Abstract
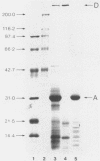
The protein antigens A and D were purified from culture filtrates and sonic extracts of laboratory strains of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis by salt precipitation and chromatography. The characterization of antigen A is shown here, and both antigens were evaluated along with lipoarabinomannan antigen in indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) for the serodiagnosis of ovine paratuberculosis. After anion-exchange (DEAE-5PW) and hydrophobic (phenyl-5PW) chromatography using high-performance liquid chromatography, antigen A showed a prominant band in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) at 31 kDa with small amounts of low-molecular-mass proteins but with no evidence of antigen D. A single precipitin arc was evident with purified antigen A in crossed immunoelectrophoresis. The determination of the N-terminal amino acid sequence showed a high degree of homology between the 31-kDa component of antigen A and antigens of the BCG85 complex of Mycobacterium bovis BCG, a total of 24 of 26 residues being identical to those of BCG85C. A prominant SDS-PAGE band at 400 kDa and a single crossed-immunoelectrophoresis arc was also evident for antigen D after gel filtration (Sephacryl S-200), anion-exchange (DEAE-Sephacel), and concanavalin A-Sepharose affinity chromatography. By ELISA, purified antigen A detected antibody in the sera of 18 of 22 paratuberculosis-infected sheep (82% sensitivity), whereas the purified antigen D detected antibody in all 22 infected animals (100% sensitivity). Combined ELISA results showed increased specificity with some loss in sensitivity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas B., Riemann H. P., Lonnerdal B. Isolation of specific peptides from Mycobacterium paratuberculosis protoplasm and their use in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of paratuberculosis (Johne's disease) in cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Dec;44(12):2229–2236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S. Coupling of enzymes to proteins with glutaraldehyde. Use of the conjugates for the detection of antigens and antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlough J. E., Jacobson R. H., Downing D. R., Lynch T. J., Scott F. W. The kinetics-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for coronavirus antibodies in cats: calibration to the indirect immunofluorescence assay and computerized standardization of results through normalization to control values. Can J Vet Res. 1987 Jan;51(1):56–59. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. W., Robertson R. H., Corner A. H., Samagh B. S., Garcia M. M., Turcotte C., Duncan J. R. Evaluation of the serological response of sheep in one flock to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Apr;52(2):199–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. W., Young N. M., Watson D. C., Robertson R. H., Sugden E. A., Nielsen K. H., Becker S. A. Mycobacterium paratuberculosis antigen D: characterization and evidence that it is a bacterioferritin. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Aug;29(8):1652–1658. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.8.1652-1658.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S. Ruminant paratuberculosis (Johne's disease): the current status and future prospects. Cornell Vet. 1984 Jul;74(3):218–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz G. A., Wayne L. G. Isolation and characterization of catalase produced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Sep;110(3):312–319. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.3.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe M., Wiker H. G., Duncan J. R., Garcia M. M., Dukes T. W., Brooks B. W., Turcotte C., Nagai S. Protein G-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for anti-MPB70 antibodies in bovine tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):913–921. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.913-921.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy M. R., Townsend R. R., Lee Y. C. Monosaccharide analysis of glycoconjugates by anion exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection. Anal Biochem. 1988 Apr;170(1):54–62. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90089-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden E. A., Corner A. H., Samagh B. S., Brooks B. W., Turcotte C., Nielsen K. H., Stewart R. B., Duncan J. R. Serodiagnosis of ovine paratuberculosis, using lipoarabinomannan in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Jun;50(6):850–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden E. A., Samagh B. S., Bundle D. R., Duncan J. R. Lipoarabinomannan and lipid-free arabinomannan antigens of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):762–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.762-770.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiker H. G., Harboe M., Lea T. E. Purification and characterization of two protein antigens from the heterogeneous BCG85 complex in Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;81(4):298–306. doi: 10.1159/000234153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiker H. G., Harboe M., Nagai S., Patarroyo M. E., Ramirez C., Cruz N. MPB59, a widely cross-reacting protein of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;81(4):307–314. doi: 10.1159/000234154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiker H. G., Sletten K., Nagai S., Harboe M. Evidence for three separate genes encoding the proteins of the mycobacterial antigen 85 complex. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):272–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.272-274.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. F., Kelly W. A., Gall D. E. Application of a timing protocol to the reduction of inter-plate variability in the indirect enzyme immunoassay for detection of anti-Brucella antibody. J Immunoassay. 1985;6(3):189–205. doi: 10.1080/01971528508063029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokomizo Y., Merkal R. S., Lyle P. A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of bovine immunoglobulin G1 antibody to a protoplasmic antigen of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Nov;44(11):2205–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]