Abstract
Rotavirus is the most important worldwide cause of severe gastroenteritis. Extensive efforts have been devoted to the design of a vaccine that will prevent disease, but development of a more effective vaccine strategy may require progress in the understanding of the mucosal immune response to replicating viral antigens. In this article, we report the characterization of the intestinal antibody response of a murine model to heterologous infection with the rhesus rotavirus vaccine strain. We have adapted the enzyme-linked immunospot assay to measure this response without the difficulties associated with measurement of antibodies in intestinal contents or the artifacts associated with culturing of lymphocytes. The predominant response in terms of antibody-secreting cells (ASC) is seen in the small intestine lamina propria, which can be measured within 4 days of infection, peaks 3 weeks after infection, and remains near that level for longer than 8 weeks. The magnitude of the immunoglobulin A (IgA) cell response is approximately 10 times greater than the intestinal IgG cell response, and IgM cells are rare. Virus-specific ASC constitute approximately 50% of all ASC in the gut at the peak of the virus-specific response. This response is considerably greater than responses to nonreplicating mucosal antigens measured by similar techniques. Enteral infection engenders minimal virus-specific ASC response in the spleen. Rhesus rotavirus-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and neutralization assays of serum and intestinal contents did not correlate with virus-specific ASC response.
Full text
PDF


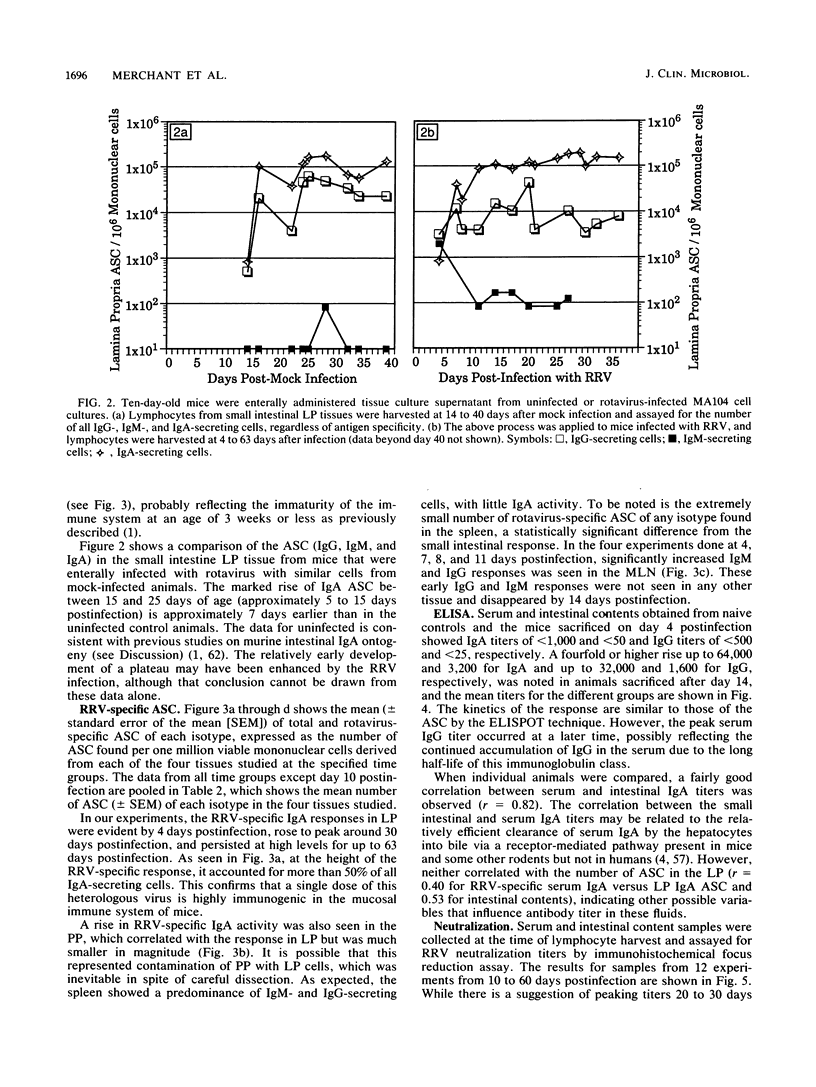
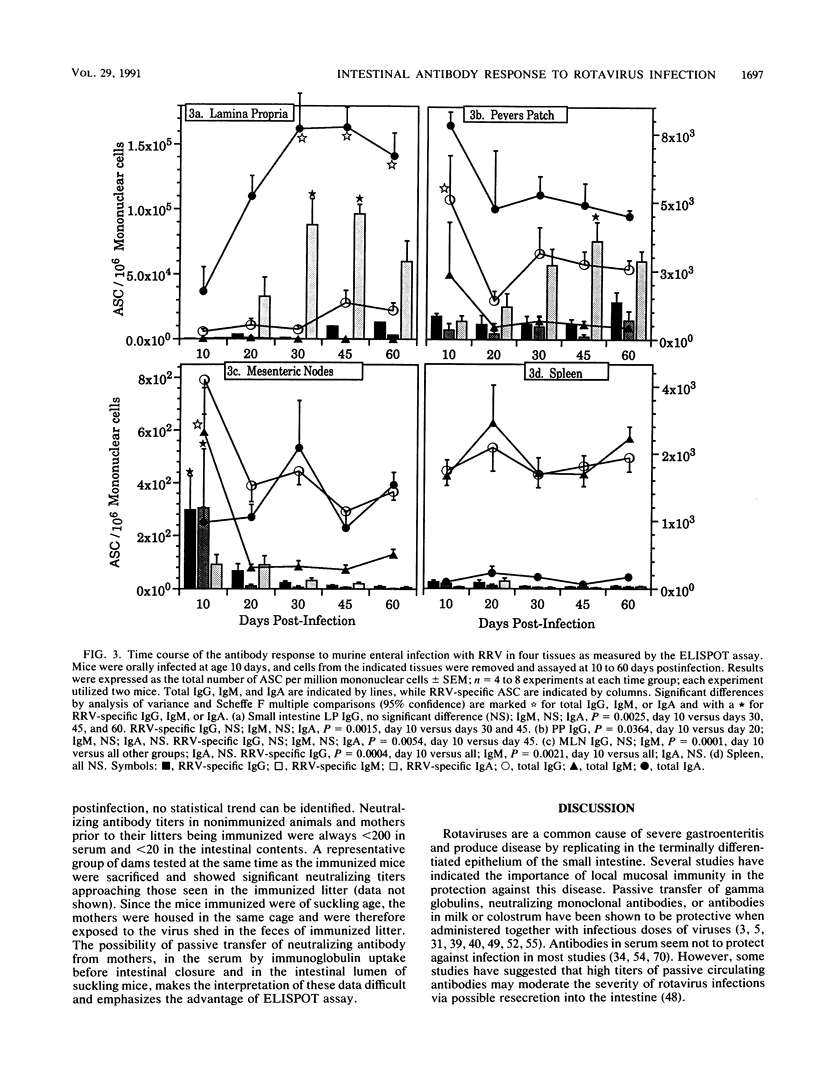
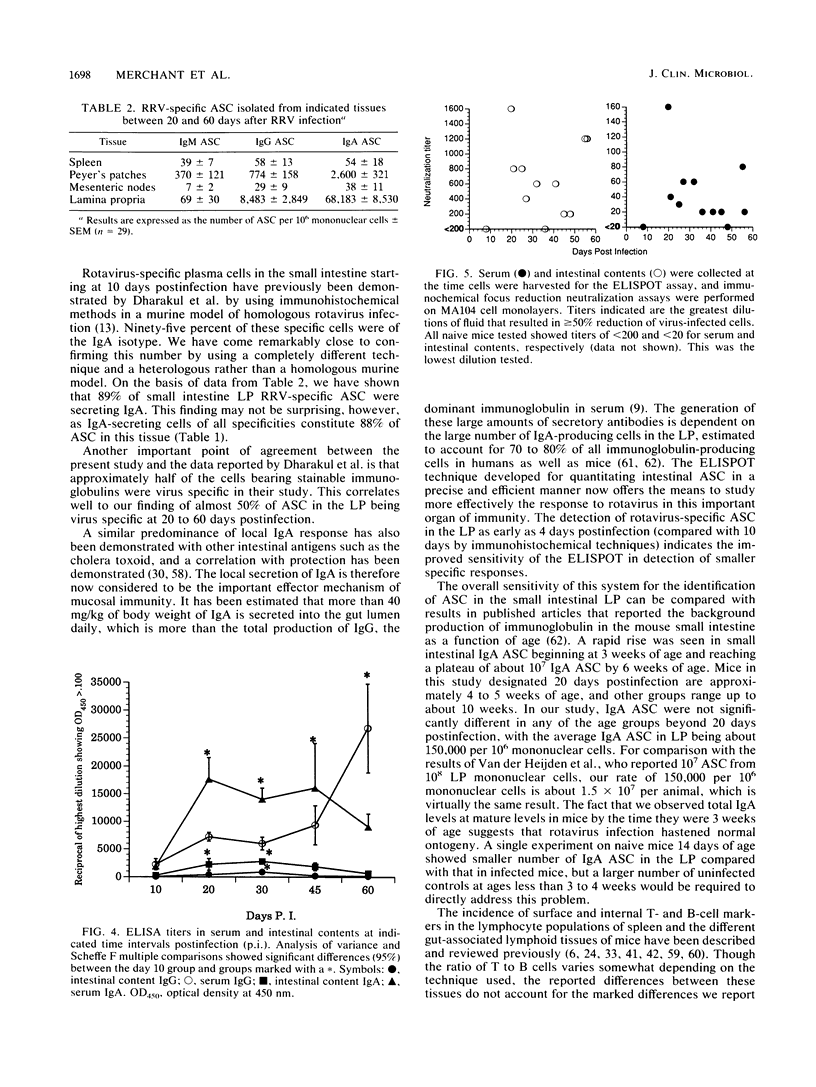



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleby P., Catty D. Transmission of immunoglobulin to foetal and neonatal mice. J Reprod Immunol. 1983 Jul;5(4):203–213. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(83)90236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein D. I., McNeal M. M., Schiff G. M., Ward R. L. Induction and persistence of local rotavirus antibodies in relation to serum antibodies. J Med Virol. 1989 Jun;28(2):90–95. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890280207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Kloppel T. M. The liver and IgA: immunological, cell biological and clinical implications. Hepatology. 1989 May;9(5):763–784. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüssow H., Hilpert H., Walther I., Sidoti J., Mietens C., Bachmann P. Bovine milk immunoglobulins for passive immunity to infantile rotavirus gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):982–986. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.982-986.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanana A. D., Schaedeli J., Hess M. W., Cottier H. Predominance of theta-positive lymphocytes in gut-associated and peripheral lymphoid tissues of newborn mice. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):283–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. S., Strober W. Cholera holotoxin and its B subunit enhance Peyer's patch B cell responses induced by orally administered influenza virus: disproportionate cholera toxin enhancement of the IgA B cell response. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):433–436. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy C., Madore H. P., Pichichero M. E., Gala C., Pincus P., Vosefski D., Hoshino Y., Kapikian A., Dolin R. Field trial of rhesus rotavirus vaccine in infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Sep;7(9):645–650. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198809000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Delacroix D. L. Intravascular and mucosal immunoglobulin A: two separate but related systems of immune defense? Ann Intern Med. 1987 Jun;106(6):892–899. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-6-892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C. C., Nilsson L. A., Nygren H., Ouchterlony O., Tarkowski A. A solid-phase enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay for enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. D., Parrott D. M. Preparation and purification of lymphocytes from the epithelium and lamina propria of murine small intestine. Gut. 1981 Jun;22(6):481–488. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.6.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharakul T., Riepenhoff-Talty M., Albini B., Ogra P. L. Distribution of rotavirus antigen in intestinal lymphoid tissues: potential role in development of the mucosal immune response to rotavirus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Oct;74(1):14–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W., Lefkowitz J. A lavage technique allowing repeated measurement of IgA antibody in mouse intestinal secretions. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Feb 24;67(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90089-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Palmer E. L., Obijeski J. F. Rotaviruses: a review. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;105:123–184. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69159-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eydelloth R. S., Vonderfecht S. L., Sheridan J. F., Enders L. D., Yolken R. H. Kinetics of viral replication and local and systemic immune responses in experimental rotavirus infection. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):947–950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.947-950.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Daoud G., Daoud N., Puig M., Martinez M., Perez-Schael I., Shaw R., Greenberg H. B., Midthun K., Kapikian A. Z. Reactogenicity and antigenicity of rhesus rotavirus vaccine (MMU-18006) in newborn infants in Venezuela. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Nov;7(11):776–780. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198811000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Perez-Schael I., Gonzalez M., Garcia D., Perez M., Daoud N., Cunto W., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Protection against severe rotavirus diarrhoea by rhesus rotavirus vaccine in Venezuelan infants. Lancet. 1987 Apr 18;1(8538):882–884. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92858-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gothefors L., Wadell G., Juto P., Taniguchi K., Kapikian A. Z., Glass R. I. Prolonged efficacy of rhesus rotavirus vaccine in Swedish children. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):753–757. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. S., Glass R. I., Pinsky P. F., Anderson L. J. Rotavirus as a cause of diarrheal morbidity and mortality in the United States. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1112–1116. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. S., Glass R. I., Pinsky P. F., Young-Okoh N. C., Sappenfield W. M., Buehler J. W., Gunter N., Anderson L. J. Diarrheal deaths in American children. Are they preventable? JAMA. 1988 Dec 9;260(22):3281–3285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrdy D. B. Epidemiology of rotaviral infection in adults. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 May-Jun;9(3):461–469. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.3.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ijaz M. K., Dent D., Haines D., Babiuk L. A. Development of a murine model to study the pathogenesis of rotavirus infection. Exp Mol Pathol. 1989 Oct;51(2):186–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(89)90019-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaljot K. T., Shaw R. D., Rubin D. H., Greenberg H. B. Infectious rotavirus enters cells by direct cell membrane penetration, not by endocytosis. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1136–1144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1136-1144.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Flores J., Midthun K., Hoshino Y., Green K. Y., Gorziglia M., Nishikawa K., Chanock R. M., Potash L., Perez-Schael I. Strategies for the development of a rotavirus vaccine against infantile diarrhea with an update on clinical trials of rotavirus vaccines. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1989;257:67–89. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5712-4_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman D. M., Ishigatsubo Y., Steinberg A. D. Acquisition and maturation of expressed B cell repertoires in normal and autoimmune mice. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):801–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumate J., Isibasi A. Pediatric diarrheal diseases: a global perspective. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;5(1 Suppl):S21–S28. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198601001-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange S., Hansson H. A., Molin S. O., Nygren H. Local cholera immunity in mice: intestinal antitoxin-containing cells and their correlation with protective immunity. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):743–750. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.743-750.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losonsky G. A., Johnson J. P., Winkelstein J. A., Yolken R. H. Oral administration of human serum immunoglobulin in immunodeficient patients with viral gastroenteritis. A pharmacokinetic and functional analysis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2362–2367. doi: 10.1172/JCI112248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N. A sensitive method for the detection of specific antibody production in different isotypes from single lamina propria plasma cells. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Oct;24(4):393–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWilliams M., Lamm M. E., Phillips-Quagliata J. M. Surface and intracellular markers of mouse mesenteric and peripheral lymph node and Peyer's patch cells. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1326–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Clark H. F., Kornstein M. J., Plotkin S. A. A murine model for oral infection with a primate rotavirus (simian SA11). J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):233–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.233-236.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Clark H. F. Maternal antibody-mediated protection against gastroenteritis due to rotavirus in newborn mice is dependent on both serotype and titer of antibody. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1152–1158. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Clark H. F. Protection against rotavirus-induced gastroenteritis in a murine model by passively acquired gastrointestinal but not circulating antibodies. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):58–64. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.58-64.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Dudzik K. I. Rotavirus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes appear at the intestinal mucosal surface after rotavirus infection. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3507–3512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3507-3512.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Dudzik K. I. Rotavirus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes cross-react with target cells infected with different rotavirus serotypes. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):127–131. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.127-131.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Greenberg H. B., Dudzik K. I. Rotavirus-specific protein synthesis is not necessary for recognition of infected cells by virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3279–3283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3279-3283.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Shaw R. D., Greenberg H. B. Passive protection against rotavirus-induced diarrhea by monoclonal antibodies to surface proteins vp3 and vp7. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):700–703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.700-703.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Nase S., Mitchison N. A. Mouse specific bone marrow-derived lymphocyte antigen as a marker for thymus-independent lymphocytes. Nature. 1971 Mar 5;230(5288):50–51. doi: 10.1038/230050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Owen J. J. Thymus-derived lymphocytes: their distribution and role in the development of peripheral lymphoid tissues of the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Jan;1(1):27–30. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F. The effects of host age, virus dose, and virus strain on heterologous rotavirus infection of suckling mice. Microb Pathog. 1988 Mar;4(3):189–202. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennels M. B., Losonsky G. A., Young A. E., Shindledecker C. L., Kapikian A. Z., Levine M. M. An efficacy trial of the rhesus rotavirus vaccine in Maryland. The Clinical Study Group. Am J Dis Child. 1990 May;144(5):601–604. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1990.02150290095037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riepenhoff-Talty M., Dharakul T., Kowalski E., Sterman D., Ogra P. L. Rotavirus infection in mice: pathogenesis and immunity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1987;216B:1015–1023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Czerkinsky C., Moldoveanu Z. Detection and specificity of antibodies secreted by spleen cells in mice immunized with Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):317–323. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.317-323.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Redman D. R., Smith K. L., Theil K. W. Passive immunity to bovine rotavirus in newborn calves fed colostrum supplements from immunized or nonimmunized cows. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1118–1131. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1118-1131.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Smith K. L. Enteric viral infections of calves and passive immunity. J Dairy Sci. 1985 Jan;68(1):206–228. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(85)80813-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Stoner-Ma D. L., Estes M. K., Greenberg H. B. Specific enzyme-linked immunoassay for rotavirus serotypes 1 and 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.286-291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Vo P. T., Offit P. A., Coulson B. S., Greenberg H. B. Antigenic mapping of the surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):434–451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan J. F., Eydelloth R. S., Vonderfecht S. L., Aurelian L. Virus-specific immunity in neonatal and adult mouse rotavirus infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):917–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.917-927.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan J. F., Smith C. C., Manak M. M., Aurelian L. Prevention of rotavirus-induced diarrhea in neonatal mice born to dams immunized with empty capsids of simian rotavirus SA-11. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):434–438. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Wells P. W. Passive immunity in rotaviral infections. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 2):565–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Wells P. W. Rotavirus infection in lambs: studies on passive protection. Arch Virol. 1976;52(3):201–205. doi: 10.1007/BF01348017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. D., Merson M. H. The magnitude of the global problem of acute diarrhoeal disease: a review of active surveillance data. Bull World Health Organ. 1982;60(4):605–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A., Lange S., Holmgren J. Correlation between intestinal synthesis of specific immunoglobulin A and protection against experimental cholera in mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.1-6.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Old L. J., McIntire K. R., Boyse E. A. Immunoglobulin and other surface antigens of cells of the immune system. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):815–832. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng J. Expression of immunoglobulin isotypes by lymphoid cells of mouse intestinal lamina propria. Cell Immunol. 1982 Nov 1;73(2):324–336. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turesson I. Distribution of immunoglobulin-containing cells in human bone marrow and lymphoid tissues. Acta Med Scand. 1976;199(4):293–304. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1976.tb06735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Loveren H., Osterhaus A. D., Nagel J., Schuurman H. J., Vos J. G. Detection of IgA antibodies and quantification of IgA antibody-producing cells specific for ovalbumin or Trichinella spiralis in the rat. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Sep;28(3):377–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb01463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Heijden P. J., Bianchi A. T., Stok W., Bokhout B. A. Background (spontaneous) immunoglobulin production in the murine small intestine as a function of age. Immunology. 1988 Oct;65(2):243–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Heijden P. J., Stok W. Improved procedure for the isolation of functionally active lymphoid cells from the murine intestine. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Nov 5;103(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheul A. F., Versteeg A. A., Westerdaal N. A., Van Dam G. J., Jansze M., Snippe H. Measurement of the humoral immune response against Streptococcus pneumoniae type 14-derived antigens by an ELISA and ELISPOT assay based on biotin-avidin technology. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Jan 24;126(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90014-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Kapikian A. Z., Delem A., Zissis G. A comparative trial of rhesus monkey (RRV-1) and bovine (RIT 4237) oral rotavirus vaccines in young children. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):832–839. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., McNeal M. M., Sheridan J. F. Development of an adult mouse model for studies on protection against rotavirus. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5070–5075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5070-5075.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. D., Clarke C. J., Stokes C. R. Whole cholera toxin and B subunit act synergistically as an adjuvant for the mucosal immune response of mice to keyhole limpet haemocyanin. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Apr;31(4):443–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Jones J., Bridger J. Levels of colostral antibodies against neonatal calf diaahoea virus. Vet Rec. 1975 Aug 23;97(8):148–149. doi: 10.1136/vr.97.8.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijden P. J., Stok W., Bianchi A. T. Contribution of immunoglobulin-secreting cells in the murine small intestine to the total 'background' immunoglobulin production. Immunology. 1987 Dec;62(4):551–555. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



