Abstract
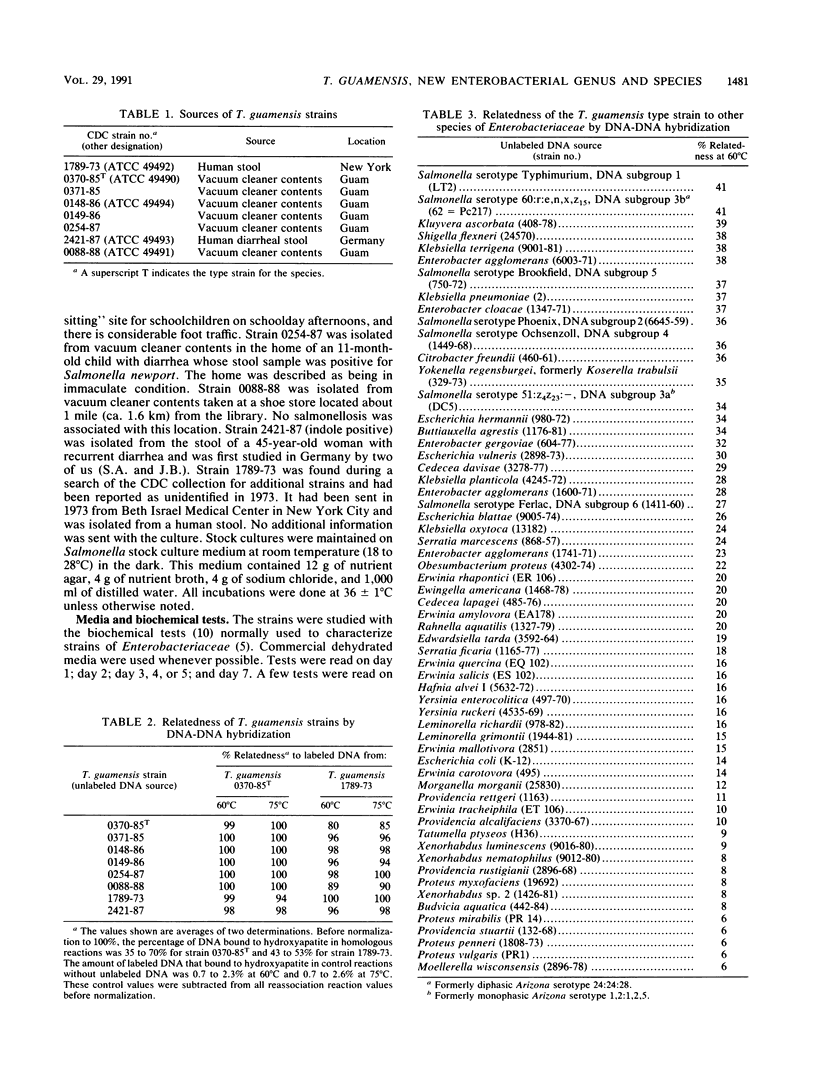
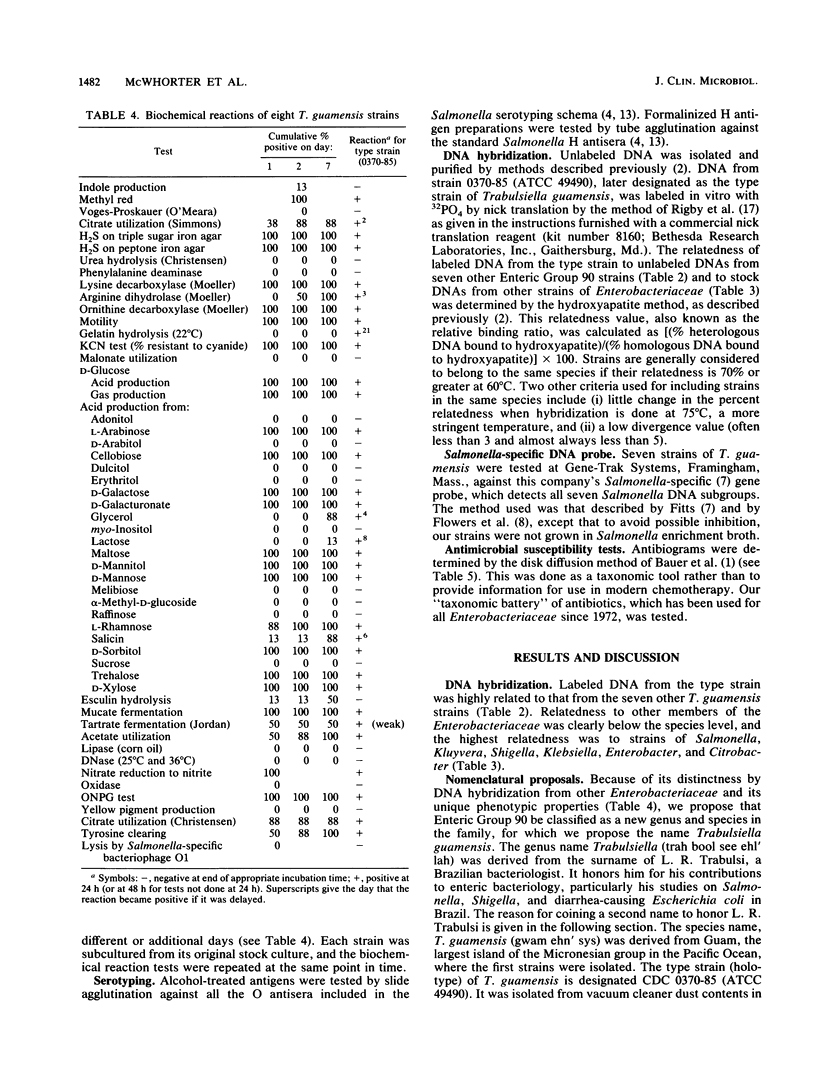
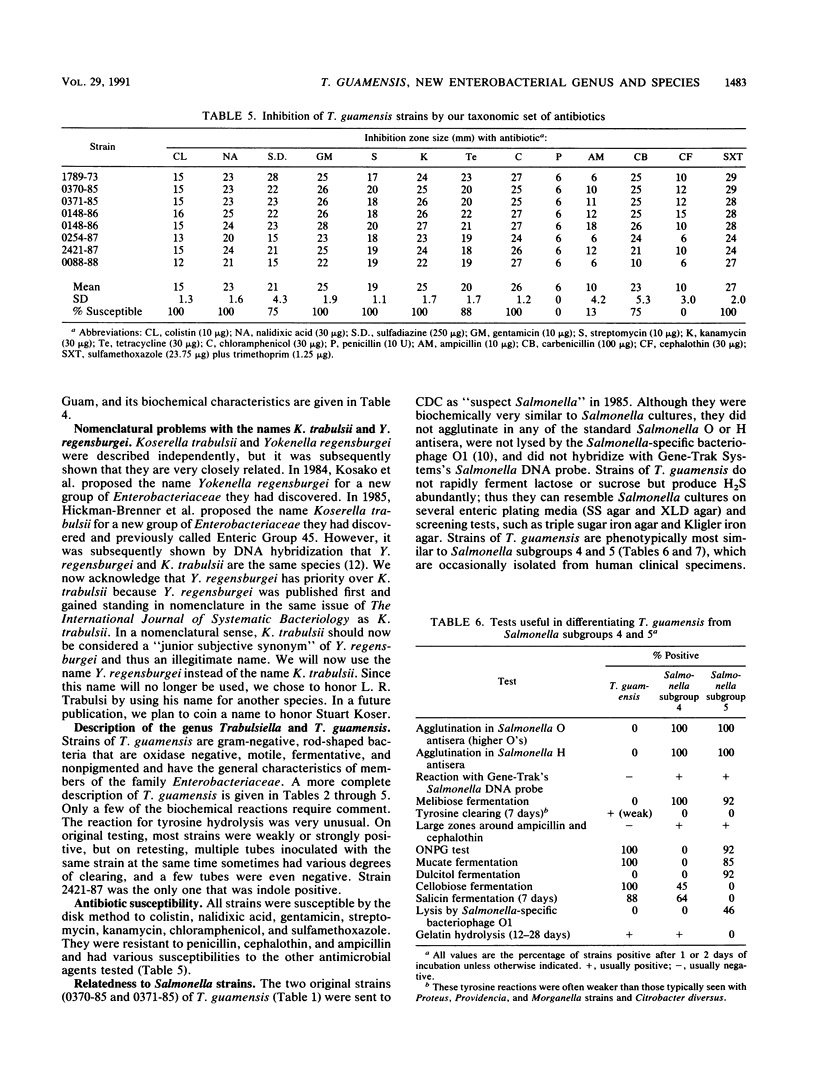
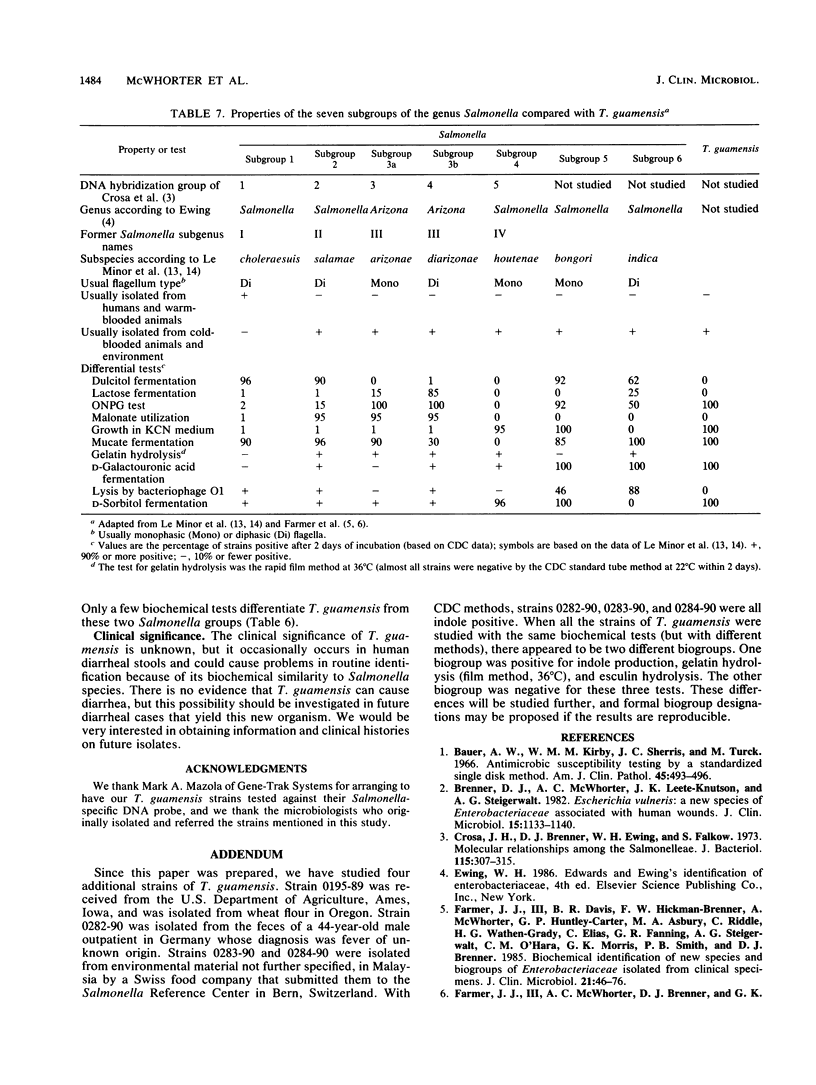
In 1985 the vernacular name Enteric Group 90 was coined for a small group of strains that had been referred to our laboratory as probable strains of Salmonella but did not agglutinate in Salmonella typing antisera. By DNA-DNA hybridization (hydroxyapatite method, 32P), seven strains of Enteric Group 90 were found to be closely related (98 to 100% at 60 degrees C and 94 to 100% at 75 degrees C) to the first strain received (0370-85). The relatedness of Enteric Group 90 to 62 strains of other species of the family Enterobacteriaceae was only 6 to 41%, with the highest values obtained with strains of Salmonella, Kluyvera, Shigella, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, and Citrobacter. We propose a new genus, Trabulsiella, with a single new species, Trabulsiella guamensis, for the highly related group of eight strains formerly known as Enteric Group 90. The type strain is designated ATCC 49490 (CDC 0370-85). T. guamensis strains grew well at 36 degrees C and had positive reactions in the following tests: methyl red, citrate utilization (Simmons) (38% positive at day 1, 88% positive at 2 days), H2S production, lysine decarboxylase, arginine dihydrolase (50% positive at 2 days, 100% positive at 7 days), ornithine decarboxylase, motility, growth in KCN medium, mucate fermentation, acetate utilization, nitrate reduction to nitrite, weak tyrosine hydrolysis (88% positive at 2 days, 100% positive at 7 days), and ONPG (o-nitrophenyl-beta-D-galactopyranoside) test. The strains fermented D-glucose with gas production and fermented L-arabinose, cellobiose, D-galactose, D-galacturonate, maltose, D-mannitol, D-mannose, L-rhamnose, D-sorbitol, trehalose, and D-xylose. T. guamensis strains had negative reactions in the following tests: indole production (13% positive), Voges-Proskauer, urea hydrolysis, phenylalanine deaminase, malonate utilization, lipase (corn oil), DNase, oxidase, pigment production, and acid production from adonitol, D-arabitol, dulcitol, erythritol, myo-inositol, melibiose, alpha-methyl-D-glucoside, raffinose, and sucrose. There were delayed positive reactions for gelatin liquefaction (22 degrees C), which was positive at 12 to 23 days, esculin hydrolysis (13% positive at day 1, 50% positive at 7 days), lactose fermentation (13% positive at 3 to 7 days, 100% positive at 8 to 10 days), glycerol fermentation (88% positive at 7 days), and salicin fermentation (13% positive at day 1, 88% positive at 7 days). All strains were susceptible by the disk diffusion method to colistin, nalidixic acid, gentamicin, streptomycin, kanamycin, chloramphenicol, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and most strains were susceptible to sulfadiazine (75% susceptible), tetracycline (88%), and carbenicillin (75%). The strains were resistant to penicillin, cephalothin, and ampicillin. The strains were isolated from vacuum cleaner dust (five strains), soil (one strain), and human feces (two strains). Although T. guamensis can occur in human diarrheal stools, there is no evidence that it actually causes diarrhea. Its main interest to clinical microbiologists may be its possible misidentification as a strain Salmonella.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., McWhorter A. C., Knutson J. K., Steigerwalt A. G. Escherichia vulneris: a new species of Enterobacteriaceae associated with human wounds. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1133-1140.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Brenner D. J., Ewing W. H., Falkow S. Molecular relationships among the Salmonelleae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):307–315. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.307-315.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Davis B. R., Hickman-Brenner F. W., McWhorter A., Huntley-Carter G. P., Asbury M. A., Riddle C., Wathen-Grady H. G., Elias C., Fanning G. R. Biochemical identification of new species and biogroups of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):46–76. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.46-76.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddock R. L., Malilay J. A search for infant salmonellosis risk factors on Guam. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1986 Mar;17(1):38–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., Huntley-Carter G. P., Fanning G. R., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Koserella trabulsii, a new genus and species of Enterobacteriaceae formerly known as Enteric Group 45. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):39–42. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.39-42.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman F. W., Farmer J. J., 3rd Salmonella typhi: identification, antibiograms, serology, and bacteriophage typing. Am J Med Technol. 1978 Dec;44(12):1149–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor L., Popoff M. Y., Laurent B., Hermant D. Individualisation d'une septième sous-espèce de Salmonella: S. choleraesuis subsp. indica subsp. nov. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor L., Véron M., Popoff M. Taxonomie des Salmonella. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Sep-Oct;133(2):223–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



