Abstract
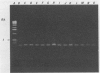
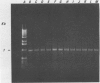
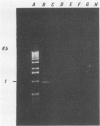
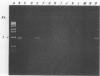
A 1.5-kb Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae 4074 DNA fragment from a genomic library was found to hybridization. No cross-hybridization hybridization. No cross-hybridization was detected with DNAs from hemolytic members of the family Pasteurellaceae. From the nucleotide sequence of the putative genomic probe, three primers were synthesized for use in polymerase chain reactions (PCRs), with 31 strains tested by using purified and crude DNA targets. PCR amplification products of 610 and 985 bp were observed in nucleic acids extracted from the 12 known serotypes and a biotype 2 strain. Template DNAs from other gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, some of them found in the normal flora of swine and the upper respiratory tract, were not amplified by PCR. The only exception was an amplification of a similar 610- or 985-bp sequence in Actinobacillus lignieresii, a species that is closely related to A. pleuropneumoniae but that has never been isolated from swine. Amplification of specific A. pleuropneumoniae sequences by PCR directly from clinical specimens may find applications in the identification of asymptomatic carriers as well as in efforts to eradicate porcine pleuropneumonia.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry T., Powell R., Gannon F. A general method to generate DNA probes for microorganisms. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Mar;8(3):233–236. doi: 10.1038/nbt0390-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K., Neimark H., Rumore P., Steinman C. R. Broad range DNA probes for detecting and amplifying eubacterial nucleic acids. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 1;48(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Nicolet J. Hemolysin patterns of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):232–236. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.232-236.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson A., Biberstein E. L., Hurvell B. Serologic studies on porcine strains of Haemophilus parahaemolyticus (pleuropneumoniae): agglutination reactions. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Aug;38(8):1111–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hance A. J., Grandchamp B., Lévy-Frébault V., Lecossier D., Rauzier J., Bocart D., Gicquel B. Detection and identification of mycobacteria by amplification of mycobacterial DNA. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):843–849. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Ross R. F., Switzer W. P. Incidence of certain microorganisms in nasal cavities of swine in Iowa. Am J Vet Res. 1969 Sep;30(9):1621–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume K., Nagano I., Nakai T. Bacteriological, serological, and pathological examinations of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae infection in 200 slaughtered pigs. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1986 Oct;48(5):965–970. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.48.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume K., Nakai T., Sawata A. Isolation of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae from the nasal cavities of healthy pigs. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1984 Oct;46(5):641–647. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.46.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. H., Gyllensten U. B., Cui X. F., Saiki R. K., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Amplification and analysis of DNA sequences in single human sperm and diploid cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):414–417. doi: 10.1038/335414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J. N., Inzana T. J. Indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibody to a 110,000-molecular-weight hemolysin of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1356–1361. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1356-1361.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., Levesque R., Jacoby G. A. An animal source for the ROB-1 beta-lactamase of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Feb;29(2):212–215. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.2.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Higgins R., Larivière S. Detection of type-specific antigens in the lungs of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae-infected pigs by coagglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1355–1357. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1355-1357.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet J. Sur l'hémophilose du pore. 3. Différenciation sérologique de Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1971;216(4):487–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R., O'Connor P. J. Serological characterization of 8 Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae strains and proposal of a new serotype: serotype 8. Acta Vet Scand. 1984;25(1):96–106. doi: 10.1186/BF03547283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Serological characterization of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae (Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae) strains and proposal of a new serotype: serotype 10. Acta Vet Scand. 1985;26(4):581–585. doi: 10.1186/BF03546528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Serological characterization of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae (Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae) strains and proposal of a new serotype: serotype 9. Acta Vet Scand. 1985;26(4):501–512. doi: 10.1186/BF03546522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Serology of Haemophilus (Actinobacillus) pleuropneumoniae serotype 5 strains: establishment of subtypes a and b. Acta Vet Scand. 1986;27(1):49–58. doi: 10.1186/BF03548558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli after polymerase chain reaction amplification with a thermostable DNA polymerase. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):261–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.261-265.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pijoan C., Morrison R. B., Hilley H. D. Dilution technique for isolation of Haemophilus from swine lungs collected at slaughter. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):143–145. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.143-145.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Boyd D. A. Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotyping. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):840–843. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.840-843.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOPE R. E. PORCINE CONTAGIOUS PLEUROPNEUMONIA. I. EXPERIMENTAL TRANSMISSION, ETIOLOGY, AND PATHOLOGY. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:357–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebunya T. N., Saunders J. R. Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae infection in swine: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1983 Jun 15;182(12):1331–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Hedge P. J., te Heesen S., Edelman A., Broome-Smith J. K. Kanamycin-resistant vectors that are analogues of plasmids pUC8, pUC9, pEMBL8 and pEMBL9. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnbach M. N., Falkow S., Tompkins L. S. Species-specific detection of Legionella pneumophila in water by DNA amplification and hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1257–1261. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1257-1261.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. B., Gold L. Overproduction of bacteriophage Q beta maturation (A2) protein leads to cell lysis. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]