Abstract
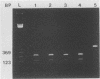
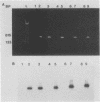
A polymerase chain reaction assay was developed for detection of budgerigar fledgling disease virus (BFDV). The assay used a single set of primers complementary to sequences located in the putative coding region for the BFDV VP1 gene. The observed amplification product had the expected size of 550 bp and was confirmed to derive from BFDV DNA by its restriction digestion pattern. This assay was specific for BFDV and highly sensitive, being able to detect as few as 20 copies of the virus. By using the polymerase chain reaction, BFDV was detected in adult, nestling, and embryo budgerigar (Melopsitticus undulatus) tissue DNAs and in sera from adult and nestling budgerigars. These results suggest the possibility of persistent infections in adult birds and lend further support to previously described evidence of possible in ovo transmission. BFDV was also detected in chicken embryo fibroblast cell cultures and chicken eggs inoculated with the virus. A 550-bp product with identical restriction enzyme sites was amplified from a suspected polyomavirus isolated from a peach-faced lovebird (Agapornis pesonata) and from tissue DNA from a Hahn's macaw (Ara nobilis) and a sun conure (Aratinga solstitialis) with histological lesions suggestive of polyomavirus infection. These fragments also hybridized with a BFDV-derived probe, proving that they were derived from a polyomavirus very similar, if not identical, to BFDV.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur R. R., Dagostin S., Shah K. V. Detection of BK virus and JC virus in urine and brain tissue by the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1174–1179. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1174-1179.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier G., Morin M., Marsolais G. A generalized inclusion body disease in the budgerigar (Melopsittacus undulatus) caused by a papovavirus-like agent. Avian Dis. 1981 Oct-Dec;25(4):1083–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier G., Morin M., Marsolais G. Papovavirus induced feather abnormalities and skin lesions in the budgerigar: clinical and pathological findings. Can Vet J. 1984 Aug;25(8):307–310. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozeman L. H., Davis R. B., Gaudry D., Lukert P. D., Fletcher O. J., Dykstra M. J. Characterization of a papovavirus isolated from fledgling budgerigars. Avian Dis. 1981 Oct-Dec;25(4):972–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. B., Bozeman L. H., Gaudry D., Fletcher O. J., Lukert P. D., Dykstra M. J. A viral disease of fledgling budgerigars. Avian Dis. 1981 Jan-Mar;25(1):179–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykstra M. J., Dykstra C. C., Lukert P. D., Bozeman L. H. Investigations of budgerigar fledgling disease virus. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Sep;45(9):1883–1887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden F. C., Hendrick J. P. Unusual organization of DNA sequences in the chicken. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5838–5844. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forshaw D., Wylie S. L., Pass D. A. Infection with a virus resembling papovavirus in Gouldian finches (Erythrura gouldiae). Aust Vet J. 1988 Jan;65(1):26–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1988.tb14927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouvea V., Glass R. I., Woods P., Taniguchi K., Clark H. F., Forrester B., Fang Z. Y. Polymerase chain reaction amplification and typing of rotavirus nucleic acid from stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):276–282. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.276-282.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. L., Calnek B. W. Papovavirus infection in hand-fed parrots: virus isolation and pathology. Avian Dis. 1987 Apr-Jun;31(2):398–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Nonaka H., Fukushi H., Shimakura S., Masegi T., Mizoguchi T. Isolation of a papovavirus-like agent from young budgerigars with feather abnormalities. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1984 Aug;46(4):577–582. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.46.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Impraim C. C., Saiki R. K., Erlich H. A., Teplitz R. L. Analysis of DNA extracted from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues by enzymatic amplification and hybridization with sequence-specific oligonucleotides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):710–716. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. R., Hines S. A., Quesenberry K., Mladinich C., Davis R. B., Kollias G. V., Olsen J. Epornitic of papova-like virus-associated disease in a psittacine nursery. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Dec 1;185(11):1337–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. M., Riddell C. Intranuclear inclusion bodies in finches. Can Vet J. 1986 Nov;27(11):432–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W. C., Adler S. P. Detection of human parvovirus B19 DNA by using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jan;28(1):65–69. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.1.65-69.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehn H., Müller H. Cloning and characterization of budgerigar fledgling disease virus, an avian polyomavirus. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):362–370. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H., Nitschke R. A polyoma-like virus associated with an acute disease of fledgling budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus). Med Microbiol Immunol. 1986;175(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02123124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M., Simsek M., Al-Mufti S. Polymerase chain reaction assay for detection of human cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1238–1242. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1238-1242.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pass D. A. A papova-like virus infection of lovebirds (Agapornis sp). Aust Vet J. 1985 Sep;62(9):318–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1985.tb14916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pass D. A., Prus S. E., Riddell C. A papova-like virus infection of splendid parakeets (Neophema splendida). Avian Dis. 1987 Jul-Sep;31(3):680–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers B. B., Alpert L. C., Hine E. A., Buffone G. J. Analysis of DNA in fresh and fixed tissue by the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Pathol. 1990 Mar;136(3):541–548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott O., Kröger M., Müller H., Hobom G. The genome of budgerigar fledgling disease virus, an avian polyomavirus. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):74–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90660-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata D. K., Arnheim N., Martin W. J. Detection of human papilloma virus in paraffin-embedded tissue using the polymerase chain reaction. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):225–230. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]