Abstract
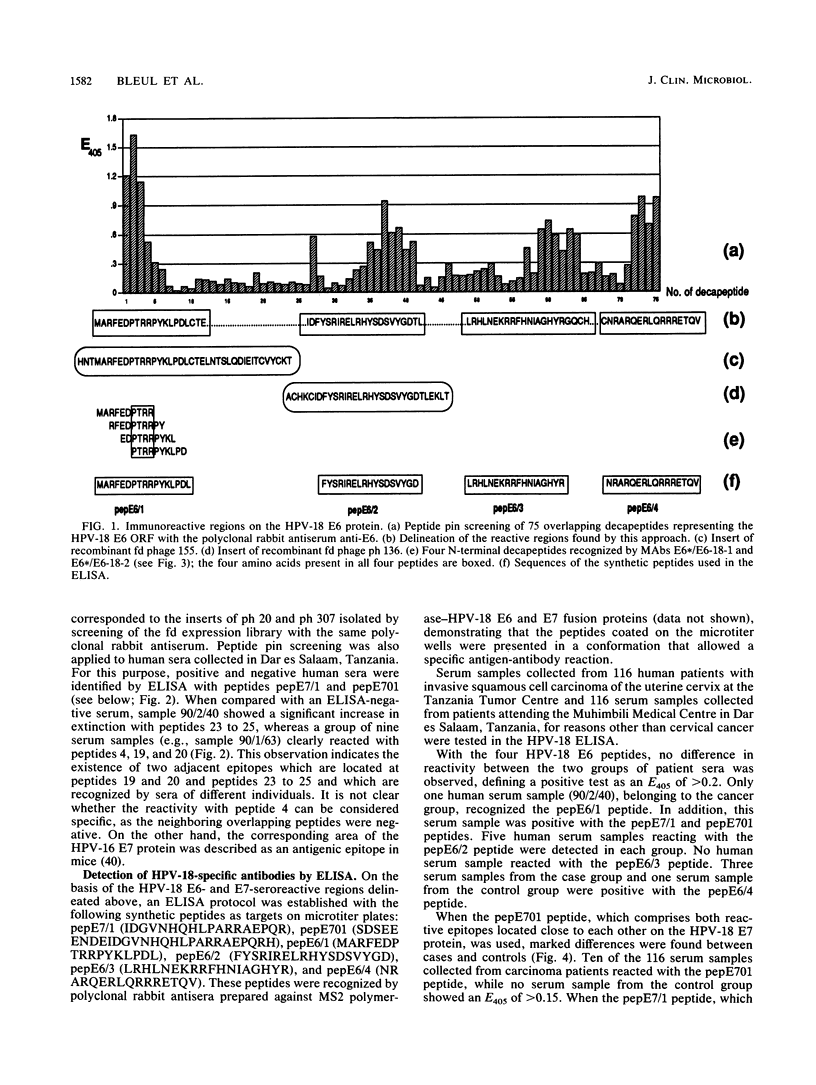
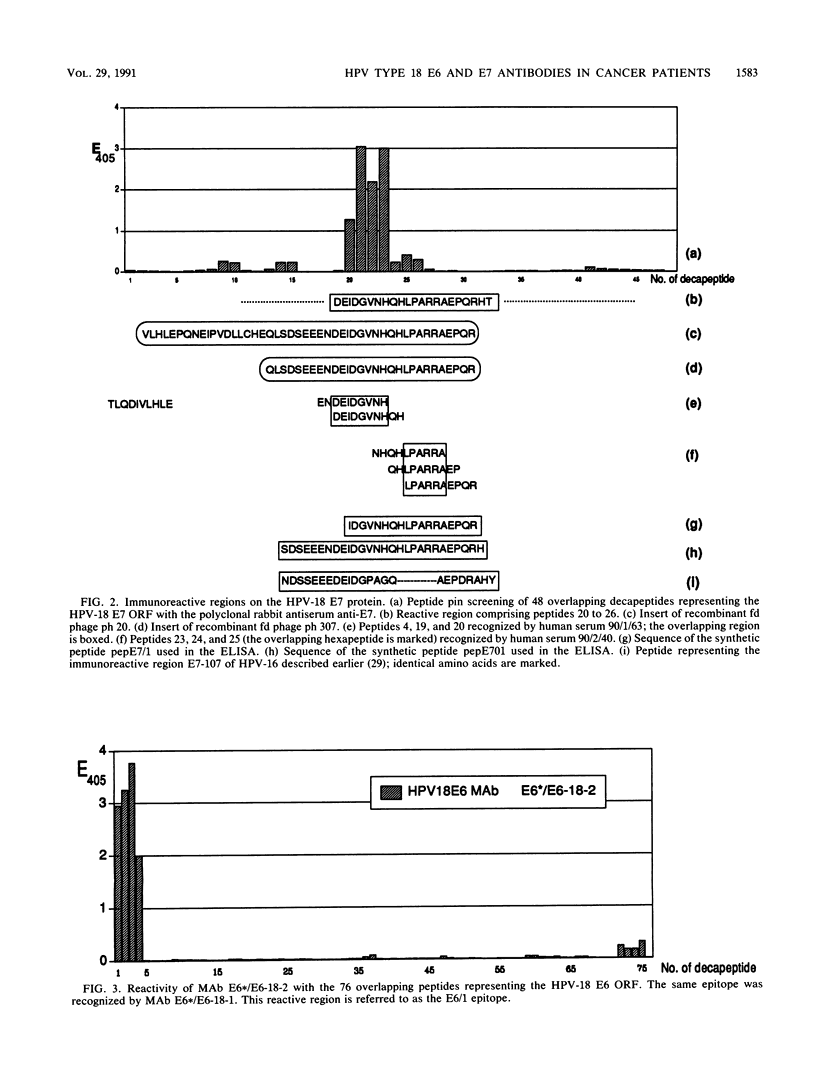
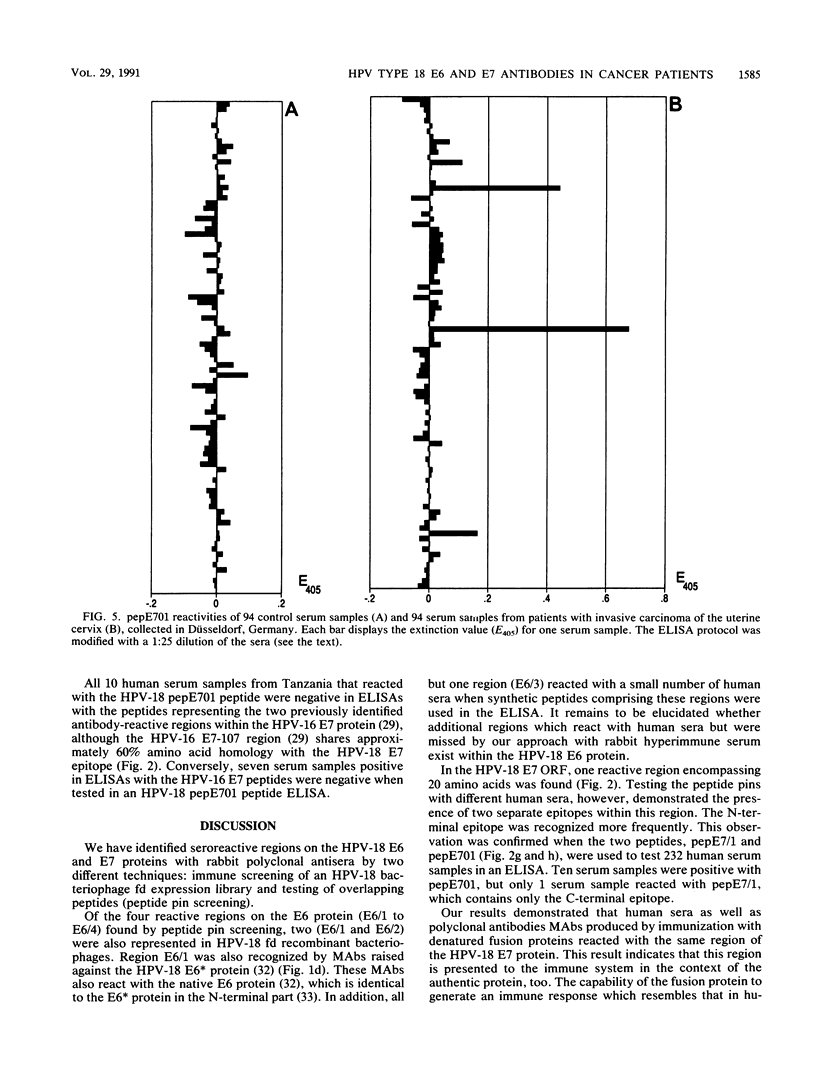
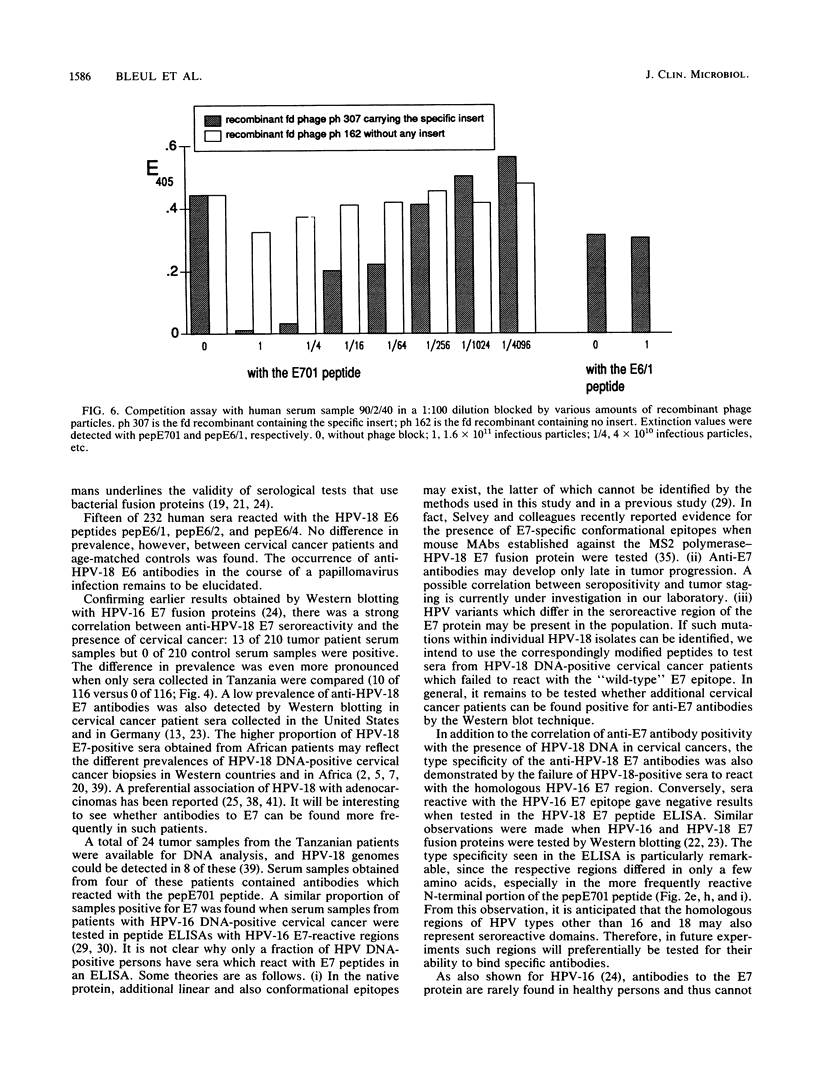
Antibody-reactive regions on the human papillomavirus type 18 (HPV-18) E6 and E7 proteins were identified with rabbit polyclonal anti-fusion protein sera by screening of an fd phage expression library containing subgenomic HPV-18 DNA fragments and by testing of overlapping decapeptides representing the E6 and E7 open reading frames. Peptides comprising the delineated regions (designated E6/1 to E6/4 and E7/1) were synthesized and used in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect anti-HPV-18 antibodies in human sera. A total of 232 human serum samples (identical numbers of cervical cancer patients and age-matched controls) collected in Tanzania were tested. Similar prevalences (between 0.8 and 4.3%) of antibodies recognizing the different E6 peptides were found in the sera from tumor patients and controls. With a synthetic 28-mer peptide (designated pepE701) comprising the E7/1 region, a significant difference was found: 10 of 116 tumor serum samples but 0 of 116 control serum samples showed a specific reaction (P less than 0.001). This observation confirms earlier results with HPV-16 E7 fusion proteins (I. Jochmus-Kudielka, A. Schneider, R. Braun, R. Kimmig, U. Koldovsky, K. E. Schneweis, K. Seedorf, and L. Gissmann, J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 81:1698-1704, 1989). A lower prevalence of anti-HPV-18 E7 antibodies was observed when 188 human serum samples collected in Germany from tumor patients and controls were tested (3 of 94 positive in the cancer group; 0 of 94 positive in the control group). The type specificity of anti-HPV-18 E7 antibodies was demonstrated when the HPV type found by Southern hybridization in the cervical cancer biopsies was compared with seroreactivity: 4 of 8 serum samples obtained from HPV-18 DNA-positive but 0 of 16 serum samples from HPV-18 DNA-negative tumor patients reacted in the HPV-18 E7 ELISA. In addition, HPV-18-positive sera failed to react in a peptide ELISA with the homologous HPV-16 E7 region (M. Müller, H. Gausepohl, G. de Martinoff, R. Frank, R. Brasseur, and L. Gissmann, J. Gen. Virol. 71:2709-2717, 1990) and vice versa.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes W., Delgado G., Kurman R. J., Petrilli E. S., Smith D. M., Ahmed S., Lorincz A. T., Temple G. F., Jenson A. B., Lancaster W. D. Possible prognostic significance of human papillomavirus type in cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 1988 Mar;29(3):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0090-8258(88)90225-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor M. E., Stern P. L. Loss of MHC class-I expression in cervical carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1990 Dec 15;46(6):1029–1034. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910460614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover W. J., Salsburg D. S. Locally most powerful tests for detecting treatment effects when only a subset of patients can be expected to "respond" to treatment. Biometrics. 1988 Mar;44(1):189–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czeglédy J., Gergely L., Hernádi Z., Póka R. Detection of human papillomavirus deoxyribonucleic acid in the female genital tract. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1989;178(6):309–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00197449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Dillner L., Robb J., Willems J., Jones I., Lancaster W., Smith R., Lerner R. A synthetic peptide defines a serologic IgA response to a human papillomavirus-encoded nuclear antigen expressed in virus-carrying cervical neoplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3838–3841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Dillner L., Utter G., Eklund C., Rotola A., Costa S., DiLuca D. Mapping of linear epitopes of human papillomavirus type 16: the L1 and L2 open reading frames. Int J Cancer. 1990 Mar 15;45(3):529–535. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Barteling S. J., Meloen R. H. Small peptides induce antibodies with a sequence and structural requirement for binding antigen comparable to antibodies raised against the native protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):178–182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Meloen R. H., Barteling S. J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höpfl R., Sandbichler M., Sepp N., Heim K., Müller-Holzner E., Wartusch B., Dapunt O., Jochmus-Kudielka I., ter Meulen J., Gissmann L. Skin test for HPV type 16 proteins in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Lancet. 1991 Feb 9;337(8737):373–374. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91014-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenison S. A., Firzlaff J. M., Langenberg A., Galloway D. A. Identification of immunoreactive antigens of human papillomavirus type 6b by using Escherichia coli-expressed fusion proteins. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2115–2123. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2115-2123.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenison S. A., Yu X. P., Valentine J. M., Koutsky L. A., Christiansen A. E., Beckmann A. M., Galloway D. A. Evidence of prevalent genital-type human papillomavirus infections in adults and children. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):60–69. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jochmus-Kudielka I., Schneider A., Braun R., Kimmig R., Koldovsky U., Schneweis K. E., Seedorf K., Gissmann L. Antibodies against the human papillomavirus type 16 early proteins in human sera: correlation of anti-E7 reactivity with cervical cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Nov 15;81(22):1698–1704. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.22.1698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L. A., Tase T., Twiggs L. B., Okagaki T., Savage J. E., Adcock L. L., Prem K. A., Carson L. F. Prognostic significance of the presence of human papillomavirus DNA in patients with invasive carcinoma of the cervix. Cancer. 1989 Mar 1;63(5):897–900. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890301)63:5<897::aid-cncr2820630517>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorincz A. T., Temple G. F., Kurman R. J., Jenson A. B., Lancaster W. D. Oncogenic association of specific human papillomavirus types with cervical neoplasia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Oct;79(4):671–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons L. B., Zinder N. D. The genetic map of the filamentous bacteriophage f1. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):45–60. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Gausepohl H., de Martynoff G., Frank R., Brasseur R., Gissmann L. Identification of seroreactive regions of the human papillomavirus type 16 protein E4, E6, E7 and L1. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2709–2717. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmley S. F., Smith G. P. Antibody-selectable filamentous fd phage vectors: affinity purification of target genes. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):305–318. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90495-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Schwarz E. Different human cervical carcinoma cell lines show similar transcription patterns of human papillomavirus type 18 early genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2285–2292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Oltersdorf T., Krämmer G., Röwekamp W. Identification of early proteins of the human papilloma viruses type 16 (HPV 16) and type 18 (HPV 18) in cervical carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):139–144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04731.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvey L. A., Tindle R. W., Geysen H. M., Haller C. J., Smith J. A., Frazer I. H. Identification of B-epitopes in the human papillomavirus 18 E7 open reading frame protein. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3105–3110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirasawa H., Tomita Y., Sekiya S., Takamizawa H., Simizu B. Integration and transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 and 18 sequences in cell lines derived from cervical carcinomas. J Gen Virol. 1987 Feb;68(Pt 2):583–591. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-2-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Filamentous fusion phage: novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1315–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.4001944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Berek J. S., Fu Y. S., Hacker N. F., Major F. J., Wettstein F. O. Human papillomavirus deoxyribonucleic acid in adenocarcinoma and adenosquamous carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Aug;68(2):241–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindle R. W., Smith J. A., Geysen H. M., Selvey L. A., Frazer I. H. Identification of B epitopes in human papillomavirus type 16 E7 open reading frame protein. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jun;71(Pt 6):1347–1354. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-6-1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J., Bloss J. D., Liao S. Y., Berman M., Bergen S., Wilczynski S. P. Human papillomavirus genotype as a prognostic indicator in carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Nov;74(5):781–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B. Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli: bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee C., Krishnan-Hewlett I., Baker C. C., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. Presence and expression of human papillomavirus sequences in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):361–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacher A. N., 3rd, Stock C. A., Golden J. W., 2nd, Smith G. P. A new filamentous phage cloning vector: fd-tet. Gene. 1980 Apr;9(1-2):127–140. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Papillomaviruses in anogenital cancer as a model to understand the role of viruses in human cancers. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4677–4681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


