Abstract
The largest recorded epidemic of sporotrichosis in the United States occurred in 1988 and involved a total of 84 cases in 15 states. All cases were associated with Wisconsin-grown sphagnum moss. Twenty-one clinical isolates of Sporothrix schenckii and 69 environmental isolates of Sporothrix spp. from the epidemic were characterized and compared. The environmental isolates were recovered from 102 samples of sphagnum moss and other material by using direct plating techniques. Characteristics examined included macroscopic and microscopic morphology, conversion to a yeast phase, exoantigen reactions, and virulence in mice. On the basis of these studies, eight environmental isolates were identified as S. schenckii, five were identified as Ophiostoma stenoceras, and the remainder were identified as Sporothrix species. The environmental isolates of S. schenckii were recovered from moss samples from one Pennsylvania nursery and from three New York State Soil and Water Conservation districts, but none were recovered from moss directly from the bogs in Wisconsin.
Full text
PDF

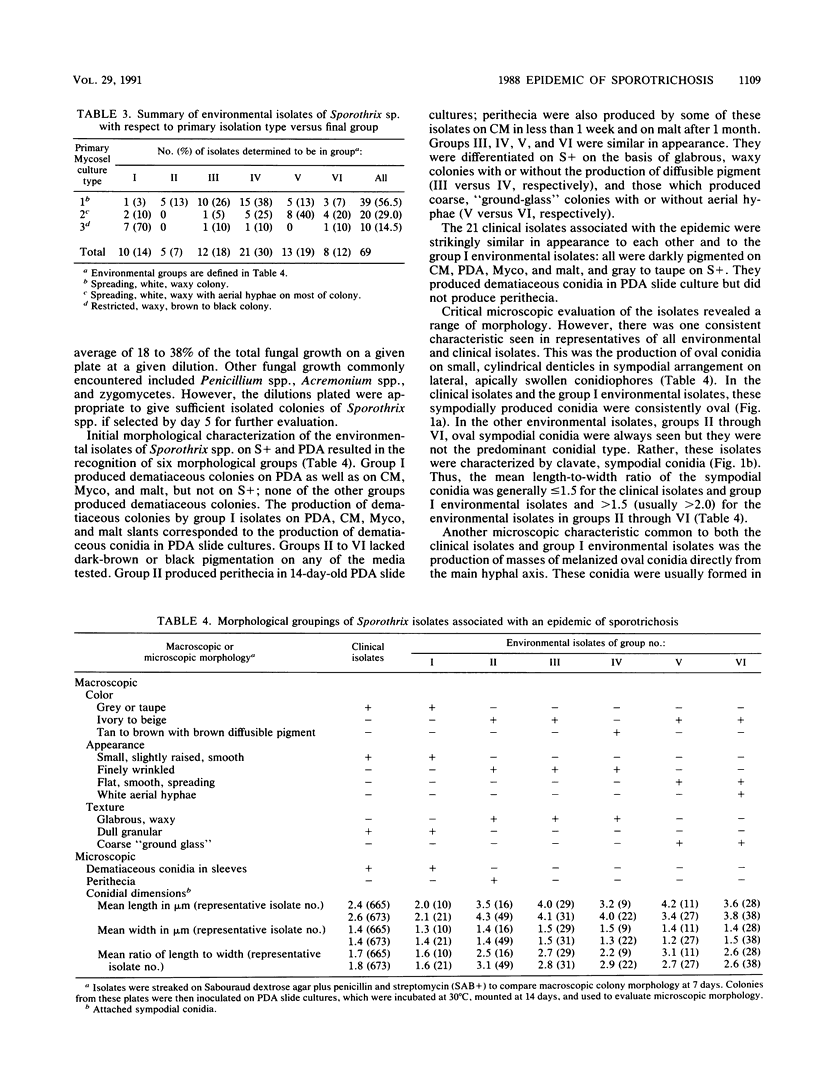
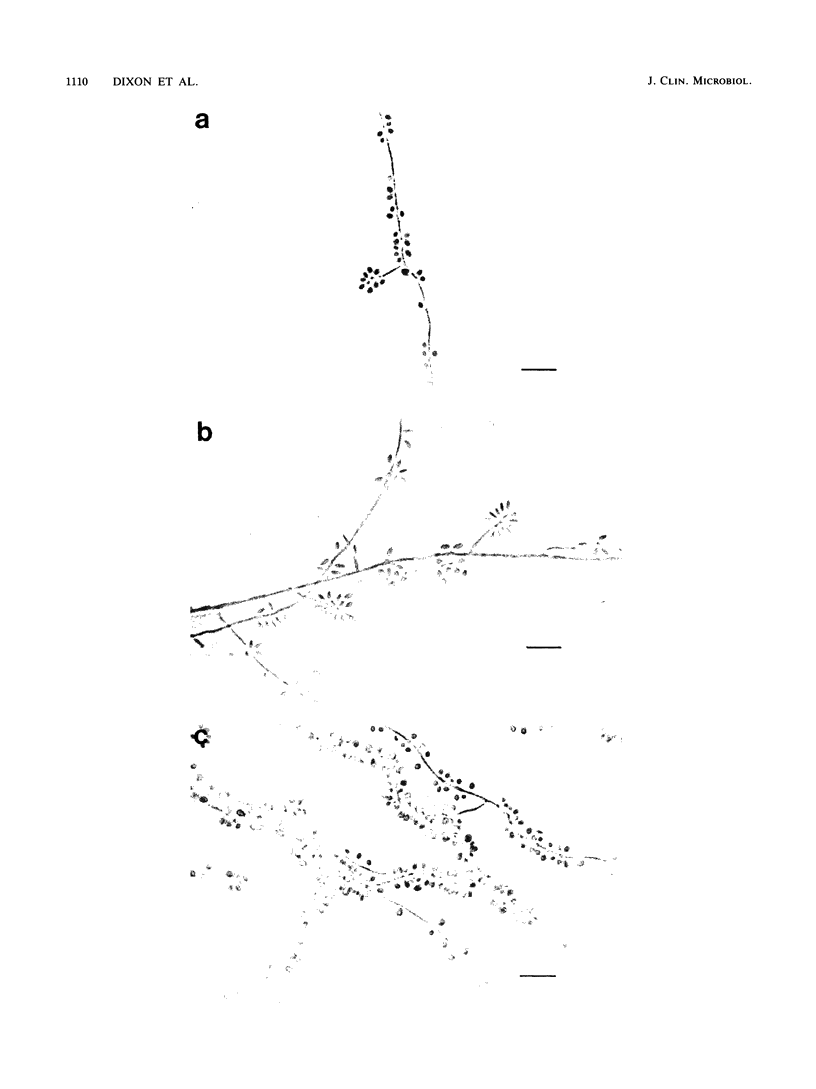



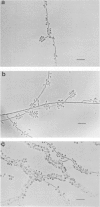
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CREVASSE L., ELLNER P. D. An outbreak of sporotrichosis in Florida. J Am Med Assoc. 1960 May 7;173:29–33. doi: 10.1001/jama.1960.03020190031006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D ALESSIO D. J., LEAVENS L. J., STRUMPF G. B., SMITH C. D. AN OUTBREAK OF SPOROTRICHOSIS IN VERMONT ASSOCIATED WITH SPHAGNUM MOSS AS THE SOURCE OF INFECTION. N Engl J Med. 1965 May 20;272:1054–1058. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196505202722005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon M. A., Lapa E. W. Adherence of digested tissue sections for fungal immunofluorescence. Mycopathologia. 1984 Dec 30;88(2-3):181–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00436451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotte M., Younger B. Sporotrichosis associated with sphagnum moss exposure. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1981 Jan;105(1):50–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYES W. N. Sporotrichosis in employees of a tree nursery. GP. 1960 Oct;22:114–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD D. H., ORR G. F. COMPARISON OF STRAINS OF SPOROTRICHUM SCHENCKII ISOLATED FROM NATURE. J Bacteriol. 1963 Apr;85:816–821. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.4.816-821.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L., Standard P. Improved version of the exoantigen test for identification of Coccidioides immitis and Histoplasma capsulatum cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):42–45. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.42-45.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis M. R., Padhye A. A., Ajello L. Storage of stock cultures of filamentous fungi, yeasts, and some aerobic actinomycetes in sterile distilled water. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):218–222. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.218-222.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. E., Taylor A., Phillips B. J., Blakey D. L., Campbell G. D., Kaufman L., Kaplan W. Cutaneous sporotrichosis in forestry workers. Epidemic due to contaminated Sphagnum moss. JAMA. 1978 Jul 21;240(3):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kawasaki M., Ishizaki H. Analysis of restriction profiles of mitochondrial DNA from Sporothrix schenckii and related fungi. Mycopathologia. 1988 Sep;103(3):147–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00436813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travassos L. R., Lloyd K. O. Sporothrix schenckii and related species of Ceratocystis. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Dec;44(4):683–721. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.683-721.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]