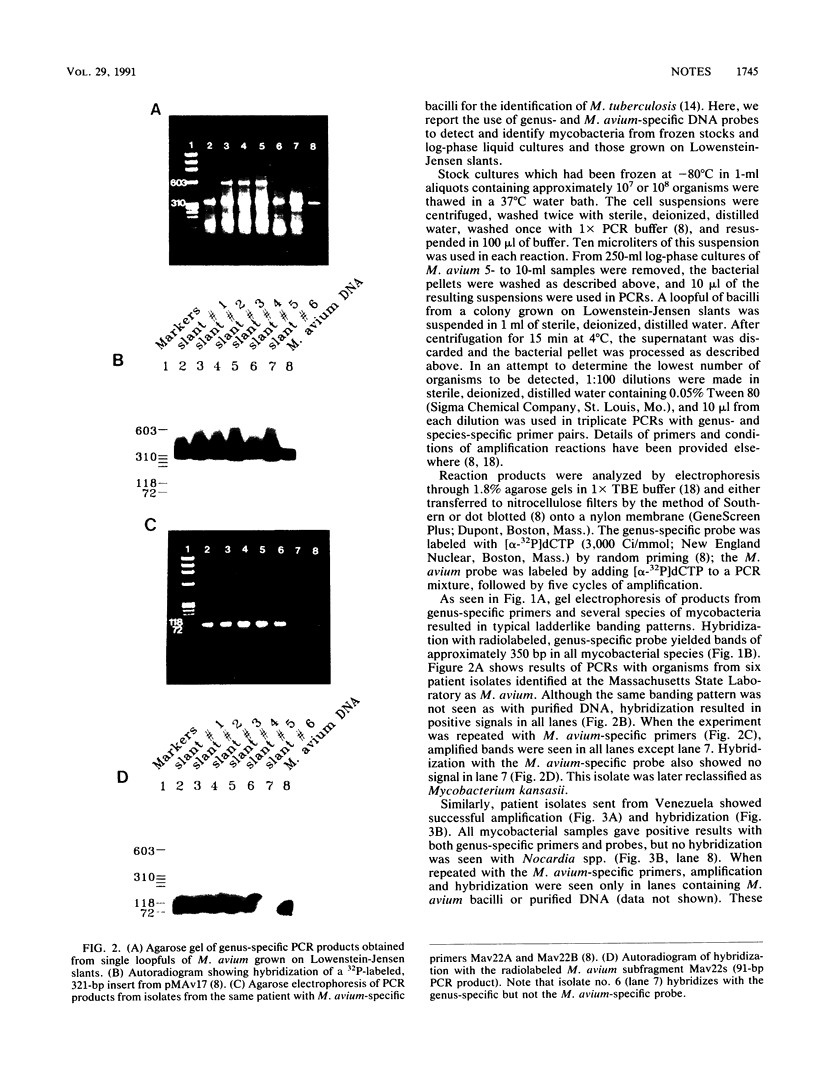
Abstract
A method for specific identification of mycobacteria by using the polymerase chain reaction on organisms taken from liquid cultures, frozen suspensions, or colonies grown on Lowenstein-Jensen slants is presented. This direct detection of mycobacterial organisms has important implications for strain typing and diagnosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biron F., Reveil J. C., Penalba C., Boibieux A., Bertrand J. L., Peyramond D. Direct visualization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a blood sample from an AIDS patient. AIDS. 1990 Mar;4(3):259–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson-Noël A., Gicquel B., Lecossier D., Lévy-Frébault V., Nassif X., Hance A. J. Rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis by amplification of mycobacterial DNA in clinical samples. Lancet. 1989 Nov 4;2(8671):1069–1071. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böddinghaus B., Rogall T., Flohr T., Blöcker H., Böttger E. C. Detection and identification of mycobacteria by amplification of rRNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1751–1759. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1751-1759.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J. Characterization of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and organisms of the Mycobacterium avium complex by restriction polymorphism of the rRNA gene region. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):489–494. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.489-494.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., Gabric D. M., de Lisle G. W. Identification of two groups of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis strains by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1591–1596. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1591-1596.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenach K. D., Cave M. D., Bates J. H., Crawford J. T. Polymerase chain reaction amplification of a repetitive DNA sequence specific for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):977–981. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I. New molecular techniques for microbial epidemiology and the diagnosis of infectious diseases. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):595–602. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries J. W., Patel R. J., Piessens W. F., Wirth D. F. Genus- and species-specific DNA probes to identify mycobacteria using the polymerase chain reaction. Mol Cell Probes. 1990 Apr;4(2):87–105. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(90)90011-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackel C., Houard S., Portaels F., van Elsen A., Herzog A., Bollen A. Specific identification of Mycobacterium leprae by the polymerase chain reaction. Mol Cell Probes. 1990 Jun;4(3):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(90)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampson S. J., Portaels F., Thompson J., Green E. P., Moss M. T., Hermon-Taylor J., McFadden J. J. DNA probes demonstrate a single highly conserved strain of Mycobacterium avium infecting AIDS patients. Lancet. 1989 Jan 14;1(8629):65–68. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartskeerl R. A., de Wit M. Y., Klatser P. R. Polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Mycobacterium leprae. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Sep;135(9):2357–2364. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-9-2357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P. W., Schuitema A. R., Van Soolingen D., Verstynen C. P., Bik E. M., Thole J. E., Kolk A. H., van Embden J. D. Specific detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1204–1213. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1204-1213.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolk A. H., Evers R., Groothuis D. G., Gilis H., Kuijper S. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against specific serotypes of Mycobacterium avium and the Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare-Mycobacterium scrofulaceum complex. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2514–2521. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2514-2521.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Thompson J., Chiodini R., Hermon-Taylor J. The use of DNA probes identifying restriction-fragment-length polymorphisms to examine the Mycobacterium avium complex. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Nov;1(3):283–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb01934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum J. M., Dealist C., Lewis W., Heseltine P. N. Rapid diagnosis by buffy coat smear of disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex infection in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):631–632. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.631-632.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pao C. C., Yen T. S., You J. B., Maa J. S., Fiss E. H., Chang C. H. Detection and identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by DNA amplification. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1877–1880. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1877-1880.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R. J., Fries J. W., Piessens W. F., Wirth D. F. Sequence analysis and amplification by polymerase chain reaction of a cloned DNA fragment for identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):513–518. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.513-518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R. J., Piessens W. F., David J. R., Wirth D. F. A cloned DNA fragment for identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Mar-Apr;11 (Suppl 2):S411–S419. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_2.s411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E. M., Lu R., Floyd C., Nakasone A., Friedly G., de la Maza L. M. Direct identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium, and Mycobacterium intracellulare from amplified primary cultures in BACTEC media using DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1543–1547. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1543-1547.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddi P. P., Talwar G. P., Khandekar P. S. Repetitive DNA sequence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: analysis of differential hybridization pattern with other mycobacteria. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1988 Dec;56(4):592–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivoire B., Ranchoff B. J., Chatterjee D., Gaylord H., Tsang A. Y., Kolk A. H., Aspinall G. O., Brennan P. J. Generation of monoclonal antibodies to the specific sugar epitopes of Mycobacterium avium complex serovars. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3147–3158. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3147-3158.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse D. A., Morris S. L., Karpas A. B., Probst P. G., Chaparas S. D. Production, characterization, and species specificity of monoclonal antibodies to Mycobacterium avium complex protein antigens. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1445–1449. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1445-1449.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Tomioka H., Sato K., Tasaka H., Tsukamura M., Kuze F., Asano K. Identification and partial characterization of Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium intracellulare by using DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):994–997. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.994-997.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathe S. S., Reichman L. B. Mycobacterial disease in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Chest Med. 1989 Sep;10(3):445–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I., Harrington N., Rothrock A., George H. Use of a cutoff range in identifying mycobacteria by the Gen-Probe Rapid Diagnostic System. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):241–244. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.241-244.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stackebrandt E., Smida J., Kazda J. The primary structure of the 16SrRNA of Mycobacterium leprae: its use in phylogeny and development of DNA probes. Acta Leprol. 1989;7 (Suppl 1):222–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstijnen C. P., Schöningh R., Kuijper S., Bruins J., von Ketel R. J., Groothuis D. G., Kolk A. H. Rapid identification of cultured Mycobacterium tuberculosis with a panel of monoclonal antibodies in western blot and immunofluorescence. Res Microbiol. 1989 Nov-Dec;140(9):653–666. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L., Gillis T. P., Booth R. J., Looker D., Watson J. D. The use of a specific DNA probe and polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Mycobacterium leprae. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):193–200. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. A., Cole S. T. A rapid method for the detection of potentially viable Mycobacterium leprae in human biopsies: a novel application of PCR. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Dec;53(3):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zainuddin Z. F., Dale J. W. Polymorphic repetitive DNA sequences in Mycobacterium tuberculosis detected with a gene probe from a Mycobacterium fortuitum plasmid. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Sep;135(9):2347–2355. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-9-2347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]