Abstract
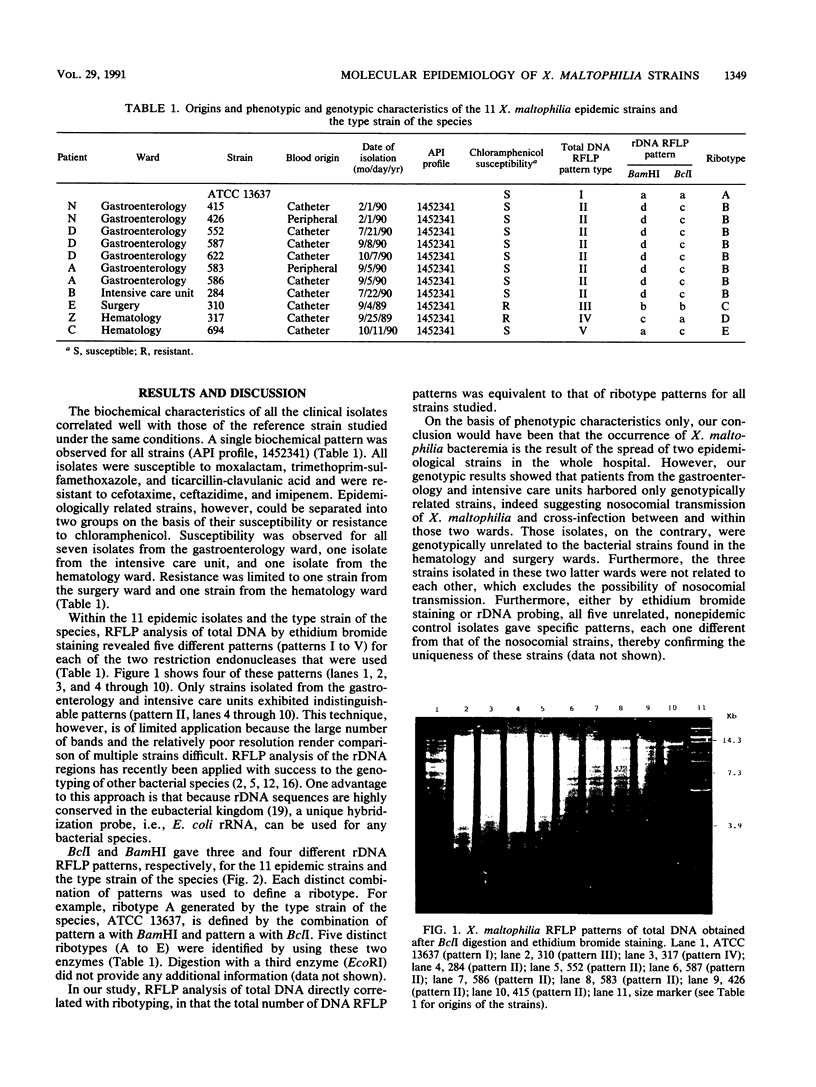
Restriction fragment length polymorphisms of total DNA and rDNA were used to study the relationship between 11 isolates of Xanthomonas maltophilia, obtained from seven patients with nosocomial bacteremia in four distinct wards of a single hospital, and the type strain of the species, ATCC 13637. Our results indicated that there were episodes of cross-infection among the patients of two wards, but there were also independent infectious episodes in the two other wards.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elting L. S., Khardori N., Bodey G. P., Fainstein V. Nosocomial infection caused by Xanthomonas maltophilia: a case-control study of predisposing factors. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1990 Mar;11(3):134–138. doi: 10.1086/646136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M. C., Long S. S., Roberts E. M., Dunn J. M., Balsara R. K. Pseudomonas maltophilia bacteremia in children undergoing open heart surgery. JAMA. 1981 Oct 2;246(14):1571–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakoyiannis C. K., Winter P. J., Marshall R. B. Identification of Campylobacter coli isolates from animals and humans by bacterial restriction endonuclease DNA analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):545–549. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.545-549.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall W. F., Keating M. R., Anhalt J. P., Steckelberg J. M. Xanthomonas maltophilia: an emerging nosocomial pathogen. Mayo Clin Proc. 1989 Sep;64(9):1097–1104. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)64979-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClenaghan M., Herring A. J., Aitken I. D. Comparison of Chlamydia psittaci isolates by DNA restriction endonuclease analysis. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):384–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.384-389.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A. J., Jr, Hoffmann K. K., Wenzel R. P. Associated mortality and clinical characteristics of nosocomial Pseudomonas maltophilia in a university hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):52–55. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.52-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M., Davis G. H. Enzymatic profile of Pseudomonas maltophilia. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):417–421. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.417-421.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle J. W., Janda J. M., Woods D. E., Vasil M. L. Characterization and use of a DNA probe as an epidemiological marker for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):119–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard-Pasquier N., Ouagued M., Picard B., Goullet P., Krishnamoorthy R. A simple, sensitive method of analyzing bacterial ribosomal DNA polymorphism. Electrophoresis. 1989 Mar;10(3):186–189. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schable B., Rhoden D. L., Hugh R., Weaver R. E., Khardori N., Smith P. B., Bodey G. P., Anderson R. L. Serological classification of Xanthomonas maltophilia (Pseudomonas maltophilia) based on heat-stable O antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):1011–1014. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.1011-1014.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semel J. D., Trenholme G. M., Harris A. A., Jupa J. E., Levin S. Pseudomonas maltophilia pseudosepticemia. Am J Med. 1978 Mar;64(3):403–406. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishart M. M., Riley T. V. Infection with Pseudomonas maltophilia hospital outbreak due to contaminated disinfectant. Med J Aust. 1976 Nov 6;2(19):710–712. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1976.tb128238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuravleff J. J., Yu V. L. Infections caused by Pseudomonas maltophilia with emphasis on bacteremia: case reports and a review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):1236–1246. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.6.1236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]