Abstract
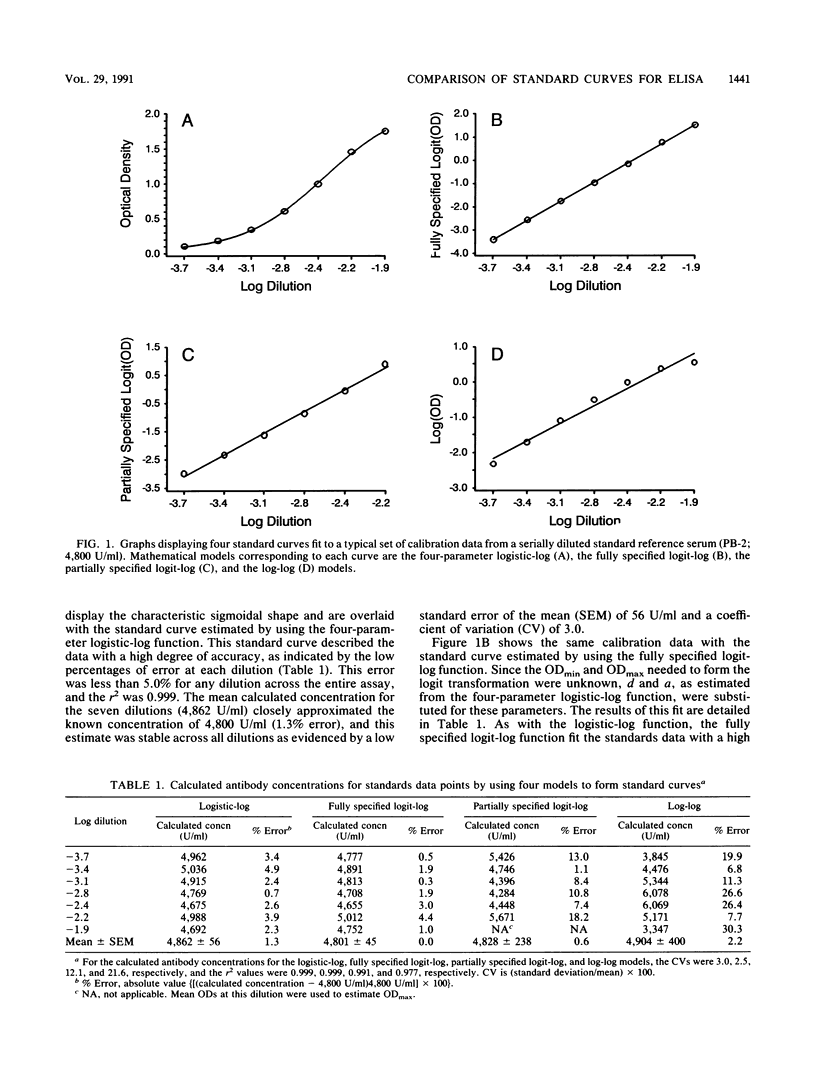
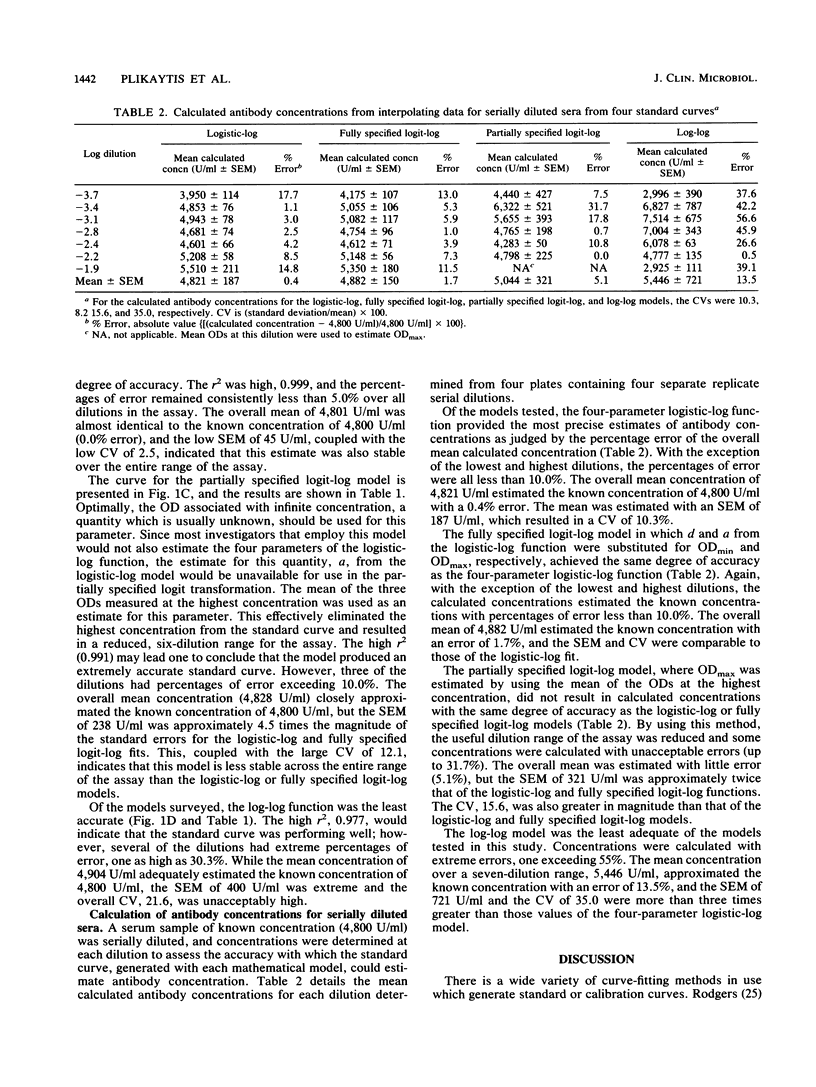
We examined several of the more commonly used models (log-log, two forms of the logit-log, and the four-parameter logistic-log transformations) for forming standard or calibration curves by using a standardized enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Assay range, accuracy, and error for each function were measured and compared. Antibody levels to Neisseria meningitidis group A polysaccharide were estimated by calculating antibody concentrations of a serially diluted standard reference serum of known concentration. Each function achieved a high squared correlation coefficient (r2 greater than 0.97), indicating a high degree of accuracy in forming the standard curves. However, when predicted antibody concentrations were compared with the known values, the log-log function exhibited the least precision, with extreme percentages of error occurring at several dilutions. A partially specified logit-log transformation performed better than the log-log model over a reduced range of standard dilutions. This indicated that a high r2 alone was not a reliable measure of the accuracy of the standard curve. Of the methods surveyed, the logistic-log and fully specified logit-log functions were the most accurate models for forming standard curves and for interpolating antibody concentrations from the standard curve. The accuracy of the fully specified logit-log function is highly dependent on the precise specification of two unknown quantities, the optical densities at zero and infinite concentrations, prior to fitting the model to a typical set of calibration data. The four-parameter logistic-log function was the preferred choice for quantitating N. meningitidis group A total polysaccharide antibody by using a standardized ELISA. The function does not require prespecification of any parameters before estimating the standard curve, and the four parameters are readily interpretable in terms of identifiable physical quantities. This model also has the advantage that it is easiest to visualize since it does not incorporate complex transformations of the optical density scale.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beuvery E. C., Kayhty M. H., Leussink A. B., Kanhai V. Comparison of radioimmunoassay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in measurement of antibodies to Neisseria meningitidis group A capsular polysaccharide. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):672–676. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.672-676.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuvery E. C., Leussink A. B., Van Delft R. W., Tiesjema R. H., Nagel J. Immunoglobulin M and G antibody responses and persistence of these antibodies in adults after vaccination with a combined meningococcal group A and group C polysaccharide vaccine. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):579–585. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.579-585.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black C. M., Plikaytis B. D., Wells T. W., Ramirez R. M., Carlone G. M., Chilmonczyk B. A., Reimer C. B. Two-site immunoenzymometric assays for serum IgG subclass infant/maternal ratios at full-term. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Jan 21;106(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boctor F. N., Barka N. E., Agopian M. S. Quantitation of IgG antibody to Streptococcus pneumoniae vaccine by ELISA and FAST-ELISA using tyraminated antigen. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jun 21;120(2):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canellas P. F., Karu A. E. Statistical package for analysis of competition ELISA results. J Immunol Methods. 1981;47(3):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattom A., Lue C., Szu S. C., Mestecky J., Schiffman G., Bryla D., Vann W. F., Watson D., Kimzey L. M., Robbins J. B. Serum antibody response in adult volunteers elicited by injection of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 12F polysaccharide alone or conjugated to diphtheria toxoid. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2309–2312. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2309-2312.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney D. J. Radioligand Assay. Biometrics. 1976 Dec;32(4):721–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guardabasso V., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. A versatile method for simultaneous analysis of families of curves. FASEB J. 1988 Mar 1;2(3):209–215. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.3.3350235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guardabasso V., Rodbard D., Munson P. J. A model-free approach to estimation of relative potency in dose-response curve analysis. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 1):E357–E364. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.3.E357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpinski K. F., Hayward S., Tryphonas H. Statistical considerations in the quantitation of serum immunoglobulin levels using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). J Immunol Methods. 1987 Nov 5;103(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90289-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortlandt W., Endeman H. J., Hoeke J. O. A three-parameter Langmuir-type model for fitting standard curves of sandwich enzyme immunoassays with special attention to the alpha-fetoprotein assay. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):5–10. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plikaytis B. D., Carlone G. M., Edmonds P., Mayer L. W. Robust estimation of standard curves for protein molecular weight and linear-duplex DNA base-pair number after gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):346–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90420-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. G., Nickerson J. M., Fuller G. M. Two simple programs for the analysis of data from enzyme-linked immunosorbent (ELISA) assays on a programmable desk-top calculator. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 15;110(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Bridson W., Rayford P. L. Rapid calculation of radioimmunoassay results. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Nov;74(5):770–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Lewald J. E. Computer analysis of radioligand assay and radioimmunoassay data. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1970;147:79–103. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.065s079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D. Statistical quality control and routine data processing for radioimmunoassays and immunoradiometric assays. Clin Chem. 1974 Oct;20(10):1255–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiede J. J., Pagano M. The application of robust calibration to radioimmunoassay. Biometrics. 1979 Sep;35(3):567–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


