Abstract
We describe two rapid, simple, and reliable procedures for routine purification of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA from serum. HBV DNA could be purified from 24 serum samples in 1.5 to 2 h and was recovered in the initial reaction vessel. Both procedures have in common that HBV DNA is complexed with silica particles in the chaotropic agent guanidinium thiocyanate (GuSCN) but differ in lysis conditions and in the conditions used to elute HBV DNA from the silica particles after purification of the silica-DNA complexes. In one procedure (protocol H), serum HBV lysis was mediated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-proteinase treatment and HBV DNA was subsequently complexed with silica particles in the presence of GuSCN. After washing and drying of the silica-DNA complexes, HBV DNA was eluted from the silica particles in a low-salt buffer. In the other procedure (protocol Y*), serum HBV was directly lysed in GuSCN and HBV DNA was simultaneously complexed with silica particles. After washing and drying of the complexes, HBV DNA was eluted by proteinase treatment in low-salt buffer. Omission of proteinase treatment prevented efficient elution, presumably because of copurification of the protein which is covalently bound to the HBV DNA genome. We show, by Southern blot analysis, that HBV DNA could be reproducibly purified from human serum with the same yields by either procedure (30 to 50% relative to a classic procedure) and apparently independent of serum composition. HBV DNA purified by either method was a good substrate in the polymerase chain reaction compared with DNA purified by the classic procedure.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
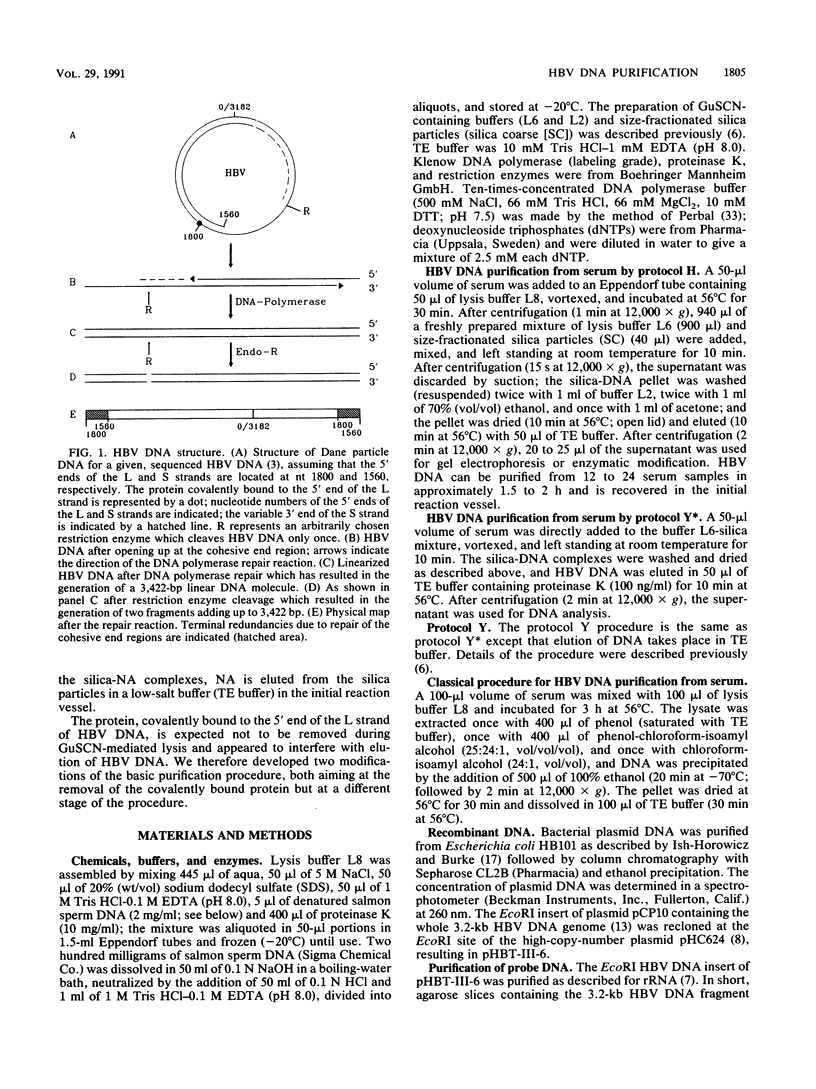






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaij C., Borst P. The gel electrophoresis of DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 10;269(2):192–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berninger M., Hammer M., Hoyer B., Gerin J. L. An assay for the detection of the DNA genome of hepatitis B virus in serum. J Med Virol. 1982;9(1):57–68. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichko V., Pushko P., Dreilina D., Pumpen P., Gren E. Subtype ayw variant of hepatitis B virus. DNA primary structure analysis. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):208–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80771-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonino F., Hoyer B., Nelson J., Engle R., Verme G., Gerin J. Hepatitis B virus DNA in the sera of HBsAg carriers: a marker of active hepatitis B virus replication in the liver. Hepatology. 1981 Sep-Oct;1(5):386–391. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom R., Sol C. J., Salimans M. M., Jansen C. L., Wertheim-van Dillen P. M., van der Noordaa J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.495-503.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom R., Sol C., Wertheim-van Dillen P. Rapid purification of ribosomal RNAs from neutral agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2195–2195. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros I., Pósfai G., Venetianer P. High-copy-number derivatives of the plasmid cloning vector pBR322. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brechot C., Hadchouel M., Scotto J., Degos F., Charnay P., Trepo C., Tiollais P. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in liver and serum: a direct appraisal of the chronic carrier state. Lancet. 1981 Oct 10;2(8250):765–768. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bréchot C., Degos F., Lugassy C., Thiers V., Zafrani S., Franco D., Bismuth H., Trépo C., Benhamou J. P., Wands J. Hepatitis B virus DNA in patients with chronic liver disease and negative tests for hepatitis B surface antigen. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 31;312(5):270–276. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501313120503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnay P., Pourcel C., Louise A., Fritsch A., Tiollais P. Cloning in Escherichia coli and physical structure of hepatitis B virion DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2222–2226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejean A., Lugassy C., Zafrani S., Tiollais P., Brechot C. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in pancreas, kidney and skin of two human carriers of the virus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Mar;65(Pt 3):651–655. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-3-651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M. F., Pourcel C., Rousset S., Chany C., Tiollais P. Excretion of hepatitis B surface antigen particles from mouse cells transformed with cloned viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4549–4553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich W. H., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B virus contains protein attached to the 5' terminus of its complete DNA strand. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):801–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90443-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruska J. F., Clayton D. A., Rubenstein J. L., Robinson W. S. Structure of hepatitis B Dane particle DNA before and after the Dane particle DNA polymerase reaction. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):666–672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.666-672.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenison S. A., Lemon S. M., Baker L. N., Newbold J. E. Quantitative analysis of hepatitis B virus DNA in saliva and semen of chronically infected homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):299–307. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kam W., Rall L. B., Smuckler E. A., Schmid R., Rutter W. J. Hepatitis B viral DNA in liver and serum of asymptomatic carriers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7522–7526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Feinstone S. M., Miller R. H. Rapid and sensitive method for the detection of serum hepatitis B virus DNA using the polymerase chain reaction technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):1930–1933. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.1930-1933.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogsgaard K. Hepatitis B virus DNA in serum. Applied molecular biology in the evaluation of hepatitis B infection. Liver. 1988 Oct;8(5):257–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1988.tb01004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Higuchi R. Avoiding false positives with PCR. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):237–238. doi: 10.1038/339237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers T. A., Greenberg H. B., Robinson W. S. Structure of hepatitis B Dane particle DNA and nature of the endogenous DNA polymerase reaction. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):368–376. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.368-376.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larzul D., Guigue F., Sninsky J. J., Mack D. H., Bréchot C., Guesdon J. L. Detection of hepatitis B virus sequences in serum by using in vitro enzymatic amplification. J Virol Methods. 1988 Jul;20(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman H. M., LaBrecque D. R., Kew M. C., Hadziyannis S. J., Shafritz D. A. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA directly in human serum by a simplified molecular hybridization test: comparison to HBeAg/anti-HBe status in HBsAg carriers. Hepatology. 1983 May-Jun;3(3):285–291. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. J., Chung H. T., Lai C. L., Leong S., Tam O. S. Detection of supercoiled hepatitis B virus DNA and related forms by means of molecular hybridization to an oligonucleotide probe. J Med Virol. 1989 Dec;29(4):284–288. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890290412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. J., Lai C. L., Wu P. C. Serum hepatitis B viral DNA in HBsAg-positive hepatocellular carcinoma treated with interferon or adriamycin. Br J Cancer. 1986 Jul;54(1):67–73. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. J., Wu P. C., Lai C. L., Leong S. Molecular hybridization study of plasma hepatitis B virus DNA from different carriers. J Infect Dis. 1986 Dec;154(6):983–989. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.6.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo Y. M., Mehal W. Z., Fleming K. A. False-positive results and the polymerase chain reaction. Lancet. 1988 Sep 17;2(8612):679–679. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monjardino J., Fowler M. J., Montano L., Weller I., Tsiquaye K. N., Zuckerman A. J., Jones D. M., Thomas H. C. Analysis of hepatitis virus DNA in the liver and serum of HBe antigen positive chimpanzee carriers. J Med Virol. 1982;9(3):189–199. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Onda H., Sasada R., Igarashi K., Sugino Y., Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA; subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1747–1757. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Opazo N., Chakraborty P. R., Shafritz D. A. Evidence for supercoiled hepatitis B virus DNA in chimpanzee liver and serum Dane particles: possible implications in persistent HBV infection. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattler F., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B viral DNA molecules have cohesive ends. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):226–233. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.226-233.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochetman G., Ou C. Y., Jones W. K. Polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1154–1157. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotto J., Hadchouel M., Hery C., Yvart J., Tiollais P., Brechot C. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum by a simple spot hybridization technique: comparison with results for other viral markers. Hepatology. 1983 May-Jun;3(3):279–284. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotto J., Hadchouel M., Wain-Hobson S., Sonigo P., Couroucé A. M., Tiollais P., Bréchot C. Hepatitis B virus DNA in Dane particles: evidence for the presence of replicative intermediates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):610–617. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Sattler F., Robinson W. S. Restriction endonuclease cleavage map and location of unique features of the DNA of hepatitis B virus, subtype adw2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4664–4668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sninsky J. J., Siddiqui A., Robinson W. S., Cohen S. N. Cloning and endonuclease mapping of the hepatitis B viral genome. Nature. 1979 May 24;279(5711):346–348. doi: 10.1038/279346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., O'Connell A., Millman I. Genome of hepatitis B virus: restriction enzyme cleavage and structure of DNA extracted from Dane particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4597–4601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiers V., Nakajima E., Kremsdorf D., Mack D., Schellekens H., Driss F., Goudeau A., Wands J., Sninsky J., Tiollais P. Transmission of hepatitis B from hepatitis-B-seronegative subjects. Lancet. 1988 Dec 3;2(8623):1273–1276. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92891-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Pourcel C., Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):489–495. doi: 10.1038/317489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich P. P., Bhat R. A., Seto B., Mack D., Sninsky J., Vyas G. N. Enzymatic amplification of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum compared with infectivity testing in chimpanzees. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):37–43. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Gray P., Quiroga M., Zaldivar J., Goodman H. M., Rutter W. J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the major protein of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Nature. 1979 Aug 30;280(5725):815–819. doi: 10.1038/280815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller I. V., Fowler M. J., Monjardino J., Thomas H. C. The detection of HBV-DNA in serum by molecular hybridisation: a more sensitive method for the detection of complete HBV particles. J Med Virol. 1982;9(4):273–280. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









