Abstract
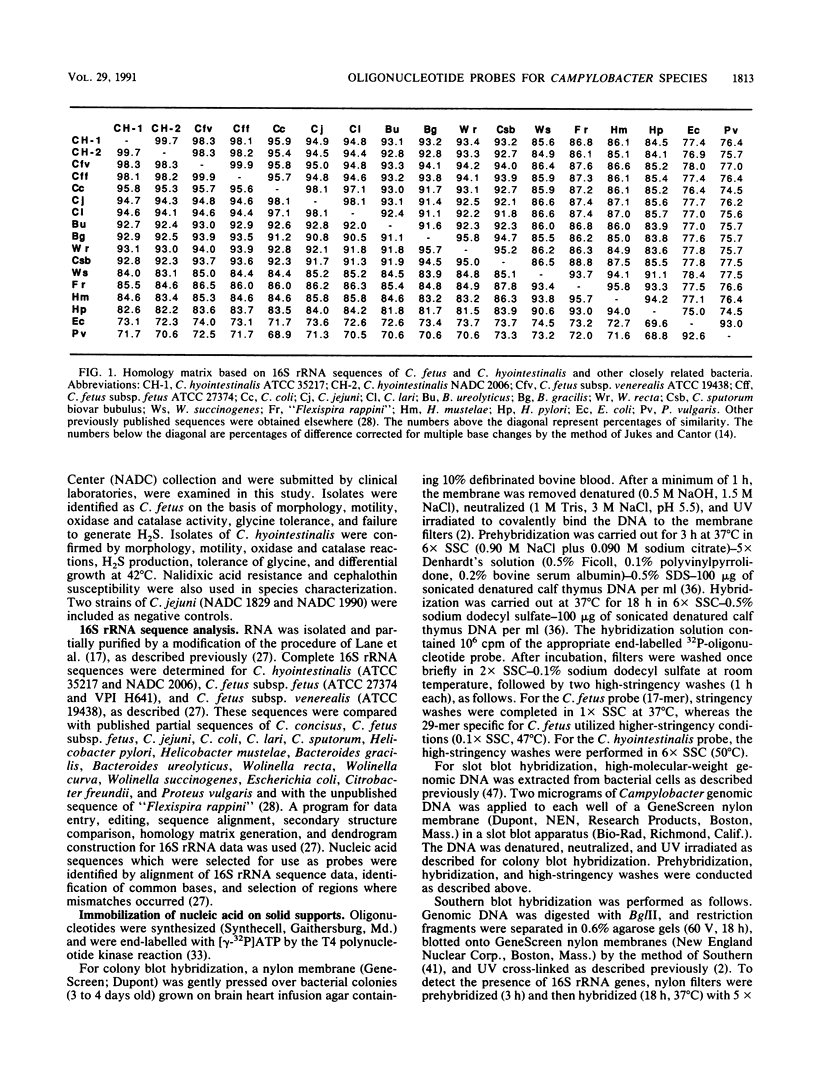
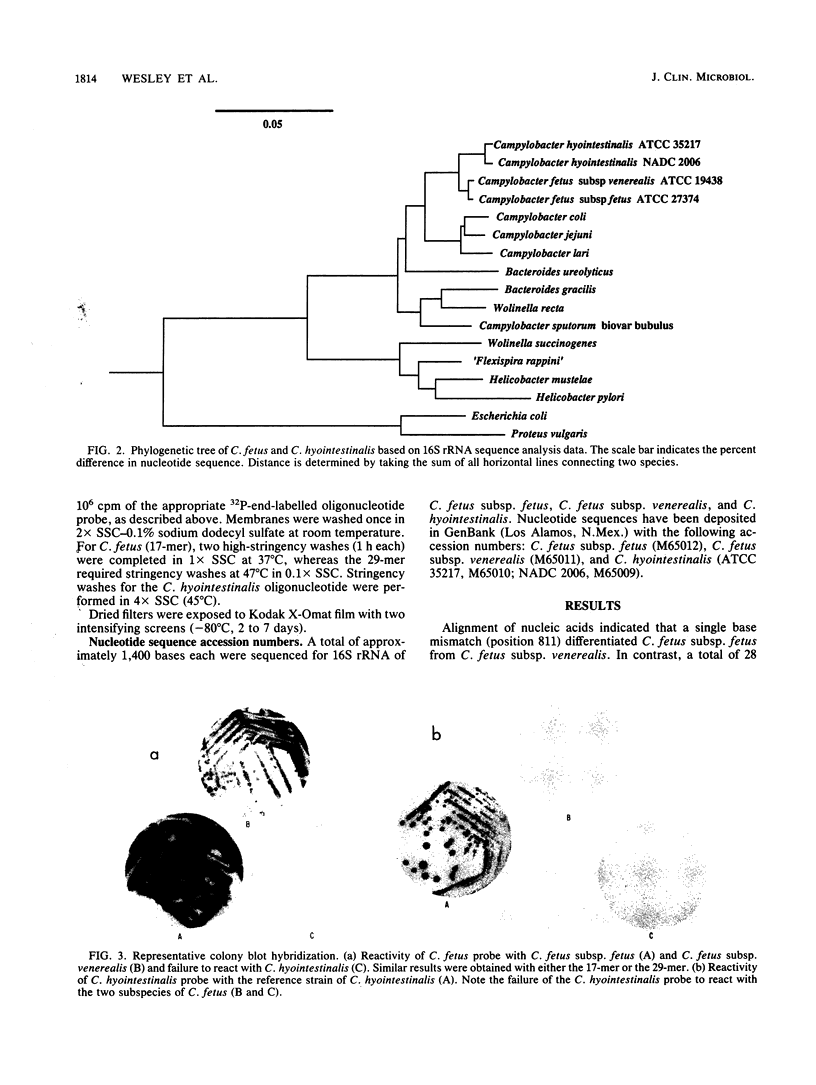
Deoxyoligonucleotide probes were constructed for the identification of Campylobacter fetus and Campylobacter hyointestinalis based on 16S rRNA sequence data. Probes were targeted to hypervariable regions of 16S rRNA. Specificity of oligonucleotide probes was tested in a colony blot assay with type strains of 15 Campylobacter and Arcobacter species as well as in a slot blot format using genomic DNA extracted from field strains of C. fetus and C. hyointestinalis. Two oligonucleotides were constructed for C. fetus that hybridized with equal specificity with each of 57 biochemically confirmed isolates of C. fetus but not with any other Campylobacter species. The C. hyointestinalis probe reacted with 47 of 48 biochemically confirmed field isolates of C. hyointestinalis. In Southern blot hybridization of BglII digests of genomic DNA, the respective probes reacted within three restriction fragments of either C. hyointestinalis (7.2, 8.2, and 10.1 kb) or C. fetus (7.0, 7.7, and 9.0 kb). This suggests multiple copies of genes encoding 16S rRNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chevrier D., Larzul D., Megraud F., Guesdon J. L. Identification and classification of Campylobacter strains by using nonradioactive DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):321–326. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.321-326.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diker K. S., Diker S., Ozlem M. B. Bovine diarrhea associated with Campylobacter hyointestinalis. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1990 Mar;37(2):158–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1990.tb01040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds P., Patton C. M., Griffin P. M., Barrett T. J., Schmid G. P., Baker C. N., Lambert M. A., Brenner D. J. Campylobacter hyointestinalis associated with human gastrointestinal disease in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):685–691. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.685-691.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennell C. L., Rompalo A. M., Totten P. A., Bruch K. L., Flores B. M., Stamm W. E. Isolation of "Campylobacter hyointestinalis" from a human. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):146–148. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.146-148.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhart C. J., Edmonds P., Ward G. E., Kurtz H. J., Brenner D. J. "Campylobacter hyointestinalis" sp. nov.: a new species of Campylobacter found in the intestines of pigs and other animals. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):715–720. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.715-720.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhart C. J., Lin G. F., McOrist S. M., Lawson G. H., Murtaugh M. P. Cloned DNA probes specific for the intracellular Campylobacter-like organism of porcine proliferative enteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):1011–1015. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.1011-1015.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhart C. J., Murtaugh M. P., Lin G. F., Ward G. E. Species-specific DNA probes for Campylobacter species isolated from pigs with proliferative enteritis. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Sep;24(3-4):367–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhart C. J., Ward G. E., Chang K., Kurtz H. J. Campylobacter hyointestinalis (new species) isolated from swine with lesions of proliferative ileitis. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Mar;44(3):361–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhart C. J., Ward G. E., Murtaugh M. P. Species-specific cloned DNA probes for the identification of Campylobacter hyointestinalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2717–2723. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2717-2723.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korolik V., Coloe P. J., Krishnapillai V. A specific DNA probe for the identification of Campylobacter jejuni. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Feb;134(2):521–529. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-2-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M., Jones J. M., Lister S. A. Isolation of Campylobacter hyointestinalis from pigs in the United Kingdom. Vet Rec. 1984 Aug 11;115(6):128–129. doi: 10.1136/vr.115.6.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau P. P., DeBrunner-Vossbrinck B., Dunn B., Miotto K., MacDonnell M. T., Rollins D. M., Pillidge C. J., Hespell R. B., Colwell R. R., Sogin M. L. Phylogenetic diversity and position of the genus Campylobacter. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1987;9:231–238. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(87)80027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minet J., Grosbois B., Megraud F. Campylobacter hyointestinalis: an opportunistic enteropathogen? J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2659–2660. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2659-2660.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moureau P., Derclaye I., Gregoire D., Janssen M., Cornelis G. R. Campylobacter species identification based on polymorphism of DNA encoding rRNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1514–1517. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1514-1517.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng L. K., Stiles M. E., Taylor D. E. Classification of Campylobacter strains using DNA probes. Mol Cell Probes. 1987 Sep;1(3):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(87)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M., Johny M., Sethi S. K. Use of an alkaline phosphatase-labeled synthetic oligonucleotide probe for detection of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1565–1569. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1565-1569.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Lane D. J., Giovannoni S. J., Pace N. R., Stahl D. A. Microbial ecology and evolution: a ribosomal RNA approach. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:337–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paster B. J., Lee A., Fox J. G., Dewhirst F. E., Tordoff L. A., Fraser G. J., O'Rourke J. L., Taylor N. S., Ferrero R. Phylogeny of Helicobacter felis sp. nov., Helicobacter mustelae, and related bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;41(1):31–38. doi: 10.1099/00207713-41-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L. The genus Campylobacter: a decade of progress. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr;1(2):157–172. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken R. N., Wang Z., Yang H. L. Molecular cloning of a species-specific DNA probe for Campylobacter jejuni. Mol Cell Probes. 1987 Sep;1(3):245–259. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(87)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashtchian A., Eldredge J., Ottaviani M., Abbott M., Mock G., Lovern D., Klinger J., Parsons G. Immunological capture of nucleic acid hybrids and application to nonradioactive DNA probe assay. Clin Chem. 1987 Sep;33(9):1526–1530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop R. M., 2nd, Smibert R. M., Johnson J. L., Krieg N. R. Differential characteristics of catalase-positive campylobacters correlated with DNA homology groups. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Jul;30(7):938–951. doi: 10.1139/m84-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEBALD M., VERON M. TENEUR EN BASES DE L'ADN ET CLASSIFICATION DES VIBRIONS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1963 Nov;105:897–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne G. M., Macone A., Goldmann D. A. Enzymatically labelled nucleic acid (NA) probe assays for detection of Campylobacter spp. in human faecal specimens and in culture. Mol Cell Probes. 1990 Apr;4(2):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(90)90014-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Krajden M. Approaches to the detection of enteric pathogens, including Campylobacter, using nucleic acid hybridization. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;4(3 Suppl):71S–78S. doi: 10.1016/s0732-8893(86)80044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandamme P., Falsen E., Rossau R., Hoste B., Segers P., Tytgat R., De Ley J. Revision of Campylobacter, Helicobacter, and Wolinella taxonomy: emendation of generic descriptions and proposal of Arcobacter gen. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;41(1):88–103. doi: 10.1099/00207713-41-1-88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesley I. V., Bryner J. H. Antigenic and restriction enzyme analysis of isolates of Campylobacter fetus subsp venerealis recovered from persistently infected cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Jun;50(6):807–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Stackebrandt E., Macke T. J., Fox G. E. A phylogenetic definition of the major eubacterial taxa. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1985;6:143–151. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(85)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]