Abstract
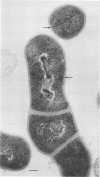
Gardnerella vaginalis has been isolated from women with bacterial vaginosis, from the genital tracts of asymptomatic women, and from several other infected body sites in humans. However, until recently, it has not been isolated from any other animal species. Between June 1988 and October 1989, 31 isolates identified as G. vaginalis and 70 isolates identified as G. vaginalis-like organisms have been recovered from the genital tracts of 93 mares from Michigan and Ohio. Identification was based on biochemical reactions, hemolysis on media containing blood from various animal sources, and susceptibility to select antimicrobial agents. This report details the characterization of G. vaginalis and G. vaginalis-like organism isolates obtained from the reproductive tracts of these mares and compares the equine isolates with human isolates.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey R. K., Voss J. L., Smith R. F. Factors affecting isolation and identification of Haemophilus vaginalis (Corynebacterium vaginale). J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):65–71. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.65-71.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkelberg W. E., Jr, Skaggs R., Kellogg D. S., Jr Method for isolation and identification of Corynebacterium vaginale (Haemophilus vaginalis). Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):47–52. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.47-52.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER H. L., DUKES C. D. Haemophilus vaginalis vaginitis: a newly defined specific infection previously classified non-specific vaginitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1955 May;69(5):962–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood J. R., Pickett M. J., Martin W. J., Mack E. G. Heamophilus vaginalis (Corynebacterium vaginal): method for isolation and rapid biochemical identification. Health Lab Sci. 1977 Apr;14(2):102–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood J. R., Pickett M. J. Salient features of Haemophilus vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):200–204. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.200-204.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst E. Reservoir of four organisms associated with bacterial vaginosis suggests lack of sexual transmission. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2035–2039. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2035-2039.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Human R. P., Tillotson G. S. Identification of Gardnerella vaginalis with the API 20 Strep system. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):985–986. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.985-986.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly J. L. Minimal criteria for the identification of Gardnerella vaginalis isolated from the vagina. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Apr;36(4):476–478. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.4.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam M. H., Birch D. F., Fairley K. F. Prevalence of Gardnerella vaginalis in the urinary tract. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1130–1133. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1130-1133.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. A., Moss C. W. Comparison of the effects of acid and base hydrolyses on hydroxy and cyclopropane fatty acids in bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1370–1377. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1370-1377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton P. M. Gardnerella vaginalis: laboratory isolation and clinical significance. Can J Public Health. 1982 Sep-Oct;73(5):335–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lien E. A., Hillier S. L. Evaluation of the enhanced rapid identification method for Gardnerella vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):566–567. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.566-567.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. M., Hayes C. H., Rosner B., Evrard J. R., Crockett V. A., Alpert S., Zinner S. H. Vaginal colonization with Corynebacterium vaginale (Haemophilus vaginalis). J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):740–745. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien S., Lewis J. F. Identification of Haemophilus vaginalis. Am J Med Technol. 1969 Mar;35(3):158–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pheifer T. A., Forsyth P. S., Durfee M. A., Pollock H. M., Holmes K. K. Nonspecific vaginitis: role of Haemophilus vaginalis and treatment with metronidazole. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 29;298(26):1429–1434. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806292982601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Van Dyck E. Isolation and identification of Gardnerella vaginalis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1983;40:15–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Van Dyck E., Totten P. A., Holmes K. K. Identification of Gardnerella (Haemophilus) vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):19–24. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.19-24.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnam S., Fitzgerald B. L. Semiquantitative culture of Gardnerella vaginalis in laboratory determination of nonspecific vaginitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):344–347. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.344-347.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer L. G., Reller L. B. Use of a sodium polyanetholesulfonate disk for the identification of Gardnerella vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):146–149. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.146-149.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon S. A., Walker R. D., Carleton C. L., Robinson B. E. Isolation of Gardnerella vaginalis from the reproductive tract of four mares. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1990 Jul;2(3):167–170. doi: 10.1177/104063879000200302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. E., Forsyth M. E., Bowie W. R., Black W. A. Rapid presumptive identification of Gardnerella vaginalis (Haemophilus vaginalis) from human blood agar media. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):108–110. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.108-110.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E., Phillips I. The identification of Gardnerella vaginalis. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Feb;16(1):83–92. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Amsel R., Hale J., Piot P., Holmes K. K. Selective differential human blood bilayer media for isolation of Gardnerella (Haemophilus) vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):141–147. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.141-147.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yong D. C., Thompson J. S. Rapid microbiochemical method for identification of Gardnerella (Haemophilus) vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):30–33. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.30-33.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]