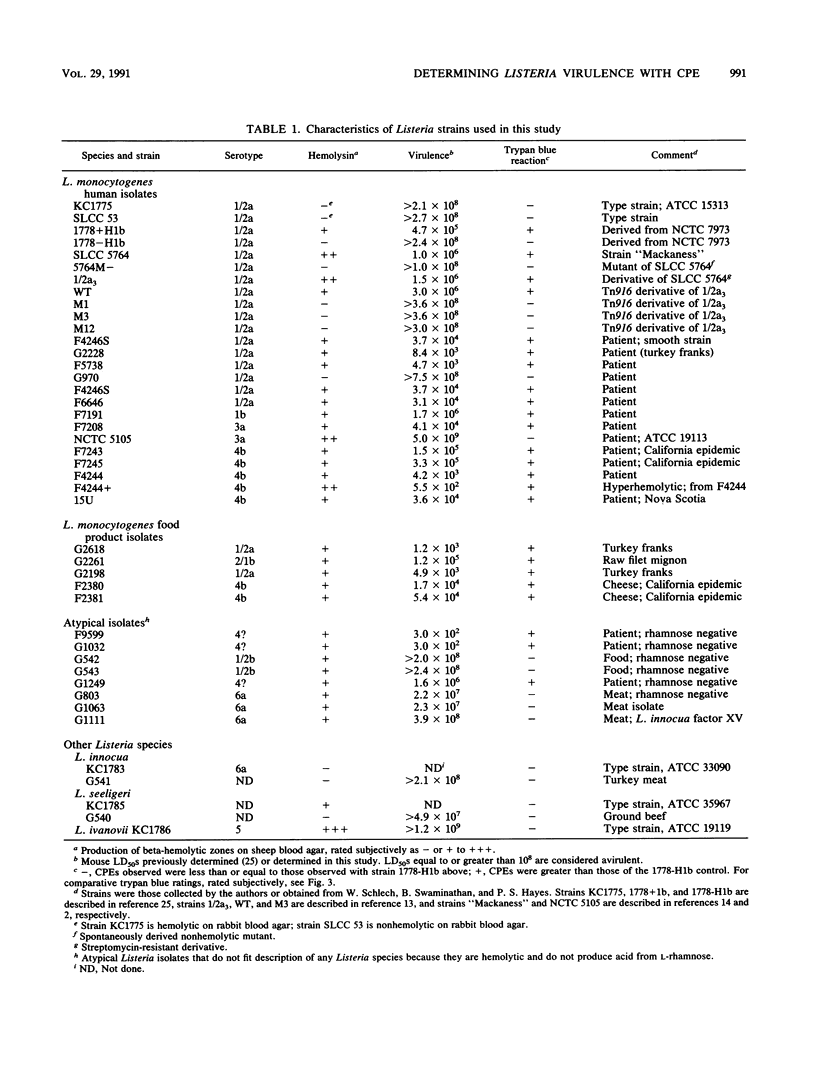
We have developed a simple test that differentiates between virulent and avirulent Listeria species as defined by the mouse 50% lethal doses (LD50S). The assay is based on trypan blue-revealed cytopathogenic effects that are produced during the infection of the human enterocytelike cell line Caco-2. These effects were elicited only by Listeria strains that had an intraperitoneal mouse LD50 less than 10(8) and were not produced by nonhemolytic, avirulent strains of Listeria monocytogenes generated spontaneously or by Tn916 mutagenesis or by avirulent Listeria species. A negative test was also obtained with hemolysin-producing, avirulent L. monocyotogenes NCTC5105 and Listeria ivanovii KC1786. The test was negative with avirulent L. monocytogenes strains which are strong inducers of opacity in egg yolk agar. However, a strain which has a low LD50, such as 10(4), may show less severe cytopathogenic effects than a strain having a higher LD50, such as 10(6). The test has been effectively used to screen for virulent listerial isolates, spontaneous mutants, and transposon-induced mutants.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton W. L., Cochi S. L., Feeley J. C. Overview of neonatal listeriosis. Clin Invest Med. 1984;7(4):311–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldridge J. R., Thomashow M. F., Hinrichs D. J. Induction of immunity with avirulent Listeria monocytogenes 19113 depends on bacterial replication. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2109–2113. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2109-2113.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basher H. A., Seaman A., Woodbine M. Infection, haemorrhagia and death of chick embryos experimentally inoculated with Listeria monocytogenes by the intra-allantoic route. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Sep;255(2-3):239–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb W. F., Gellin B. G., Weaver R., Schwartz B., Plikaytis B. D., Reeves M. W., Pinner R. W., Broome C. V. Analysis of clinical and food-borne isolates of Listeria monocytogenes in the United States by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and application of the method to epidemiologic investigations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2133–2141. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2133-2141.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Vicente M. F., Mengaud J., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Berche P. Listeriolysin O is essential for virulence of Listeria monocytogenes: direct evidence obtained by gene complementation. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3629–3636. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3629-3636.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. W., Cochi S. L., MacDonald K. L., Brondum J., Hayes P. S., Plikaytis B. D., Holmes M. B., Audurier A., Broome C. V., Reingold A. L. Pasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection in an outbreak of listeriosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 14;312(7):404–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502143120704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Sansonetti P. Transposon mutagenesis as a tool to study the role of hemolysin in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellin B. G., Broome C. V. Listeriosis. JAMA. 1989 Mar 3;261(9):1313–1320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. L., Killinger A. H. Listeria monocytogenes and listeric infections. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):309–382. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.309-382.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. The role of cell-mediated immunity in bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1221–1250. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Synthesis and secretion of interferon by murine fibroblasts in response to intracellular Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):787–792. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.787-792.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hof H. Virulence of different strains of Listeria monocytogenes serovar 1/2a. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1984;173(4):207–218. doi: 10.1007/BF02122112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathariou S., Metz P., Hof H., Goebel W. Tn916-induced mutations in the hemolysin determinant affecting virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1291–1297. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1291-1297.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathariou S., Rocourt J., Hof H., Goebel W. Levels of Listeria monocytogenes hemolysin are not directly proportional to virulence in experimental infections of mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):534–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.534-536.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knorz W., Hof H. Zur Pathogenität von Listerien. Immun Infekt. 1986 Apr;14(2):76–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Kathariou S., Goebel W. Hemolysin supports survival but not entry of the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):79–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.79-82.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattmann C., Schwarzkopf A., Seeliger H. P. Pathogenicity testing of Listeria strains isolated from food in fertilized hen's eggs. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1989 Jan;270(3):400–405. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(89)80009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnan M. J., Mascola L., Lou X. D., Goulet V., May S., Salminen C., Hird D. W., Yonekura M. L., Hayes P., Weaver R. Epidemic listeriosis associated with Mexican-style cheese. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 29;319(13):823–828. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809293191303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinverni R., Bille J., Perret C., Regli F., Tanner F., Glauser M. P. Listériose épidémique. Observation de 25 cas en 15 mois au Centre hospitalier universitaire vaudois. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1985 Jan 5;115(1):2–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuyama M., Igarashi K., Kawamura I., Ohmori T., Nomoto K. Difference in the induction of macrophage interleukin-1 production between viable and killed cells of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1254–1260. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1254-1260.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Ryter A., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular and cell-to-cell spread of Listeria monocytogenes involves interaction with F-actin in the enterocytelike cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1048-1058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'LEARY W. M., WELD J. T. LIPOLYTIC ACTIVITIES OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. I. NATURE OF THE ENZYME PRODUCING FREE FATTY ACIDS FROM PLASMA LIPIDS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1356–1363. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1356-1363.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piffaretti J. C., Kressebuch H., Aeschbacher M., Bille J., Bannerman E., Musser J. M., Selander R. K., Rocourt J. Genetic characterization of clones of the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes causing epidemic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3818–3822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., Weaver R. E., Carlone G. M., Pienta P. A., Rocourt J., Goebel W., Kathariou S., Bibb W. F., Malcolm G. B. Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 35152 and NCTC 7973 contain a nonhemolytic, nonvirulent variant. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2247–2251. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2247-2251.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Schreiber R. D., Connelly P., Tilney L. G. Gamma interferon limits access of Listeria monocytogenes to the macrophage cytoplasm. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2141–2146. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset M. The human colon carcinoma cell lines HT-29 and Caco-2: two in vitro models for the study of intestinal differentiation. Biochimie. 1986 Sep;68(9):1035–1040. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlech W. F., 3rd, Lavigne P. M., Bortolussi R. A., Allen A. C., Haldane E. V., Wort A. J., Hightower A. W., Johnson S. E., King S. H., Nicholls E. S. Epidemic listeriosis--evidence for transmission by food. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 27;308(4):203–206. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301273080407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeliger H. P. Apathogene listerien: L. innocua sp. n. (Seeliger et Schoofs, 1977). Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1981;249(4):487–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelma G. N., Jr, Reyes A. L., Peeler J. T., Francis D. W., Hunt J. M., Spaulding P. L., Johnson C. H., Lovett J. Pathogenicity test for Listeria monocytogenes using immunocompromised mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2085–2089. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2085-2089.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]